Related Research Articles

Lwa, also called loa, are spirits in the African diasporic religion of Haitian Vodou and Dominican Vúdu. They have also been incorporated into some revivalist forms of Louisiana Voodoo. Many of the lwa derive their identities in part from deities venerated in the traditional religions of West Africa, especially those of the Fon and Yoruba.
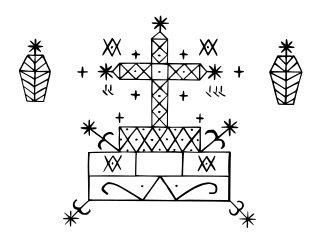
Baron Samedi, also written Baron Samdi, Bawon Samedi or Bawon Sanmdi, is one of the lwa of Haitian Vodou. He is a lwa of the dead, along with Baron's numerous other incarnations Baron Cimetière, Baron La Croix and Baron Criminel.
The Gede are the family of lwa, spirits or deities associated with Ancestor worship in Haitian Vodou, that represent the powers of death and fertility. They are often said to be found at burial sites, where they escort the deceased to their afterlife. Gede spirits include Gede Doub, Guede-Linto, Guede L'Orage, Guede Oussou, Guede Nibo and Guede Masaka, and Guede Ti Malice. All are known for the drum rhythm and dance called the "banda". In possession, they will drink or rub themselves with a mixture of clairin and twenty-one scotch bonnet or goat peppers. Fèt Gede is celebrated on 2 November, All Souls' Day. Boons granted by the Gede not repaid by this date will be avenged afterwards.

Papa Legba is a lwa, or loa, in West African Vodun and its diasporic derivatives, who serves as the intermediary between God and humanity. He stands at a spiritual crossroads and gives permission to speak with the spirits of Guineé, and is believed to speak all human languages. In Haiti, he is the great elocutioner. Legba facilitates communication, speech, and understanding. He is commonly associated with dogs. Papa Legba is invoked at the beginning of every ceremony. Papa Legba has his origins in the historic West African kingdom of Dahomey, located within present-day Benin.
The Tonton Macoute or simply the Macoute, was a Haitian paramilitary and secret police force created in 1959 by dictator François "Papa Doc" Duvalier. Haitians named this force after the Haitian mythological bogeyman, Tonton Macoute, who kidnaps and punishes unruly children by snaring them in a gunny sack before carrying them off to be consumed for breakfast. The Macoute were known for their brutality, state terrorism, and assassinations. In 1970, the militia was renamed the Volontaires de la Sécurité Nationale. Though formally disbanded in 1986, its members continued to terrorize the country.

George Gaylord Simpson was an American paleontologist. Simpson was perhaps the most influential paleontologist of the twentieth century, and a major participant in the modern synthesis, contributing Tempo and Mode in Evolution (1944), The Meaning of Evolution (1949) and The Major Features of Evolution (1953). He was an expert on extinct mammals and their intercontinental migrations. Simpson was extraordinarily knowledgeable about Mesozoic fossil mammals and fossil mammals of North and South America. He anticipated such concepts as punctuated equilibrium and dispelled the myth that the evolution of the horse was a linear process culminating in the modern Equus caballus. He coined the word hypodigm in 1940, and published extensively on the taxonomy of fossil and extant mammals. Simpson was influentially, and incorrectly, opposed to Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift, but accepted the theory of plate tectonics when the evidence became conclusive.
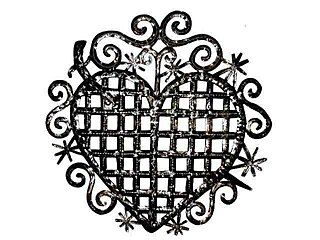
Èzili Dantò or Erzulie Dantor is the main loa or senior spirit of the Petro family in Haitian Vodou. Ezili Danto, or Èzili Dantò, is the "manifestation of Erzulie, the divinity of love." It is said that Ezili Danto has a dark complexion and is maternal in nature. The Ezili are feminine spirits in Haitian Vodou that personify womanhood. The Erzulie is a goddess, spirit, or loa of love in Haitian Voudou. She has several manifestations or incarnations, but most prominent and well-known manifestations are Lasirenn, Erzulie Freda, and Erzulie Dantor. There are spelling variations of Erzulie, the other being Ezili. They are English interpretations of a Creole word, but do not differ in meaning.
Haitian mythology consists of many folklore stories from different time periods, involving sacred dance and deities, all the way to Vodou. Haitian Vodou is a syncretic mixture of Roman Catholic rituals developed during the French colonial period, based on traditional African beliefs, with roots in Dahomey, Kongo and Yoruba traditions, and folkloric influence from the indigenous Taino peoples of Haiti. The lwa, or spirits with whom Vodou adherents work and practice, are not gods but servants of the Supreme Creator Bondye. A lot of the Iwa identities come from deities formed in the West African traditional regions, especially the Fon and Yoruba. In keeping with the French-Catholic influence of the faith, Vodou practioneers are for the most part monotheists, believing that the lwa are great and powerful forces in the world with whom humans interact and vice versa, resulting in a symbiotic relationship intended to bring both humans and the lwa back to Bondye. "Vodou is a religious practice, a faith that points toward an intimate knowledge of God, and offers its practitioners a means to come into communion with the Divine, through an ever evolving paradigm of dance, song and prayers."

François Mackandal was a Haitian Maroon leader in the French colony of Saint-Domingue. He is sometimes described as a Haitian vodou priest, or houngan. For joining Maroons to kill slave owners in Saint-Domingue, he was captured and burned alive by French colonial authorities. His actions were seen as a precursor to the Haitian Revolution.

Oungan is the term for a male priest in Haitian Vodou. The term is derived from Gbe languages. The word hounnongan means chief priest. Hounnongan or oungans are also known as makandals.
"Lisa the Iconoclast" is the sixteenth episode of the seventh season of the American animated television series The Simpsons. It originally aired on Fox in the United States on February 18, 1996. In this episode, Lisa writes an essay on Springfield founder Jebediah Springfield for the town's bicentennial. While doing research, she learns he was a murderous pirate who viewed the town's citizens with contempt. Lisa and Homer try to reveal the truth about Jebediah but only anger Springfield's residents. It was originally advertised in commercials as a Presidents' Day special episode; the episode aired the day before Presidents' Day.

Homosexuality in Haitian Vodou is religiously acceptable and homosexuals are allowed to participate in all religious activities. However, in West African countries with major conservative Christian and Islamic views on LGBTQ people, the attitudes towards them may be less tolerant if not openly hostile and these influences are reflected in African diaspora religions following Atlantic slave trade which includes Haitian Vodou.
The Rada are a family of lwa spirits in the religion of Haitian Vodou. They are regarded as being sweet-tempered and "cool", in this contrasting with the Petro lwa, which are regarded as volatile and "hot".

Haitian Vodou is an African diasporic religion that developed in Haiti between the 16th and 19th centuries. It arose through a process of syncretism between several traditional religions of West and Central Africa and Roman Catholicism. There is no central authority in control of the religion and much diversity exists among practitioners, who are known as Vodouists, Vodouisants, or Serviteurs.

Louisiana Voodoo, also known as New Orleans Voodoo, is an African diasporic religion and magic tradition that originated in Louisiana. It arose through a process of syncretism between the traditional religions of West Africa, the Roman Catholic form of Christianity, and Haitian Vodou. No central authority is in control of Louisiana Voodoo, which is organized through autonomous groups.

Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups, so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans.

Haitian Vodou art is art related to the Haitian Vodou religion. This religion has its roots in West African traditional religions brought to Haiti by slaves, but has assimilated elements from Europe and the Americas and continues to evolve. The most distinctive Vodou art form is the drapo Vodou, an embroidered flag often decorated with sequins or beads, but the term covers a wide range of visual art forms including paintings, embroidered clothing, clay or wooden figures, musical instruments and assemblages. Since the 1950s there has been growing demand for Vodou art by tourists and collectors.
Pierrot Barra (1942–1999) was a Haitian Vodou artist and priest, who was president of a Bizango society. He was well-known for his use of diverse materials to create “Vodou Things,” which functioned as charms or altars for the Vodou religion.
"Heartbreak Hotel" is the 641st episode of the American animated television series The Simpsons and the second episode of the thirtieth season. It aired in the United States on Fox on October 7, 2018. The episode was directed by Steven Dean Moore and written by Renee Ridgeley and Matt Selman.

Voodoo: Truth and Fantasy is a 1993 illustrated monograph on Haitian Vodou. Written by the Haitian sociologist of religion Laënnec Hurbon, and published in pocket format by Éditions Gallimard as the 190th volume in their 'Découvertes' collection.
References
- 1 2 Simpson, George Eaton (Oct–Dec 1942). "Loup Garou and Loa Tales from Northern Haiti". Journal of American Folklore. 55 (218): 219–227. doi:10.2307/535864 . Retrieved February 21, 2024.
- ↑ Simpson, George Eaton (1980). "4.4 Ideas about Ultimate Reality and Meaning in Haitian Vodun". Ultimate Reality and Meaning. 3 (3): 189. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
- ↑ Courlander, Harold (July 1944). "Gods of the Haitian Mountains". Journal of Negro History. 29 (3): 339. Retrieved 24 August 2024.
