
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering.
In software engineering, service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural style that focuses on discrete services instead of a monolithic design. SOA is a good choice for system integration. By consequence, it is also applied in the field of software design where services are provided to the other components by application components, through a communication protocol over a network. A service is a discrete unit of functionality that can be accessed remotely and acted upon and updated independently, such as retrieving a credit card statement online. SOA is also intended to be independent of vendors, products and technologies.
In system administration, orchestration is the automated configuration, coordination, deployment, development, and management of computer systems and software. Many tools exist to automate server configuration and management.
A virtual appliance is a pre-configured virtual machine image, ready to run on a hypervisor; virtual appliances are a subset of the broader class of software appliances. Installation of a software appliance on a virtual machine and packaging that into an image creates a virtual appliance. Like software appliances, virtual appliances are intended to eliminate the installation, configuration and maintenance costs associated with running complex stacks of software.

Desktop virtualization is a software technology that separates the desktop environment and associated application software from the physical client device that is used to access it.
In computing, network virtualization is the process of combining hardware and software network resources and network functionality into a single, software-based administrative entity, a virtual network. Network virtualization involves platform virtualization, often combined with resource virtualization.
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are mechanisms controlled and monitored by computer algorithms, tightly integrated with the internet and its users. In cyber-physical systems, physical and software components are deeply intertwined, able to operate on different spatial and temporal scales, exhibit multiple and distinct behavioral modalities, and interact with each other in ways that change with context. CPS involves transdisciplinary approaches, merging theory of cybernetics, mechatronics, design and process science. The process control is often referred to as embedded systems. In embedded systems, the emphasis tends to be more on the computational elements, and less on an intense link between the computational and physical elements. CPS is also similar to the Internet of Things (IoT), sharing the same basic architecture; nevertheless, CPS presents a higher combination and coordination between physical and computational elements.

In computing, virtualization (v12n) is a series of technologies that allows dividing of physical computing resources into a series of virtual machines, operating systems, processes or containers.

Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to ISO.
Application service management (ASM) is an emerging discipline within systems management that focuses on monitoring and managing the performance and quality of service of business transactions.
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an approach to network management that uses abstraction to enable dynamic and programmatically efficient network configuration to create grouping and segmentation while improving network performance and monitoring in a manner more akin to cloud computing than to traditional network management. SDN is meant to improve the static architecture of traditional networks and may be employed to centralize network intelligence in one network component by disassociating the forwarding process of network packets from the routing process. The control plane consists of one or more controllers, which are considered the brains of the SDN network, where the whole intelligence is incorporated. However, centralization has certain drawbacks related to security, scalability and elasticity.

Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. These components typically consist of a front end platform, back end platforms, a cloud based delivery, and a network. Combined, these components make up cloud computing architecture.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.

HP Cloud was a set of cloud computing services available from Hewlett-Packard. It was the combination of the previous HP Converged Cloud business unit and HP Cloud Services, an OpenStack-based public cloud. It was marketed to enterprise organizations to combine public cloud services with internal IT resources to create hybrid clouds, or a mix of private and public cloud environments, from around 2011 to 2016.
CELAR was a research project which successfully developed an open source set of tools designed to provide automatic, multi-grained resource allocation for cloud applications. In this way CELAR developed a solution that competes directly with Ubuntu Juju (software), Openstack Heat and Amazon Web Services. CELAR was developed with funding from the European Commission under the Seventh Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development, sometimes abbreviated to FP7.
Contrail was a cloud federation computing project that ran from 1 October 2010 until 31 January 2014. Contrail produced open-source cloud stack software including Security, PaaS components, Distributed file system, Application Lifecycle management middleware, and SLA Management. Contrail supports OVF standard and runs on OpenStack and OpenNebula. Contrail software is a full IaaS + PaaS Cloud stack ready to implement Cloud Federations.
Cloud robotics is a field of robotics that attempts to invoke cloud technologies such as cloud computing, cloud storage, and other Internet technologies centered on the benefits of converged infrastructure and shared services for robotics. When connected to the cloud, robots can benefit from the powerful computation, storage, and communication resources of modern data center in the cloud, which can process and share information from various robots or agent. Humans can also delegate tasks to robots remotely through networks. Cloud computing technologies enable robot systems to be endowed with powerful capability whilst reducing costs through cloud technologies. Thus, it is possible to build lightweight, low-cost, smarter robots with an intelligent "brain" in the cloud. The "brain" consists of data center, knowledge base, task planners, deep learning, information processing, environment models, communication support, etc.
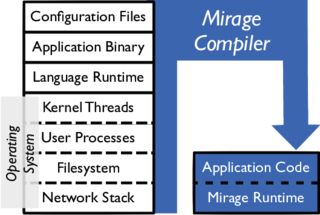
A unikernel is a type of computer program that is statically linked with the operating system code on which it depends. Unikernels are built with a specialized compiler that identifies the operating system services that a program uses and links it with one or more library operating systems that provide them. Such a program requires no separate operating system and can run instead as the guest of a hypervisor.
"X as a service" is a phrasal template for any business model in which a product use is offered as a subscription-based service rather than as an artifact owned and maintained by the customer. Originating from the software as a service concept that appeared in the 2010s with the advent of cloud computing, the template has expanded to numerous offerings in the field of information technology and beyond it. The term XaaS can mean "anything as a service".
Serverless computing is "a cloud service category in which the customer can use different cloud capabilities types without the customer having to provision, deploy and manage either hardware or software resources, other than providing customer application code or providing customer data. Serverless computing represents a form of virtualized computing." according to ISO/IEC 22123-2. Serverless computing is a broad ecosystem that includes the cloud provider, Function as a Service, managed services, tools, frameworks, engineers, stakeholders, and other interconnected elements, according to Sheen Brisals.






