Slavey is a group of Athabaskan languages and a dialect continuum spoken amongst the Dene peoples of Canada in the Northwest Territories – or central Denendeh – where it also has official status. The languages are primarily written using a modified Latin script, with some using Canadian Aboriginal syllabics. In their own languages, these languages are referred to as: Sahtúgot’įné Yatı̨́, K’ashógot’įne Goxedǝ́ and Shíhgot’įne Yatı̨́ in the North, and Dené Dháh, Dene Yatıé or Dene Zhatıé in the South.
A relative clause is a clause that modifies a noun or noun phrase and uses some grammatical device to indicate that one of the arguments in the relative clause refers to the noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence I met a man who wasn't too sure of himself, the subordinate clause who wasn't too sure of himself is a relative clause since it modifies the noun man and uses the pronoun who to indicate that the same "man" is referred to in the subordinate clause.

In linguistic typology, nominative–accusative alignment is a type of morphosyntactic alignment in which subjects of intransitive verbs are treated like subjects of transitive verbs, and are distinguished from objects of transitive verbs in basic clause constructions. Nominative–accusative alignment can be coded by case-marking, verb agreement and/or word order. It has a wide global distribution and is the most common alignment system among the world's languages. Languages with nominative–accusative alignment are commonly called nominative–accusative languages.
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words.
A cleft sentence is a complex sentence that has a meaning that could be expressed by a simple sentence. Clefts typically put a particular constituent into focus. In spoken language, this focusing is often accompanied by a special intonation.
Vaeakau-Taumako is a Polynesian language spoken in some of the Reef Islands as well as in the Taumako Islands in the Temotu province of Solomon Islands.
Taba is a Malayo-Polynesian language of the South Halmahera–West New Guinea group. It is spoken mostly on the islands of Makian, Kayoa and southern Halmahera in North Maluku province of Indonesia by about 20,000 people.
In linguistics and pedagogy, an interlinear gloss is a gloss placed between lines, such as between a line of original text and its translation into another language. When glossed, each line of the original text acquires one or more corresponding lines of transcription known as an interlinear text or interlinear glossed text (IGT) – an interlinear for short. Such glosses help the reader follow the relationship between the source text and its translation, and the structure of the original language. In its simplest form, an interlinear gloss is a literal, word-for-word translation of the source text.
Kambera, also known as East Sumbanese, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in the eastern half of Sumba Island in the Lesser Sunda Islands, Indonesia. Kambera is a member of Bima-Sumba subgrouping within Central Malayo-Polynesian inside Malayo-Polynesian. The island of Sumba, located in Eastern Indonesia, has an area of 11,243.78 km2. The name Kambera comes from a traditional region which is close to a town in Waingapu. Because of export trades which concentrated in Waingapu in the 19th century, the language of the Kambera region has become the bridging language in eastern Sumba.
In linguistics, a complementizer or complementiser is a functional category that includes those words that can be used to turn a clause into the subject or object of a sentence. For example, the word that may be called a complementizer in English sentences like Mary believes that it is raining. The concept of complementizers is specific to certain modern grammatical theories. In traditional grammar, such words are normally considered conjunctions. The standard abbreviation for complementizer is C.
In linguistic typology, a verb–object–subject or verb–object–agent language, which is commonly abbreviated VOS or VOA, is one in which most sentences arrange their elements in that order. That would be the equivalent in English to "Ate oranges Sam." The relatively rare default word order accounts for only 3% of the world's languages. It is the fourth-most common default word order among the world's languages out of the six. It is a more common default permutation than OVS and OSV but is significantly rarer than SOV, SVO, and VSO. Families in which all or many of their languages are VOS include the following:
In linguistics, coordination is a complex syntactic structure that links together two or more elements; these elements are called conjuncts or conjoins. The presence of coordination is often signaled by the appearance of a coordinator, e.g. and, or, but. The totality of coordinator(s) and conjuncts forming an instance of coordination is called a coordinate structure. The unique properties of coordinate structures have motivated theoretical syntax to draw a broad distinction between coordination and subordination. It is also one of the many constituency tests in linguistics. Coordination is one of the most studied fields in theoretical syntax, but despite decades of intensive examination, theoretical accounts differ significantly and there is no consensus on the best analysis.
Bauré is an endangered Arawakan language spoken by only 40 of the thousand Baure people of the Beni Department of northwest of Magdalena, Bolivia. Some Bible portions have been translated into Bauré. Most speakers have been shifting to Spanish.
Roviana is a member of the North West Solomonic branch of Oceanic languages. It is spoken around Roviana and Vonavona lagoons at the north central New Georgia in the Solomon Islands. It has 10,000 first-language speakers and an additional 16,000 people mostly over 30 years old speak it as a second language. In the past, Roviana was widely used as a trade language and further used as a lingua franca, especially for church purposes in the Western Province, but now it is being replaced by the Solomon Islands Pijin. Published studies on Roviana include: Ray (1926), Waterhouse (1949) and Todd (1978) contain the syntax of Roviana. Corston-Oliver discuss ergativity in Roviana. Todd (2000) and Ross (1988) discuss the clause structure in Roviana. Schuelke (2020) discusses grammatical relations and syntactic ergativity in Roviana.
Ughele is an Oceanic language spoken by about 1200 people on Rendova Island, located in the Western Province of the Solomon Islands.
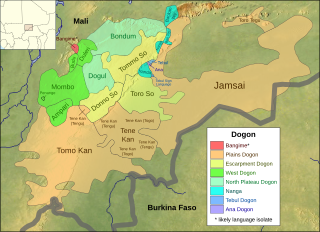
Bangime is a language isolate spoken by 3,500 ethnic Dogon in seven villages in southern Mali, who call themselves the bàŋɡá–ndɛ̀. Bangande is the name of the ethnicity of this community and their population grows at a rate of 2.5% per year. The Bangande consider themselves to be Dogon, but other Dogon people insist they are not. Bangime is an endangered language classified as 6a - Vigorous by Ethnologue. Long known to be highly divergent from the (other) Dogon languages, it was first proposed as a possible isolate by Blench (2005). Heath and Hantgan have hypothesized that the cliffs surrounding the Bangande valley provided isolation of the language as well as safety for Bangande people. Even though Bangime is not closely related to Dogon languages, the Bangande still consider their language to be Dogon. Hantgan and List report that Bangime speakers seem unaware that it is not mutually intelligible with any Dogon language.
In linguistics, pluractionality, or verbal number, if not used in its aspectual sense, is a grammatical aspect that indicates that the action or participants of a verb is, or are, plural. This differs from frequentative or iterative aspects in that the latter have no implication for the number of participants of the verb.
The Ngarnji (Ngarndji) or Ngarnka language was traditionally spoken by the Ngarnka people of the Barkly Tablelands in the Northern Territory of Australia. The last fluent speaker of the language died between 1997 and 1998. Ngarnka belongs to the Mirndi language family, in the Ngurlun branch. It is closely related to its eastern neighbours Binbinka, Gudanji and Wambaya. It is more distantly related to its western neighbour Jingulu, and three languages of the Victoria River District, Jaminjung, Ngaliwurru and Nungali. There is very little documentation and description of Ngarnka, however there have been several graduate and undergraduate dissertations written on various aspects of Ngarnka morphology, and a sketch grammar and lexicon of Ngarnka is currently in preparation.
Tamashek or Tamasheq is a variety of Tuareg, a Berber macro-language widely spoken by nomadic tribes across North Africa in Algeria, Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso. Tamasheq is one of the three main varieties of Tuareg, the others being Tamajaq and Tamahaq.
Longgu (Logu) is a Southeast Solomonic language of Guadalcanal, but originally from Malaita.

