
Richard Buckminster Fuller was an American architect, systems theorist, writer, designer, inventor, philosopher, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, publishing more than 30 books and coining or popularizing such terms as "Spaceship Earth", "Dymaxion", "ephemeralization", "synergetics", and "tensegrity".

A geodesic dome is a hemispherical thin-shell structure (lattice-shell) based on a geodesic polyhedron. The rigid triangular elements of the dome distribute stress throughout the structure, making geodesic domes able to withstand very heavy loads for their size.
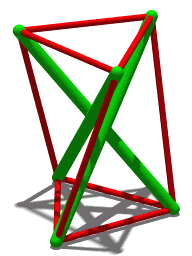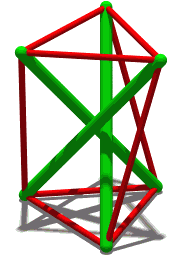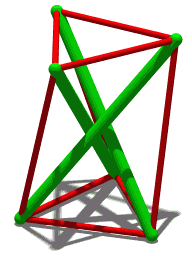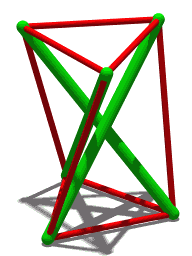
Tensegrity, tensional integrity or floating compression is a structural principle based on a system of isolated components under compression inside a network of continuous tension, and arranged in such a way that the compressed members do not touch each other while the prestressed tensioned members delineate the system spatially.

The Dymaxion House was developed by inventor and architect Buckminster Fuller to address several perceived shortcomings with existing homebuilding techniques. Fuller designed several versions of the house at different times—all of them factory manufactured kits, assembled on site, intended to be suitable for any site or environment and to use resources efficiently. A key design consideration was ease of shipment and assembly.

An aerostat is a lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of a buoyant gas. Aerostats include unpowered balloons and powered airships. A balloon may be free-flying or tethered. The average density of the craft is lower than the density of atmospheric air, because its main component is one or more gasbags, a lightweight skin containing a lifting gas to provide buoyancy, to which other components such as a gondola containing equipment or people are attached. Especially with airships, the gasbags are often protected by an outer envelope.

An Alderson disk is a hypothetical artificial astronomical megastructure, like Larry Niven's Ringworld and the Dyson sphere. The disk is a giant platter with a thickness of several thousand miles. The Sun rests in the hole at the center of the disk. The outer perimeter of an Alderson disk would be roughly equivalent to the orbit of Mars or Jupiter. According to the proposal, a sufficiently large disk would have a larger mass than its Sun.

A megastructure is a very large artificial object, although the limits of precisely how large vary considerably. Some apply the term to any especially large or tall building. Some sources define a megastructure as an enormous self-supporting artificial construct. The products of megascale engineering or astroengineering are megastructures.
Cloud Nine, cloud 9 or cloud nine is a name colloquially given to the state of euphoria, and may refer to:
A domed city is a hypothetical structure that encloses a large urban area under a single roof. In most descriptions, the dome is airtight and pressurized, creating a habitat that can be controlled for air temperature, composition and quality, typically due to an external atmosphere that is inimical to habitation for one or more reasons. Domed cities have been a fixture of science fiction and futurology since the early 20th century, offer inspirations for potential utopias and may be situated on Earth, a moon or other planet.

A solar balloon is a balloon that gains buoyancy when the air inside is heated by solar radiation, usually with the help of black or dark balloon material. The heated air inside the solar balloon expands and has lower density than the surrounding air. As such, a solar balloon is similar to a hot air balloon. Usage of solar balloons is predominantly in the toy market, although it has been proposed that they be used in the investigation of planet Mars, and some solar balloons are large enough for human flight. A vent at the top can be opened to release hot air for descent and deflation.

The Biosphere, also known as the Montreal Biosphere, is a museum dedicated to the environment in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is housed in the former United States pavilion constructed for Expo 67 located within the grounds of Parc Jean-Drapeau on Saint Helen's Island. The museum's geodesic dome was designed by Buckminster Fuller.
Colonization of Antarctica is the establishing and maintaining of control over Antarctic land for exploitation and possibly settlement.

The colonization of Venus has been a subject of many works of science fiction since before the dawn of spaceflight, and is still discussed from both a fictional and a scientific standpoint. However, with the discovery of Venus's extremely hostile surface environment, attention has largely shifted towards the colonization of the Moon and Mars instead, with proposals for Venus focused on habitats floating in the upper-middle atmosphere and on terraforming.

In science fiction and fantasy, floating cities and islands are a common trope, ranging from cities and islands that float on water to ones that float in the atmosphere of a planet by purported scientific technologies or by magical means. While very large floating structures have been constructed or proposed in real life, aerial cities and islands remain in the realm of fiction.
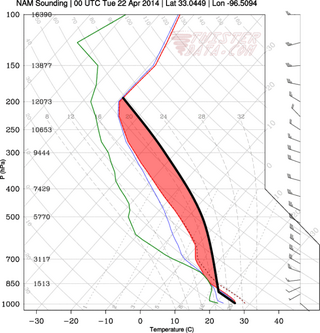
In meteorology, convective instability or stability of an air mass refers to its ability to resist vertical motion. A stable atmosphere makes vertical movement difficult, and small vertical disturbances dampen out and disappear. In an unstable atmosphere, vertical air movements tend to become larger, resulting in turbulent airflow and convective activity. Instability can lead to significant turbulence, extensive vertical clouds, and severe weather such as thunderstorms.

Tensairity is a trademarked term for a light weight structural concept that uses low pressure air to stabilize compression elements against buckling. It employs an ancient foundational splinting structure using inflated airbeams and attached stiffeners or cables that gains mechanical advantages for low mass. The structure modality has been particularly developed by Mauro Pedretti.
A lifting gas or lighter-than-air gas is a gas that has a density lower than normal atmospheric gases and rises above them as a result, making it useful in lifting lighter-than-air aircraft. Only certain lighter than air gases are suitable as lifting gases. Dry air has a density of about 1.29 g/L at standard conditions for temperature and pressure (STP) and an average molecular mass of 28.97 g/mol, and so lighter-than-air gases have a density lower than this.
Synergetics is the empirical study of systems in transformation, with an emphasis on whole system behaviors unpredicted by the behavior of any components in isolation. R. Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983) named and pioneered the field. His two-volume work Synergetics: Explorations in the Geometry of Thinking, in collaboration with E. J. Applewhite, distills a lifetime of research into book form.

Tomás Saraceno is an Argentine contemporary artist whose projects, consisting of floating sculptures, international collaborations, and interactive installations, propose and dialogue with forms of inhabiting and sensing the environment that have been suppressed in the Capitalocene era.

The skeleton of a cuboctahedron, considering its edges as rigid beams connected at flexible joints at its vertices but omitting its faces, does not have structural rigidity and consequently its vertices can be repositioned by folding at edges and face diagonals. The cuboctahedron's kinematics is noteworthy in that its vertices can be repositioned to the vertex positions of the regular icosahedron, the Jessen's icosahedron, and the regular octahedron, in accordance with the pyritohedral symmetry of the icosahedron.
















