
The United States Postal Service is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the United States, including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the United States Constitution.

The Emergency Alert System (EAS) is a national warning system in the United States put into place on January 1, 1997, when it replaced the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS), which in turn replaced CONELRAD. It is jointly coordinated by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The EAS regulations and standards are governed by the Public Safety and Homeland Security Bureau of the FCC.
E-government is the use of technological communications devices, such as computers and the Internet to provide public services to citizens and other persons in a country or region. E-government offers new opportunities for more direct and convenient citizen access to government, and for government provision of services directly to citizens.
Source-available software is software released through a source code distribution model that includes arrangements where the source can be viewed, and in some cases modified, but without necessarily meeting the criteria to be called open-source. The licenses associated with the offerings range from allowing code to be viewed for reference to allowing code to be modified and redistributed for both commercial and non-commercial purposes.
DreamHost is a Los Angeles-based web hosting provider and domain name registrar. It is owned by New Dream Network, LLC, founded in 1996 by Dallas Bethune, Josh Jones, Michael Rodriguez and Sage Weil, undergraduate students at Harvey Mudd College in Claremont, California, and registered in 1997 by Michael Rodriguez. DreamHost began hosting customers' sites in 1997. In May 2012, DreamHost spun off Inktank. Inktank is a professional services and support company for the open source Ceph file system. In November 2014, DreamHost spun off Akanda, an open source network virtualization project. As of February 2016, Dreamhost employs about 200 employees and has close to 400,000 customers.

OpenDNS is a company and service that extends the Domain Name System (DNS) by adding features such as phishing protection and optional content filtering in addition to DNS lookup in its DNS servers.

The government of the City and County of San Francisco utilizes the "strong mayor" form of mayoral/council government, composed of the Mayor, Board of Supervisors, several elected officers, and numerous other entities. It is the only consolidated city-county in California, and one of only thirteen charter counties of California. The fiscal year 2019–20 city and county budget was approximately $12.3 billion.

GovTrack.us is a website developed by then-student Joshua Tauberer. It is based in Washington, D.C., and was launched as a hobby. It enables its users to track the bills and members of the United States Congress. Users can add trackers to certain bills, thereby narrowing the scope of the information they receive. The website collects data on members of Congress, allowing users to check members' voting records and attendance relative to their peers. It propagates the ideology of increasing transparency in the government and building better communication between the general public and the government.

Vivek Kundra is a former American administrator who served as the first chief information officer of the United States from March, 2009 to August, 2011 under President Barack Obama. He is currently the Chief Operating Officer at Sprinklr, a provider of enterprise customer experience management software based in NYC. He was previously a visiting Fellow at Harvard University.

Opsview is a software company specializing in enterprise systems monitoring software for physical, virtual, and cloud-based IT infrastructures. Its headquarters is in Reading, England, with a US office in Woburn, Massachusetts. Its product, Opsview Monitor, provides a single, unified view of IT operations.

Chris C. Kemp is an American information technology executive. His career included leading IT at the NASA Ames Research Center in Mountain View, California, and as NASA's first chief technology officer (CTO) for IT.

OpenStack is a free open standard cloud computing platform, mostly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) in both public and private clouds where virtual servers and other resources are made available to users. The software platform consists of interrelated components that control diverse, multi-vendor hardware pools of processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center. Users either manage it through a web-based dashboard, through command-line tools, or through RESTful web services.
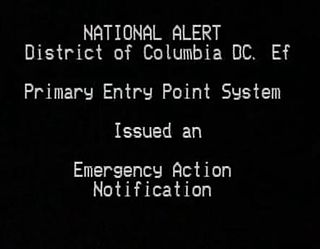
An Emergency Action Notification is the national activation of the Emergency Alert System (EAS) and is used to alert the residents of the United States of a national emergency such as a nuclear war or any other mass casualty situation. Emergency Action Notifications can only be activated by the President or the President's representative. The Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) also carried the Emergency Action Notification. No situation since the alert's creation has been serious enough to cause a US President to broadcast it.
PeopleBrowsr is a technology company that provides enterprise, government and Top Level Domain owners with the ability to launch their own blockchain integrated social networks and analyze and engage the members of those networks. An owner of new TLDs itself, PeopleBrowsr is the creator of .CEO, .Best and .Kred.

Code for America is a non-partisan, non-political 501(c)(3) organization founded in 2009 to address the widening gap between the public and private sectors in their effective use of technology and design. According to its website, the organization works to improve government services for all, starting with those who need them most. The organization began by enlisting technology and design professionals to work with city governments in the United States in order to build open-source applications and promote openness, participation, and efficiency in government, and now works with state, county, and federal government to spread the principles and practices of "delivery-driven government." It has grown into a cross-sector network of public sector change agents and a platform for "civic hacking". Code for America is also a member of the international civic technology organizations included in the Code for All organization.
OpenPlans is a non-profit technology based advocacy organization which aims to help to open up government and improve transportation systems. OpenPlans currently has a staff of 20 people. The organization was founded in 1999 by Mark Gorton, the creator of LimeWire.

Jennifer Pahlka is the founder and Executive Director of Code for America. She served as US Deputy Chief Technology Officer from June 2013 to June 2014 and helped found the United States Digital Service. Previously she had worked at CMP Media with various roles in the computer game industry. She was the co-chair and general manager of the Web 2.0 conferences.
The use of free software instead of proprietary software can give institutions better control over information technology. Therefore, a growing number of public institutions started a transition to free-software solutions. This does not only grant independence but can address the often argued need for public access to publicly funded developments. In addition, this is the only way that public services can ensure that citizen data is handled in a trustworthy manner since non-free software wouldn't allow total control over the employed functions of the needed programs.

18F is a digital services agency within the United States Government. Their purpose is to deliver digital services and technology products.
Civic technology, or civic tech, enhances the relationship between the people and government with software for communications, decision-making, service delivery, and political process. It includes information and communications technology supporting government with software built by community-led teams of volunteers, nonprofits, consultants, and private companies as well as embedded tech teams working within government.













