| Look up codeine in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Codeine is an opiate substance.
Codeine also may refer to:
- Codeine (band), American rock band (1989-1994, 2012)
- Codeine, KDE Dragon [video] Player
- "Cod'ine", song written by Buffy Sainte-Marie
| Look up codeine in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Codeine is an opiate substance.
Codeine also may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Codeine. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |

Morphine is a pain medication of the opiate family that is found naturally in a number of plants and animals, including humans. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to decrease the feeling of pain. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction and during labor. Morphine can be administered by mouth, by injection into a muscle, by injection under the skin, intravenously, injection into the space around the spinal cord, or rectally. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administered intravenously and 60 minutes when administered by mouth, while the duration of its effect is 3–7 hours. Long-acting formulations of morphine also exist.

Thebaine (paramorphine), also known as codeine methyl enol ether, is an opiate alkaloid, its name coming from the Greek Θῆβαι, Thēbai (Thebes), an ancient city in Upper Egypt. A minor constituent of opium, thebaine is chemically similar to both morphine and codeine, but has stimulatory rather than depressant effects. At high doses, it causes convulsions similar to strychnine poisoning. The synthetic enantiomer (+)-thebaine does show analgesic effects apparently mediated through opioid receptors, unlike the inactive natural enantiomer (−)-thebaine. While thebaine is not used therapeutically, it is the main alkaloid extracted from Papaver bracteatum and can be converted industrially into a variety of compounds, including hydrocodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, nalbuphine, naloxone, naltrexone, buprenorphine and etorphine. Butorphanol can also be derived from thebaine.

The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with sleep-inducing properties, and euphoric properties as well. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates and opioids, commonly morphine and heroin, as well as derivatives of many of the compounds found within raw opium latex. The primary three are morphine, codeine, and thebaine.
An opiate is any of the narcotic alkaloids found in opium.

Phenyltoloxamine is an antihistamine with sedative and analgesic effects. It is available in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol (acetominophen).
Cold water extraction is the process whereby a substance is extracted from a mixture via cold water. It is a type of fractional crystallization.

Poppy tea is a herbal tea infusion brewed from poppy straw or seeds of several species of poppy. The species most commonly used for this purpose is Papaver somniferum, which produces opium as a natural defense against predators. In the live flower, opium is released when the surface of the bulb, called the seed pod, is pierced or scraped. For the purpose of the tea, dried pods are more commonly used than the pods of the live flower. The walls of the dried pods contain opiate alkaloids, primarily consisting of morphine.

Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine.
Pantopon, also known as Opium Alkaloids Hydrochlorides, is a preparation of opiates made up of all of the alkaloids present in opium in their natural proportions as hydrochlorides salts. It can sometimes be tolerated by people who are allergic to morphine.

Thebacon, or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate, is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and is most commonly synthesised from thebaine. Thebacon is a derivative of acetyldihydrocodeine, where only the 6–7 double bond is saturated. Thebacon is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon, and as its bitartrate under Diacodin and other trade names. The hydrochloride salt has a free base conversion ratio of 0.846. Other salts used in research and other settings include thebacon's phosphate, hydrobromide, citrate, hydroiodide, and sulfate. The US DEA Administrative Controlled Substance Control Number assigned by the Controlled Substances Act 1970 for thebacon and all of its salts is 9737.

Nicocodeine is an opioid analgesic and cough suppressant, an ester of codeine closely related to dihydrocodeine and the codeine analogue of nicomorphine. It is not commonly used in most countries, but has activity similar to other opiates. Nicocodeine and nicomorphine were introduced in 1957 by Lannacher Heilmittel of Austria. Nicocodeine is metabolised in the liver by demethylation to produce nicomorphine, also known as 6-nicotinoylmorphine, and subsequently further metabolised to morphine. Side effects are similar to those of other opiates and include itching, nausea and respiratory depression. Related opioid analogues such as nicomorphine and nicodicodeine were first synthesized. The definitive synthesis, which involves treating anhydrous codeine base with nicotinic anhydride at 130 °C, was published by Pongratz and Zirm in Monatshefte für Chemie in 1957, simultaneously with the two analogues in an article about amides and esters of various organic acids.

Acetyldihydrocodeine is an opiate derivative discovered in Germany in 1914 and was used as a cough suppressant and analgesic. It is not commonly used, but has activity similar to other opiates. Acetyldihydrocodeine is a very close relative derivative of Thebacon, where only the 6-7 bond is unsaturated. Acetyldihydrocodeine can be described as the 6-acetyl derivative of dihydrocodeine and is metabolised in the liver by demethylation and deacetylation to produce dihydromorphine.
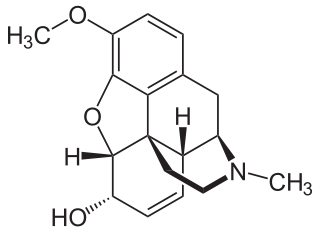
Codeine is an opiate used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours.

Benzylmorphine (Peronine) is a semi-synthetic opioid narcotic introduced to the international market in 1896 and that of the United States very shortly thereafter. It is much like codeine, containing a benzyl group attached to the morphine molecule just as the methyl group creates codeine and the ethyl group creates ethylmorphine or dionine. It is about 90% as strong as codeine by weight.

Phenampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and diampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid Co. Although never given a general release, it was trialled and 50mg codeine ≈ 60mg phenampromide. Tests on the 2 isomers showed that all of the analgesic effects were caused by the (S) isomer. In the book a 4-phenyl group added to the piperidine-ring produces a drug some x60 morphine. The potency derives from the fact that it overlays fentanyl. Phenampromide produces similar effects to other opioids, including analgesia, sedation, dizziness and nausea.
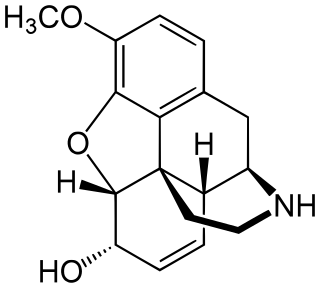
Norcodeine is an opiate analogue that is the N-demethylated derivative of codeine. It has relatively little opioid activity in its own right, but is formed as a metabolite of codeine following ingestion.

Chloromorphide (α-chloromorphide) is an opiate analog that is a derivative of morphine, where the 6-hydroxy group has been replaced by chlorine. Developed in 1933 in Germany, it has approximately ten times the potency of morphine. It has similar effects to morphine, such as sedation, analgesia, and respiratory depression.
Legal cultivation of opium for medicinal purposes is carried out in India, only in selected areas, under free licensing conditions. India is the world's largest manufacturer of legal opium for the pharmaceutical industry according to the CIA World Factbook. Legal cultivation for medical use is permissible within the ambit of United Nations, Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961.

Opiate is a term classically used in pharmacology to mean a substance derived from opium. Opioid, a more modern term, is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant Papaver somniferum. The psychoactive compounds found in the opium plant include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Opiates have long been used for a variety of medical conditions with evidence of opiate trade and use for pain relief as early as the eighth century AD. Opiates are considered drugs with moderate to high abuse potential and are listed on various "Substance-Control Schedules" under the Uniform Controlled Substances Act of the United States of America.
Tasmanian Alkaloids is the largest opium poppy processing company in the Australian state of Tasmania. Approximately forty percent of the world's legal opiate crop is grown in Tasmania. Tasmanian Alkaloids is a subsidiary of the United States pharmaceutical company Johnson & Johnson, but was formerly—as of 1980—a subsidiary of Abbott Laboratories.