
Sevier County is a county located in the central Utah, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 20,802. Its county seat and largest city is Richfield. The county was formed on January 16, 1865, as a split off from Sanpete County to the north. It was named for the Sevier River, which winding path forms its western boundary.

Beaver is a city in eastern Beaver County, Utah, United States. It is also serves as the county seat. The population was 3,112 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Beaver County.

The Paunsaugunt Plateau is a dissected plateau, rising to an elevation of 7,000–9,300 feet (2,100–2,800 m), in southwestern Utah in the United States. Located in northern Kane County and southwestern Garfield County, it is approximately 10 miles (16 km) wide, and extends southward from the Sevier Plateau approximately 25 miles (40 km), terminating in the Pink Cliffs at the southern end.

Marysvale Canyon is a canyon in Piute and Sevier counties in southwest Utah, United States which runs 8 miles (13 km) north from just north of Marysvale north to the town of Sevier.

Fremont Indian State Park and Museum is a state park of Utah, US, which interprets archaeological remains of the Fremont culture. The park is located in Sevier County, Utah in the Clear Creek Canyon.

Muddy Creek is a stream in central Utah, United States, that drains portions of Emery, Sanpete, Sevier, and Wayne counties.
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a mainline route of the Interstate Highway System in the United States connecting Utah and Maryland. The Utah section runs east–west for approximately 232 miles (373 km) across the central part of the state. Richfield is the largest Utah city served by the freeway, which does not serve or connect any urban areas in the state. The freeway was built as part of a system of highways connecting Los Angeles and the northeastern United States. I-70 was the second attempt to connect southern California to the east coast of the United States via central Utah, the first being a failed attempt to construct a transcontinental railroad. Parts of that effort were re-used in the laying out of the route of I-70.
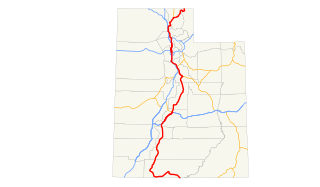
In the U.S. state of Utah, U.S. Route 89 (US-89) is a long north–south state highway spanning more than 502 miles (807.891 km) through the central part of the state. Between Provo and Brigham City, US-89 serves as a local road, paralleling Interstate 15, but the portions from Arizona north to Provo and Brigham City northeast to Wyoming serve separate corridors. The former provides access to several national parks and Arizona, and the latter connects I-15 with Logan, the state's only Metropolitan Statistical Area not on the Interstate.
State Route 72 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Utah. The current alignment is an extension of State Route 10. The highway provides access to Loa from I-70.
Mammoth Creek is a Utah creek which flows for over 20 miles (32 km) through mountains and forests from Mammoth Summit, through the Mammoth Valley, to its confluence with the Sevier River. The creek contains wild brown trout and hatchery rainbow trout.

Quitchupah Creek is a stream draining portions of Emery and Sevier Counties in central Utah, in the western United States. Quitchupah Creek is significant for its rock art remains of the Fremont culture that line its banks. Quitchupah is Ute for "animals fare poorly." The drainage area is located within the Colorado River Basin near the south end of the Wasatch Plateau. All drainage from the area flows to Quitchupah Creek or its tributaries, including East Spring Canyon, Water Hollow, and North Fork and flows through Convulsion Canyon.
Salina Creek is a tributary of the Sevier River, in Utah.
Chalk Creek is a stream in Millard County, Utah. It was originally known as 3rd Creek south of Sevier River to the early travelers on the Mormon Road. Its mouth is at the endorheic basin called "The Sink" in the Pahvant Valley at an elevation of 4,639 feet (1,414 m). Its source is located at the confluence of North Fork Chalk Creek with South Fork Chalk Creek, at an elevation of 5,482 feet (1,671 m), at 38°56′59″N 112°16′06″W in the Pahvant Range. Filmore is 3 miles (4.8 km) below the source of Chalk Creek along the south bank of the stream.
Meadow Creek is a stream in Millard County, Utah. It was originally known as 4th Creek south of Sevier River to the early travelers on the Mormon Road. Its mouth is located at an elevation of 4,842 feet or 1,476 meters. Its source is located an elevation of 9,760 feet, at 38°51′50″N 112°14′16″W near the summit of White Pine Peak in the Pahvant Range. Meadow is located north of the mouth of the stream.
Sulphur Creek is a slot canyon canyoneering route found in Capitol Reef National Park in the state of Utah. It is a 6.25 mile hike one way and has been categorized by the state of Utah as an easy hiking trail. The canyon contains waterfalls, pools, overhangs and red sandstone, and a shallow stream that runs through it year-round. The route begins from the Chimney Rock trailhead and ends at the Visitor Center. The rocks at Sulphur Creek are some of the oldest exposed rocks in Capitol Reef.
Fremont Wash sometimes called Fremont Canyon in its upper reach, is a stream and a valley in the north end of Parowan Valley, in Iron County, Utah. Its mouth lies at its confluence with Little Salt Lake at an elevation of 5,686 feet / 1,733 meters. Its head is found at 38°07′46″N 112°34′36″W, the mouth of Fremont Canyon, an elevation of 6,476 feet / 1,974 meters.
Fremont Canyon is a stream and a deep valley or canyon that runs from its mouth at its confluence with Coyote Creek at the head of Fremont Wash in Iron County, Utah, eastward across the Tushar Mountains to its head at 38°05′05″N 112°27′35″W on the west side of Fremont Pass in Garfield County, Utah.










