Related Research Articles
Clinical trials are experiments or observations done in clinical research. Such prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants are designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
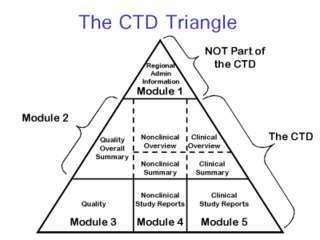
The Common Technical Document (CTD) is a set of specifications for an application dossier for the registration of Medicines and designed to be used across Europe, Japan and the United States and beyond.
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is an initiative that brings together regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss scientific and technical aspects of pharmaceutical product development and registration.
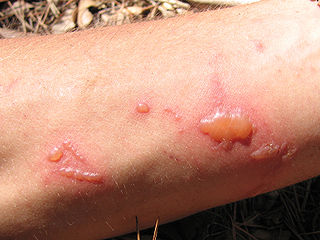
Phototoxicity, also called photoirritation, is a chemically induced skin irritation, requiring light, that does not involve the immune system. It is a type of photosensitivity.
A serious adverse event (SAE) in human drug trials is defined as any untoward medical occurrence that at any dose
- Results in death
- Is life-threatening
- Requires inpatient hospitalization or causes prolongation of existing hospitalization
- Results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity
- May have caused a congenital anomaly/birth defect
- Requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage
Good clinical practice (GCP) is an international quality standard, which governments can then transpose into regulations for clinical trials involving human subjects. GCP follows the International Council on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), and enforces tight guidelines on ethical aspects of clinical research.
A source document is a document in which data collected for a clinical trial is first recorded. This data is usually later entered in the case report form. The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH-GCP) guidelines define source documents as "original documents, data, and records." Source documents contain source data, which is defined as "all information in original records and certified copies of original records of clinical findings, observations, or other activities in a clinical trial necessary for the reconstruction and evaluation of the trial."
A clinical research associate (CRA), also called a clinical monitor or trial monitor, is a health-care professional who performs many activities related to medical research, particularly clinical trials. Clinical research associates work in various settings, such as pharmaceutical companies, medical research institutes and government agencies. Depending on the jurisdiction, different education and certification requirements may be necessary to practice as a clinical research associate.
The mission of the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS) is to advance public health through guidance on health research including ethics, medical product development and safety. CIOMS is an international nongovernmental organization established jointly by World Health Organization (WHO) and United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1949. CIOMS represents a substantial proportion of the biomedical scientific community through its member organizations.
The electronic common technical document (eCTD) is an interface and international specification for the pharmaceutical industry to agency transfer of regulatory information. The specification is based on the Common Technical Document (CTD) format and was developed by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Multidisciplinary Group 2 Expert Working Group.
In drug development and medical device development the Investigator's Brochure (IB) is a comprehensive document summarizing the body of information about an investigational product obtained during a drug trial. The IB is a document of critical importance throughout the drug development process and is updated with new information as it becomes available. The purpose of the IB is to compile data relevant to studies of the IP in human subjects gathered during preclinical and other clinical trials.
A Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC) is a person responsible for conducting clinical trials using good clinical practice (GCP) under the auspices of a Principal Investigator (PI).
Safety pharmacology is a branch of pharmacology specialising in detecting and investigating potential undesirable pharmacodynamic effects of new chemical entities (NCEs) on physiological functions in relation to exposure in the therapeutic range and above.
A confirmatory trial is an adequately controlled trial where hypotheses are stated in advance and evaluated according to a protocol. This type of trial may be implemented when it is necessary to provide additional or firm evidence of efficacy or safety.
An estimand is a quantity that is to be estimated in a statistical analysis. The term is used to more clearly distinguish the target of inference from the method used to obtain an approximation of this target and the specific value obtained from a given method and dataset. For instance, a normally distributed random variable has two defining parameters, its mean and variance . A variance estimator:
In the clinical research trial industry, loss to follow-up refers to patients who at one point in time were actively participating in a clinical research trial, but have become lost at the point of follow-up in the trial. These patients can become lost for many reasons. Without properly informing the investigator associated with the clinical trial, they may have opted to withdraw from the clinical trial, moved away from the particular study site during the clinical trial, became ill and unable to communicate, are missing or are deceased.
In order to comply with government regulatory requirements pertinent to clinical trials, every organization involved in clinical trials must maintain and store certain documents, images and content related to the clinical trial. Depending on the regulatory jurisdiction, this information may be stored in the trial master file or TMF, which today takes the form of an electronic trial master file (eTMF). The International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) published a consolidated guidance for industry on Good Clinical Practice in 1996 with the objective of providing a unified standard for the European Union, Japan, and the United States of America to facilitate mutual acceptance of clinical data by the regulatory authorities in those jurisdictions. This guidance document established the requirement across all ICH regions to establish trial master files containing essential documents that individually and collectively permit evaluation of the conduct of a trial and the quality of the data produced.[2] In some jurisdictions, for example the USA, there is no specific requirement for a trial master file. However, if the regulatory authority requires ICH GCP to be followed, then there is consequently a requirement to create and maintain a trial master file.[2]
An electronic trial master file (eTMF) is a trial master file in electronic format. It is a type of content management system for the pharmaceutical industry, providing a formalized means of organizing and storing documents, images, and other digital content for pharmaceutical clinical trials that may be required for compliance with government regulatory agencies. The term eTMF encompasses strategies, methods and tools used throughout the lifecycle of the clinical trial regulated content. An eTMF system consists of software and hardware that facilitates the management of regulated clinical trial content. Regulatory agencies have outlined the required components of eTMF systems that use electronic means to store the content of a clinical trial, requiring that they include: Digital content archiving, security and access control, change controls, audit trails, and system validation.
Guidances for statistics in regulatory affairs are applicable to the pharmaceutical industry and medical devices industry. These Guidances represent the current thinking of regulatory agencies on a particular subject. It is to be noted that the term “Guidances” is used in the USA, whereas the term “Guidelines” is used in Europe.
References
- ↑ Bellevue Biomedical: Writing your first clinical study report
- ↑ Ben Goldacre , Statins have no side effects? This is what our study really found …, Guardian newspaper, 15 March 2014
- ↑ ICH Web site
- ↑ ICH: Structure and content of clinical study reports E3
- ↑ Things Medical Writers Need for Clinical Study Reports (CSRs)