
Medical psychology, or Medico-psychology, is the application of psychological principles to the practice of medicine, primarily drug-oriented, for both physical and mental disorders.

A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and social processes and behavior. Their work often involves the experimentation, observation, and interpretation of how individuals relate to each other and to their environments.

Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive primary eye care.

Pharmacists, also known as chemists or druggists, are health professionals who control, formulate, preserve and dispense medications and provide advice and counselling on how medicines should be used to achieve maximum benefit, minimal side effects and to avoid drug interactions. They also serve as primary care providers in the community. Pharmacists undergo university or graduate-level education to understand the biochemical mechanisms and actions of drugs, drug uses, therapeutic roles, side effects, potential drug interactions, and monitoring parameters. This is mated to anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology. Pharmacists interpret and communicate this specialized knowledge to patients, physicians, and other health care providers.
A medical license is an occupational license that permits a person to legally practice medicine. In most countries, a person must have a medical license bestowed either by a specified government-approved professional association or a government agency before they can practice medicine. Licenses are not granted automatically to all people with medical degrees. A medical school graduate must receive a license to practice medicine to legally be called a physician. The process typically requires testing by a medical board. The medical license is the documentation of authority to practice medicine within a certain locality. An active license is also required to practice medicine as an Assistant Physician, a Physician assistant or a Clinical officer in jurisdictions with authorizing legislation.

Podiatry or podiatric medicine is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and lower extremity. The term podiatry came into use in the early 20th century in the United States and is now used worldwide, including in countries such as the United Kingdom, Australia, and Canada.
A nutritionist is a person who advises others on matters of food and nutrition and their impacts on health. Some people specialize in particular areas, such as sports nutrition, public health, or animal nutrition, among other disciplines. In many countries, a person can claim to be a nutritionist even without any training, education, or professional license, in contrast to a dietitian, who has a university degree, professional license, and certification for professional practice.
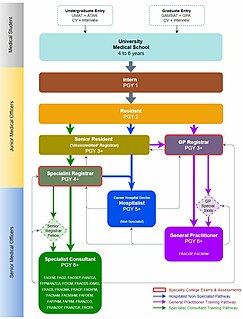
Medical education in Australia includes the educational activities involved in the initial and ongoing training of Medical Practitioners. In Australia, medical education begins in Medical School; upon graduation it is followed by a period of pre-vocational training including Internship and Residency; thereafter, enrolment into a specialist-vocational training program as a Registrar eventually leads to fellowship qualification and recognition as a fully qualified Specialist Medical Practitioner. Medical education in Australia is facilitated by Medical Schools and the Medical Specialty Colleges, and is regulated by the Australian Medical Council (AMC) and Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) of which includes the Medical Board of Australia where medical practitioners are registered nationally.
A medical intern is a physician in training who has completed medical school and has a medical degree but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised. Medical education generally ends with a period of practical training similar to internship, but the way the overall program of academic and practical medical training is structured differs depending upon the country, as does the terminology used.

The General Medical Council (GMC) is a public body that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within the United Kingdom. Its chief responsibility is to "protect, promote and maintain the health and safety of the public" by controlling entry to the register, and suspending or removing members when necessary. It also sets the standards for medical schools in the UK. Membership of the register confers substantial privileges under Part VI of the Medical Act 1983. It is a criminal offence to make a false claim of membership. The GMC is supported by fees paid by its members, and it became a registered charity in 2001.
The National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) is the main statutory authority of the Australian Government responsible for medical research. It was the eighth largest research funding body in the world in 2016, and NHMRC-funded research is globally recognised for its high quality. Around 45% of all Australian medical research from 2008–12 was funded by the federal government, through the NHMRC.
Mid-level practitioners, also called non-physician practitioners or advanced practice providers, are health care providers who have a defined scope of practice. The term mid-level refers to the complexity of healthcare situations they handle, not the quality of the care provided. This means that they are trained and legally permitted to provide healthcare in fewer situations than physicians but more than other health professionals. For example, a mid-level provider may be trained for and legally permitted to perform minor surgical procedures, but not trained for or legally permitted to perform complex or experimental surgeries.
The prescriptive authority for psychologists (RxP) movement is a movement in the United States of America among certain psychologists to give prescriptive authority to psychologists with predoctoral or postdoctoral graduate-level training in clinical psychopharmacology; successful passage of a standardized, national examination ; supervised clinical experience; or a certificate from the Department of Defense Psychopharmacology Demonstration Project; or a diploma from the Prescribing Psychologists Register to enable them, according to state law, to prescribe psychotropic medications to treat mental disorders. This approach is non-traditional medical training focused on the specialized training to prescribe for mental health disorders by a psychologist. It includes rigorous didactics and supervised clinical experience. Legislation pertaining to prescriptive authority for psychologists has been introduced over 180 times in over half of the United States. It has passed in five states, due largely to substantial lobbying efforts by the American Psychological Association (APA), the largest professional organization of psychologists in the United States with over 131,000 members. Prior to RxP legislation and in American states where it has not been passed, this role has been played by psychiatrists, who possess a medical degree and thus the authority to prescribe medication, but more frequently by primary care providers who can prescribe psychotropics, but lack extensive training in psychotropic drugs and in diagnosing and treating psychological disorders. According to the APA, the movement is a reaction to the growing public need for mental health services, particularly in under-resourced areas where patients have little or no access to psychiatrists.
Professional social workers are generally considered those who hold a professional degree in social work. In a number of countries and jurisdictions, registration or licensure of people working as social workers is required and there are mandated qualifications. In other places, the professional association sets academic and experiential requirements for admission to membership.
A clinical officer (CO) is a gazetted officer who is qualified and licensed to practice medicine.
Health professional requisites refer to the regulations used by countries to control the quality of health workers practicing in their jurisdictions and to control the size of the health labour market. They include licensure, certification and proof of minimum training for regulated health professions.
The Pharmacy and Poisons Board is the Drug Regulatory Authority established under the Pharmacy and Poisons Act, Chapter 244 of the Laws of Kenya.
Nursing in Kenya began in 1908 and was conducted without a formal framework until 1950. Over the decades, with demand for healthcare providers increasing due to marked growth in the population of Kenya, training programs were implemented.

The Pakistan Medical and Dental Council, previously known as Pakistan Medical Commission), is a statutory regulatory authority that maintains the official register of medical practitioners within Pakistan. Its chief function is to establish uniform minimum standard of basic and higher qualifications in medicine and dentistry throughout Pakistan. It also sets the education standards for Medical Colleges in Pakistan along with the Higher Education Commission.
The Sri Lanka Medical Council (SLMC) is a statutory body established in 1998, replacing the former Ceylon Medical Council. It is tasked with the regulation of the medical profession, upholding medical ethnical practices, standards of education and the safety of medical patients in Sri Lanka.









