Related Research Articles
Single sign-on (SSO) is an authentication scheme that allows a user to log in with a single ID to any of several related, yet independent, software systems.
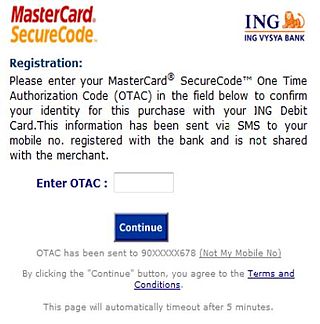
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time passcode, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital device. OTPs avoid several shortcomings that are associated with traditional (static) password-based authentication; a number of implementations also incorporate two-factor authentication by ensuring that the one-time password requires access to something a person has as well as something a person knows.
A Google Account is a user account that is required for access, authentication and authorization to certain online Google services. It is also often used as single sign-on for third party services.
Dropbox is a file hosting service operated by the American company Dropbox, Inc., headquartered in San Francisco, California, U.S. that offers cloud storage, file synchronization, personal cloud, and client software. Dropbox was founded in 2007 by MIT students Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi as a startup company, with initial funding from seed accelerator Y Combinator.
LastPass is a password manager application. The standard version of LastPass comes with a web interface, but also includes plugins for various web browsers and apps for many smartphones. It also includes support for bookmarklets.

Multi-factor authentication is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or application only after successfully presenting two or more pieces of evidence to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password.
Flipboard is a news aggregator and social network aggregation company based in Palo Alto, California, with offices in New York, Vancouver, and Beijing. Its software, also known as Flipboard, was first released in July 2010. It aggregates content from social media, news feeds, photo sharing sites, and other websites, presents it in magazine format, and allows users to "flip" through the articles, images, and videos being shared. Readers can also save stories into Flipboard magazines. As of March 2016 the company claims there have been 28 million magazines created by users on Flipboard. The service can be accessed via web browser, or by a Flipboard application for Microsoft Windows and macOS, and via mobile apps for iOS and Android. The client software is available at no charge and is localized in 21 languages.
Twilio Inc. is an American cloud communications company based in San Francisco, California, which provides programmable communication tools for making and receiving phone calls, sending and receiving text messages, and performing other communication functions using its web service APIs.

EyeEm, pronounced "I am", is a German technology company that provides services related to photography. It was co-founded by Florian Meissner, Ramzi Rizk, Gen Sadakane, and Lorenz Aschoff in Berlin in 2011.

Google Authenticator is a software-based authenticator by Google. It implements multi-factor authentication services using the time-based one-time password and HMAC-based one-time password, for authenticating users of software applications.
Backend as a service (BaaS), sometimes also referred to as mobile backend as a service (MBaaS), is a service for providing web app and mobile app developers with a way to easily build a backend to their frontend applications. Features available include user management, push notifications, and integration with social networking services. These services are provided via the use of custom software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs). BaaS is a relatively recent development in cloud computing, with most BaaS startups dating from 2011 or later. Some of the most popular service providers are AWS Amplify and Firebase.

Upptalk was a proprietary voice-over-IP service and software application that provided mobile phone numbers in the cloud and allows users to call or text any phone for free whether or not the device receiving the calls and texts has the Yuilop application. The service was discontinued in 2017 and even its domain was abandoned.
Rublon is a two-factor authentication system that acts as an additional security layer which protects the password-based login process to web applications. A protected account can only be accessed by someone who enters the correct password and scans a QR code using the Rublon mobile app, which holds the digital identity of the account's owner. In web browsers that have been previously defined as trusted, only the password is needed in order to sign in to a protected account of any supported web application.
SlickLogin was an Israeli start-up company that developed sound-based password alternatives. The company's goal was to enable end users to log in easily to password-protected websites by using a uniquely generated sound.
Firebase was a company that developed backend software. It was founded in San Francisco in 2011 and was incorporated in Delaware.

LogDog is a mobile Intrusion Detection System (IDS) app. It monitors various online accounts and scans multiple indicators that are associated with unauthorized access by taking into account a user’s routine across various devices and services. The app is currently available for Android and iOS.
Crashlytics was a Boston, Massachusetts-based software company founded in May 2011 by entrepreneurs Wayne Chang and Jeff Seibert. Crashlytics helps collecting, analyzing and organizing app crash reports.
Myki was a password manager and authenticator developed by Myki Security. Myki was available on iOS and Android, as browser extensions on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera and Microsoft Edge, and as a standalone desktop app for Windows, macOS, Linux, Arch Linux, and Debian. It was available in English, Arabic, French, German, Italian, Portuguese and Spanish. On 24 March 2022, MYKI announced Jump Cloud's acquisition of Myki and on 10 April 2022, Myki ceased to operate.

Bitwarden is a freemium open-source password management service that is used to store sensitive information, such as website credentials, in an encrypted vault. The platform hosts multiple client applications, including a web interface, desktop applications, browser extensions, mobile apps, and a command-line interface. The platform offers a free US or European cloud-hosted service as well as the ability to self-host.

Everykey designs and builds a patented universal smart key that can unlock devices and log into online accounts on those devices. The idea began as an entrepreneurship class project at Case Western Reserve University.
References
- ↑ Kyle Russell (19 February 2015). "Clef Offers Two-Factor Authentication Without All The Codes". TechCrunch. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Andy Greenberg (26 June 2016). "So Hey You Should Stop Using Texts for Two-Factor Authentication". Wired. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Nicole Perlroth (18 December 2013). "New Clef Plug-In Lets You Forget About Your Password". NyTimes. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ "Login to your WordPress Website without Typing the Password". Labnol. 7 May 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Marisa Kendall (4 October 2016). "Oakland drawing more tech startups". East Bay Times. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Ben Dickson. "5 authentication methods putting passwords to shame". TheNextWeb. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ David Nield (22 February 2015). "Clef wants to change the way we log into websites". GizMag. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Krystle Vermes (5 July 2016). "Startups & Technology That Will Probably Kill The Password". SnapMunk. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Kim Mai Cutler (24 September 2015). "Oakland To Tech: Please Don't Screw This Up Like Last Time". TechCrunch. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ Mariah Carle (2 April 2014). "Oaktech: Oakland mobile start-up Clef ends need for password". OaklandLocal. Archived from the original on 29 August 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- ↑ FinSMEs (2014-11-18). "Clef Secures $1.6M in Seed Funding". FinSMEs. Retrieved 2020-05-04.
- ↑ "When two-factor authentication app Clef shuts down in June, its staff will join Authy". TechCrunch. Retrieved 2020-05-04.