Environmental finance is a field within finance that employs market-based environmental policy instruments to improve the ecological impact of investment strategies. The primary objective of environmental finance is to regress the negative impacts of climate change through pricing and trading schemes. The field of environmental finance was established in response to the poor management of economic crises by government bodies globally. Environmental finance aims to reallocate a businesses resources to improve the sustainability of investments whilst also retaining profit margins.

The Global Environment Facility (GEF) is a multilateral environmental fund that provides grants and blended finance for projects related to biodiversity, climate change, international waters, land degradation, persistent organic pollutants (POPs), mercury, sustainable forest management, food security, and sustainable cities in developing countries and countries with economies in transition. It is the largest source of multilateral funding for biodiversity globally and distributes more than $1 billion a year on average to address inter-related environmental challenges.

The Inter-American Development Bank is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America, and serving as the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean. Established in 1959, the IDB supports Latin American and Caribbean economic development, social development and regional integration by lending to governments and government agencies, including State corporations.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
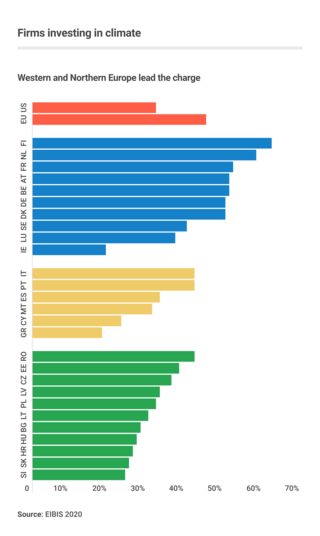
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.

Clean technology, also called cleantech or climatetech, is any process, product, or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, the sustainable use of resources, or environmental protection activities. Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy, information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lighting, grey water, and more. Environmental finance is a method by which new clean technology projects can obtain financing through the generation of carbon credits. A project that is developed with concern for climate change mitigation is also known as a carbon project.

In developing countries and some areas of more developed countries, energy poverty is lack of access to modern energy services in the home. In 2022, 759 million people lacked access to consistent electricity and 2.6 billion people used dangerous and inefficient cooking systems. Their well-being is negatively affected by very low consumption of energy, use of dirty or polluting fuels, and excessive time spent collecting fuel to meet basic needs.

The energy policy of the European Union focuses on energy security, sustainability, and integrating the energy markets of member states. An increasingly important part of it is climate policy. A key energy policy adopted in 2009 is the 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The target involved increasing the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%. After this target was met, new targets for 2030 were set at a 55% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 as part of the European Green Deal. After the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the EU's energy policy turned more towards energy security in their REPowerEU policy package, which boosts both renewable deployment and fossil fuel infrastructure for alternative suppliers.

Renewable energy in developing countries is an increasingly used alternative to fossil fuel energy, as these countries scale up their energy supplies and address energy poverty. Renewable energy technology was once seen as unaffordable for developing countries. However, since 2015, investment in non-hydro renewable energy has been higher in developing countries than in developed countries, and comprised 54% of global renewable energy investment in 2019. The International Energy Agency forecasts that renewable energy will provide the majority of energy supply growth through 2030 in Africa and Central and South America, and 42% of supply growth in China.
Conservation finance is the practice of raising and managing capital to support land, water, and resource conservation. Conservation financing options vary by source from public, private, and nonprofit funders; by type from loans, to grants, to tax incentives, to market mechanisms; and by scale ranging from federal to state, national to local.
A Green bond is a fixed-income financial instruments (bond) which is used to fund projects that have positive environmental and/or climate benefits. They follow the Green Bond Principles stated by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA), and the proceeds from the issuance of which are to be used for the pre-specified types of projects.
Eco-investing or green investing is a form of socially responsible investing where investments are made in companies that support or provide environmentally friendly products and practices. These companies encourage new technologies that support the transition from carbon dependence to more sustainable alternatives. Green finance is "any structured financial activity that’s been created to ensure a better environmental outcome."
Energy use and development in Africa varies widely across the continent, with some African countries exporting energy to neighbors or the global market, while others lack even basic infrastructures or systems to acquire energy. The World Bank has declared 32 of the 48 nations on the continent to be in an energy crisis. Energy development has not kept pace with rising demand in developing regions, placing a large strain on the continent's existing resources over the first decade of the new century. From 2001 to 2005, GDP for over half of the countries in Sub Saharan Africa rose by over 4.5% annually, while generation capacity grew at a rate of 1.2%.

Climate finance is an umbrella term for financial resources such as loans, grants, or domestic budget allocations for climate change mitigation, adaptation or resiliency. Finance can come from private and public sources. It can be channeled by various intermediaries such as multilateral development banks or other development agencies. Those agencies are particularly important for the transfer of public resources from developed to developing countries in light of UN Climate Convention obligations that developed countries have.

Ethiopia generates most of its electricity from renewable energy, mainly hydropower.

A green bank is a financial institution, typically public or quasi-public, that employs innovative financing techniques and market development tools in collaboration with the private sector to expedite the deployment of clean energy technologies. Green banks use public funds to leverage private investment in clean energy technologies that, despite their commercial viability, have struggled to establish a widespread presence in consumer markets. Green banks aim to reduce energy costs for ratepayers, stimulate private sector investment and economic activity, and expedite the transition to a low-carbon economy.

The relationship between Brazil and the World Bank has been successful for many years, despite numerous challenges.
Sustainable finance is the set of practices, standards, norms, regulations and products that pursue financial returns alongside environmental and/or social objectives. It is sometimes used interchangeably with Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) investing. However, many distinguish between ESG integration for better risk-adjusted returns and a broader field of sustainable finance that also includes impact investing, social finance and ethical investing.
Tariye Gbadegesin is a Nigerian-American businesswoman and corporate executive who is the chief executive officer of the Climate Investment Funds (CIF), effective 1 March 2024. She is the first African woman to serve in that role. She is based in Washington, DC, United States. Before that, she served as the CEO of the Lagos, Nigeria-based ARM Harith Infrastructure Investments, a joint investment fund owned by the Asset & Resource Management Company Limited ("ARM") of Nigeria and Harith General Partners (Pty) Limited ("Harith") of South Africa. Gbadegesin was also the co-chair of the Voluntary Carbon Markets Integrity Initiative (VCMI), a global initiative to mobilize high integrity carbon markets.
The Africa Renewable Energy Initiative (AREI) is an African initiative to increase the use of renewable energy on the continent.










