Related Research Articles

The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 and was named after the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, which contributed significant funding.
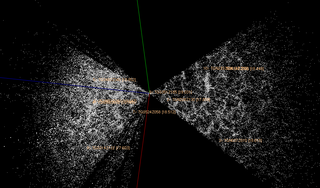
In astronomy, a redshift survey is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects: usually galaxies, but sometimes other objects such as galaxy clusters or quasars. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to estimate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift survey maps the 3D distribution of matter within a field of the sky. These observations are used to measure detailed statistical properties of the large-scale structure of the universe. In conjunction with observations of early structure in the cosmic microwave background, these results can place strong constraints on cosmological parameters such as the average matter density and the Hubble constant.

60 Andromedae is a star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda, located to the west-northwest of Gamma Andromedae. 60 Andromedae is the Flamsteed designation though the star also bears the Bayer designation b Andromedae. It is bright enough to be seen by the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.82. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, it is at a distance of roughly 530 light-years from Earth.

An ultraluminous X-ray source (ULX) is an astronomical source of X-rays that is less luminous than an active galactic nucleus but is more consistently luminous than any known stellar process (over 1039 erg/s, or 1032 watts), assuming that it radiates isotropically (the same in all directions). Typically there is about one ULX per galaxy in galaxies which host them, but some galaxies contain many. The Milky Way has not been shown to contain a ULX, although SS 433 may be a possible source. The main interest in ULXs stems from their luminosity exceeding the Eddington luminosity of neutron stars and even stellar black holes. It is not known what powers ULXs; models include beamed emission of stellar mass objects, accreting intermediate-mass black holes, and super-Eddington emission.

In cosmology, baryon acoustic oscillations (BAO) are fluctuations in the density of the visible baryonic matter of the universe, caused by acoustic density waves in the primordial plasma of the early universe. In the same way that supernovae provide a "standard candle" for astronomical observations, BAO matter clustering provides a "standard ruler" for length scale in cosmology. The length of this standard ruler is given by the maximum distance the acoustic waves could travel in the primordial plasma before the plasma cooled to the point where it became neutral atoms, which stopped the expansion of the plasma density waves, "freezing" them into place. The length of this standard ruler can be measured by looking at the large scale structure of matter using astronomical surveys. BAO measurements help cosmologists understand more about the nature of dark energy by constraining cosmological parameters.
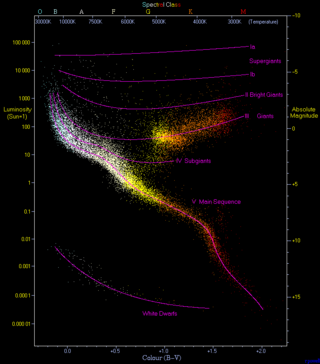
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities and their stellar classifications or effective temperatures. The diagram was created independently in 1911 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and by Henry Norris Russell in 1913, and represented a major step towards an understanding of stellar evolution.
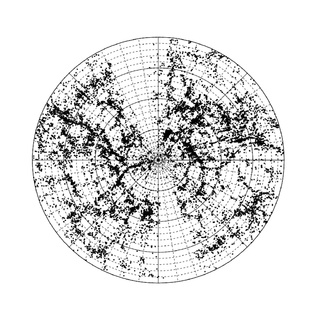
The 6dF Galaxy Survey, 6dF or 6dFGS is a redshift survey conducted by the Anglo-Australian Observatory (AAO) with the 1.2m UK Schmidt Telescope between 2001 and 2009. The data from this survey were made public on 31 March, 2009. The survey has mapped the nearby universe over nearly half the sky. Its 136,304 spectra have yielded 110,256 new extragalactic redshifts and a new catalog of 125,071 galaxies. For a subsample of 6dF a peculiar velocity survey is measuring mass distribution and bulk motions of the local Universe. As of July 2009, it is the third largest redshift survey next to the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) and the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey (2dFGRS).
The ICG is a research institute at the University of Portsmouth devoted to topics in cosmology, galaxy evolution and gravitation. It has nearly 50 staff, post-docs and students working on subjects from inflation in the early Universe to understanding the stellar populations in galaxies.
Bedrane Adam' is a binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation Ursa Minor. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.80. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.14±0.42 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, it is located roughly 460 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +5.9 km/s.
Constance "Connie" Mary Rockosi is a professor and former department chair in the Astronomy and Astrophysics Department at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She earned her PhD in 2001 and helped design the camera for the telescope that was used as part of the initial Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). She also was in charge of the SDSS-III domain for the Sloan Extension for Galactic Understanding and Exploration (SEGUE) project and is the primary investigator on SEGUE-2. Her focuses involve the study of the Milky Way galaxy, with a focus on the evolution that it took to reach its current state.
Idit Zehavi is an Israeli astrophysicist and researcher who discovered an anomaly in the mapping of the cosmos, which offered insight into how the universe is expanding. She is part of the team completing the Sloan Digital Sky Survey and is one of the world's most highly cited scientists according to the list published annually by Thomson Reuters.
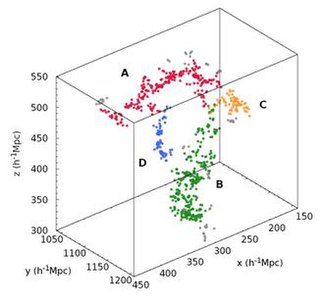
The BOSS Great Wall is a supercluster complex that was identified, using the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), in early 2016. It was discovered by a research team from several institutions, consisting of: Heidi Lietzen, Elmo Tempel, Lauri Juhan Liivamägi, Antonio Montero-Dorta, Maret Einasto, Alina Streblyanska, Claudia Maraston, Jose Alberto Rubiño-Martín and Enn Saar. The BOSS Great Wall is one of the largest superstructures in the observable universe, though there are even larger structures known.

NGC 4473 is an elliptical galaxy located about 50 million light-years away in the constellation of Coma Berenices. It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel on April 8, 1784. NGC 4473 has an inclination of about 71°. NGC 4473 is a member of a chain of galaxies called Markarian's Chain which is part of the larger Virgo Cluster of galaxies.

Karen Masters is an Astrophysicist and Full Professor of Astrophysics in Haverford College, Pennsylvania exploring galaxy formation. She is also the project scientist for the citizen science project Galaxy Zoo, and uses the classifications to study the evolution of galaxies.

NGC 2998 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Ursa Major. It is 195 million light-years away from the Earth. It is an intermediate spiral galaxy. Its stellar mass is about that of the Milky Way.

NGC 3489 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Leo. It is located at a distance of about 30 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3489 is about 30,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 8, 1784. NGC 3489 is a member of the Leo Group.

NGC 2964 is an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Leo. It is located at a distance of circa 60 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 2964 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on December 7, 1785.
Shirley Ho is an American astrophysicist and machine learning expert, currently at the Center for Computational Astrophysics at Flatiron Institute in NYC and at the New York University and the Carnegie Mellon University. Ho also has visiting appointment at Princeton University.

Maayane Tamar Soumagnac is a French-Israeli Astrophysicist and social activist, senior lecturer in the Physics department at the Bar-Ilan University.
References
- ↑ "Claudia Maraston - Portsmouth Research Portal". researchportal.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ↑ "UNIMASS - Portsmouth Research Portal". researchportal.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "UniMass | Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation". research.icg.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "Claudia Maraston". www.maraston.eu. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ↑ "Claudia's Stellar Population Models". www.icg.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ↑ "Claudia's Stellar Population Models". www-astro.physics.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "Cosmology and Astrophysics at Portsmouth - Portsmouth Research Portal". researchportal.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ Maraston, Claudia; Pforr, Janine; Henriques, Bruno M.; Thomas, Daniel; Wake, David; Brownstein, Joel R.; Capozzi, Diego; Tinker, Jeremy; Bundy, Kevin (2013-09-20). "Stellar masses of SDSS-III/BOSS galaxies at z ~ 0.5 and constraints to galaxy formation models". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 435 (4): 2764–2792. arXiv: 1207.6114 . doi: 10.1093/mnras/stt1424 . ISSN 1365-2966.
- ↑ Dawson, Kyle S.; Schlegel, David J.; Ahn, Christopher P.; Anderson, Scott F.; Aubourg, Éric; Bailey, Stephen; Barkhouser, Robert H.; Bautista, Julian E.; Beifiori, Alessandra (2013-01-01). "The Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey of SDSS-III". The Astronomical Journal. 145 (1): 10. arXiv: 1208.0022 . Bibcode:2013AJ....145...10D. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/1/10. ISSN 0004-6256.
- ↑ Dawson, Kyle S.; Schlegel, David J.; Ahn, Christopher P.; Anderson, Scott F.; Aubourg, Éric; Stephen Bailey; Barkhouser, Robert H.; Bautista, Julian E.; Beifiori, Alessandra (2013). "The Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey of SDSS-III". The Astronomical Journal. 145 (1): 10. arXiv: 1208.0022 . Bibcode:2013AJ....145...10D. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/145/1/10. ISSN 1538-3881.
- ↑ "Stellar Population Models | SDSS". www.sdss.org. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ Cras, Claire Le; Maraston, Claudia; Thomas, Daniel; York, Donald G. (2016-09-01). "Modelling the UV spectrum of SDSS-III/BOSS galaxies: hints towards the detection of the UV upturn at high-z". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 461 (1): 766–793. arXiv: 1802.10114 . doi: 10.1093/mnras/stw1024 . ISSN 0035-8711.
- ↑ "Portsmouth university professor honoured for work on stars and galaxies" . Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "RAS Eddington Prize awarded to Prof Claudia Maraston". www.icg.port.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ↑ "Professor Claudia Maraston on Evolution of galaxies - Isle of Wight Cafe Scientifique". Isle of Wight Cafe Scientifique. 2017-04-05. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "Proof that some galaxies are LIERs – Astronomy Now". astronomynow.com. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ↑ "Prof. Claudia Maraston | The Royal Astronomical Society". ras.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-10-18.