
The history of Latvia began around 9000 BC with the end of the last glacial period in northern Europe. Ancient Baltic peoples arrived in the area during the second millennium BC, and four distinct tribal realms in Latvia's territory were identifiable towards the end of the first millennium AD. Latvia's principal river Daugava, was at the head of an important trade route from the Baltic region through Russia into southern Europe and the Middle East that was used by the Vikings and later Nordic and German traders.

Courland is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia. Courland's largest city is Liepāja, which is the third largest city in Latvia. The regions of Semigallia and Selonia are sometimes considered as part of Courland as they were formerly held by the same duke.

Kuldīga is a town in the Courland region of Latvia, in the western part of the country. It is the center of Kuldīga Municipality with a population of approximately 13,500.

The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominally vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On March 28, 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland.

The Curonian colonization of the Americas was performed by the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, which was the second-smallest state to colonise the Americas, after the Knights of Malta. It had a colony on the island of Tobago from 1654 to 1659 and intermittently from 1660 to 1689.

Jelgava is a state city in central Latvia about 41 kilometres southwest of Riga. It is the largest town in the region of Zemgale (Semigalia). Jelgava was the capital of the united Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1578–1795) and was the administrative center of the Courland Governorate (1795–1918).

Historical Latvian Lands or formerly Cultural regions of Latvia are several areas within Latvia formally recognised as distinct from the rest of the country. These are: Kurzeme (Courland), Zemgale, Latgale, Vidzeme, and Sēlija (Selonia). While some of these regions are seen purely as culturally distinct, others have historically been parts of different countries and have been used to divide the country for administrative and other purposes.

The Coat of arms of the Republic of Latvia was officially adopted by the Constitutional Assembly of Latvia on 15 June 1921, and entered official use starting on 19 August 1921. It was created using new national symbols, as well as elements of the coats of arms of Polish and Swedish Livonia and of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. Thus, the coat of arms combines symbols of Latvian national statehood, as well as symbols of its historical regions. The Latvian national coat of arms was designed by Latvian artists Vilhelms Krūmiņš and Rihards Zariņš.

Semigallia, also spelt Semigalia, is one of the Historical Latvian Lands located to the south of the Daugava river and to the north of the Saule region of Samogitia. The territory is split between Latvia and Lithuania, previously inhabited by the Semigallian Baltic tribe. They are noted for their long resistance (1219–1290) against the German crusaders and Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades. Semigallians had close linguistic and cultural ties with Samogitians.

Jaunjelgava is a town on the left bank of the Daugava River in Aizkraukle Municipality, in the Selonia region of Latvia, about 80 km southeast of Riga. The population in 2020 was 1,762.

Jacob Kettler was a Baltic German Duke of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1642–1682). Under his rule, Courland and Semigallia became more independent of its Polish suzerain, reached its peak in wealth, and even engaged in its own overseas colonization, making it one of the smallest, but fastest growing states in the world at that time.

The Baltic German nobility was a privileged social class in the territories of modern-day Estonia and Latvia. It existed continuously from the Northern Crusades and the medieval foundation of Terra Mariana.
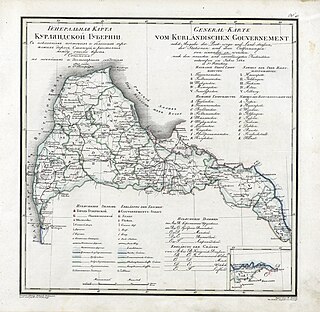
Courland Governorate, also known as the Province of Courland or Governorate of Kurland, and known from 1795 to 1796 as the Viceroyalty of Courland, was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) and one of the Baltic governorates of the Russian Empire. Its area roughly corresponded to Kurzeme, Zemgale and Sēlija of modern-day Latvia.

The Bishopric of Courland was the second smallest (4500 km2) ecclesiastical state in the Livonian Confederation founded in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade. During the Livonian War in 1559 the bishopric became a possession of Denmark, and in 1585 sold by Denmark to Poland–Lithuania.

The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was the name for a proposed client state of the German Empire during World War I which did not come into existence. It was proclaimed on 8 March 1918, in the German-occupied Courland Governorate by a council composed of Baltic Germans, who offered the crown of the once-autonomous duchy to Kaiser Wilhelm II, despite the existence of a formerly sovereign reigning family in that duchy, the Biron descendants of Ernst Johann von Biron. Although the German Reichstag supported national self-determination for the peoples of the Baltic provinces, the German High Command continued the policy of attaching these territories to the German Reich by relying on the local Baltic Germans.

Friedrich Kettler was Duke of Courland and Semigallia from 1587 to 1642.
Courland is one of the historical and cultural regions of Latvia.

The Coat of arms of Vidzeme, a region in central Latvia, depicts a white griffin in a red field. It is a version of the earlier coat of arms of Livonia granted in the 16th century.
Livonian Peasants' Laws were laws introduced in the 19th century for Governorate of Livonia of the Russian Empire. About the same time similar laws has been enacted in all Baltic governorates and Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. These laws changed and clarified peasants rights and obligations, who ethnically were mainly Estonians and Latvians. This development culminated in Peasant Community Code of 1866 which codified peasants self-governance.

The flag is an unofficial symbol of the region of Courland in Northern Europe, and historically served as the symbol of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. Today, it has no official status in Latvia.























