Related Research Articles

Albedo is the fraction of sunlight that is diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 1.
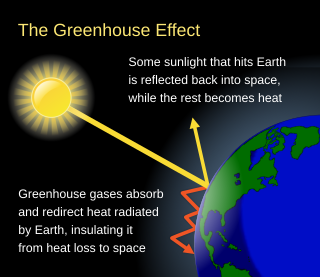
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere cause some of the heat radiated from the planet's surface to be trapped in the lower atmosphere. A planet is warmed by absorbing light from its host star and cooled by radiating energy into space. The warm surface of a planet emits infrared thermal radiation. Greenhouse gases absorb some of that radiation, reducing the amount of energy that escapes into space. This reduction in planetary cooling raises the planet's average surface temperature. Adding greenhouse gases to the atmosphere increases the warming effect.

Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light and shorter than radio waves. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). IR is commonly divided between longer wavelength thermal infrared that is emitted from terrestrial sources and shorter wavelength near-infrared that is part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.
Cloud feedback is the coupling between cloudiness and surface air temperature where a surface air temperature change leads to a change in clouds, which could then amplify or diminish the initial temperature perturbation. Cloud feedbacks can affect the magnitude of internally generated climate variability or they can affect the magnitude of climate change resulting from external radiative forcings.
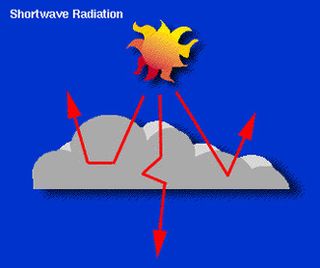
In meteorology, cloud forcing, cloud radiative forcing (CRF) or cloud radiative effect (CRE) is the difference between the radiation budget components for average cloud conditions and cloud-free conditions. Much of the interest in cloud forcing relates to its role as a feedback process in the present period of global warming.

Cloud cover refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds on average when observed from a particular location. Okta is the usual unit for measurement of the cloud cover. The cloud cover is correlated to the sunshine duration as the least cloudy locales are the sunniest ones while the cloudiest areas are the least sunny places, as clouds can block sunlight, especially on sunrise and sunset where sunlight is already limited.

The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth creates pressure, absorbs most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, warms the surface through heat retention, allowing life and liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, and reduces temperature extremes between day and night.

Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geophysics, geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines ; it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others.

Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easily visible against the environment, day or night. As a result, thermography is particularly useful to the military and other users of surveillance cameras.

Radionuclide angiography is an area of nuclear medicine which specialises in imaging to show the functionality of the right and left ventricles of the heart, thus allowing informed diagnostic intervention in heart failure. It involves use of a radiopharmaceutical, injected into a patient, and a gamma camera for acquisition. A MUGA scan involves an acquisition triggered (gated) at different points of the cardiac cycle. MUGA scanning is also called equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography, radionuclide ventriculography (RNVG), or gated blood pool imaging, as well as SYMA scanning.

Cosmic dust – also called extraterrestrial dust, space dust, or star dust – is dust that occurs in outer space or has fallen onto Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 μm), such as micrometeoroids. Larger particles are called meteoroids. Cosmic dust can be further distinguished by its astronomical location: intergalactic dust, interstellar dust, interplanetary dust, and circumplanetary dust. There are several methods to obtain space dust measurement.

The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, often from a space platform, assessing whether or not the target being observed contains live green vegetation.

Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR, is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface deformation or digital elevation, using differences in the phase of the waves returning to the satellite or aircraft. The technique can potentially measure millimetre-scale changes in deformation over spans of days to years. It has applications for geophysical monitoring of natural hazards, for example earthquakes, volcanoes and landslides, and in structural engineering, in particular monitoring of subsidence and structural stability.

Hemispherical photography, also known as canopy photography, is a technique to estimate solar radiation and characterize plant canopy geometry using photographs taken looking upward through an extreme wide-angle lens or a fisheye lens. Typically, the viewing angle approaches or equals 180-degrees, such that all sky directions are simultaneously visible. The resulting photographs record the geometry of visible sky, or conversely the geometry of sky obstruction by plant canopies or other near-ground features. This geometry can be measured precisely and used to calculate solar radiation transmitted through plant canopies, as well as to estimate aspects of canopy structure such as leaf area index. Detailed treatments of field and analytical methodology have been provided by Paul Rich and Robert Pearcy (1989).
Two instruments known as the Submillimetre Common-User Bolometer Array, or SCUBA, have been used for detecting submillimetre radiation on the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope in Hawaii.

EarthCARE is a planned joint European/Japanese satellite, the sixth of ESA's Earth Explorer Programme. The main goal of the mission is the observation and characterization of clouds and aerosols as well as measuring the reflected solar radiation and the infrared radiation emitted from Earth's surface and atmosphere.
Sea ice concentration is a useful variable for climate scientists and nautical navigators. It is defined as the area of sea ice relative to the total at a given point in the ocean. This article will deal primarily with its determination from remote sensing measurements.

N119 is a spiral-shaped H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its dimensions are large, at 131 x 175 pc. It contains several luminous stars including S Doradus, LH41-1042, and LMC195-1. Its peculiar S-shaped structure is difficult to explain with classical models.

Fixed anvil temperature hypothesis is a physical hypothesis that describes the response of cloud radiative properties to rising surface temperatures. It presumes that the temperature at which radiation is emitted by anvil clouds is constrained by radiative processes and thus does not change in response to surface warming. Since the amount of radiation emitted by clouds is a function of their temperature, it implies that it does not increase with surface warming and thus a warmer surface does not increase radiation emissions by cloud tops. The mechanism has been identified both in climate models and observations of cloud behaviour, it affects how much the world heats up for each extra tonne of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. However, some evidence suggests that it may be more correctly formulated as decreased anvil warming rather than no anvil warming.
The clearness index is a measure of atmosphere clearness. It is calculated as the fraction of the actual total solar radiation on the surface of the Earth during a certain period over the theoretical maximum (clearsky) radiation during the same period. The clearness index is a dimensionless quantity and can vary from 0 to 1.