
In botany, a seed is a plant embryo and food reserve enclosed in a protective outer covering called a seed coat (testa). More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted.

In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water.
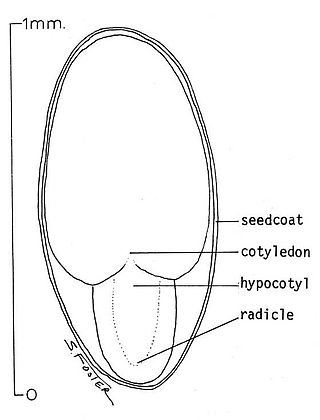
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil. Above the radicle is the embryonic stem or hypocotyl, supporting the cotyledon(s).

Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ferns, bacteria, and the growth of the pollen tube from the pollen grain of a seed plant.

The hypocotyl is the stem of a germinating seedling, found below the cotyledons and above the radicle (root).

Auxins are a class of plant hormones with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, Phytohormones, in 1937.

Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as grasses in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed. The coleoptile protects the first leaf as well as the growing stem in seedlings and eventually, allows the first leaf to emerge. Coleoptiles have two vascular bundles, one on either side. Unlike the flag leaves rolled up within, the pre-emergent coleoptile does not accumulate significant protochlorophyll or carotenoids, and so it is generally very pale. Some preemergent coleoptiles do, however, accumulate purple anthocyanin pigments.

The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread, while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and corn. Some plants, such as orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds.
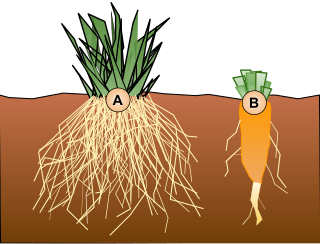
A taproot is a large, central, and dominant root from which other roots sprout laterally. Typically a taproot is somewhat straight and very thick, is tapering in shape, and grows directly downward. In some plants, such as the carrot, the taproot is a storage organ so well developed that it has been cultivated as a vegetable.
Plant embryonic development, also plant embryogenesis is a process that occurs after the fertilization of an ovule to produce a fully developed plant embryo. This is a pertinent stage in the plant life cycle that is followed by dormancy and germination. The zygote produced after fertilization must undergo various cellular divisions and differentiations to become a mature embryo. An end stage embryo has five major components including the shoot apical meristem, hypocotyl, root meristem, root cap, and cotyledons. Unlike the embryonic development in animals, and specifically in humans, plant embryonic development results in an immature form of the plant, lacking most structures like leaves, stems, and reproductive structures. However, both plants and animals including humans, pass through a phylotypic stage that evolved independently and that causes a developmental constraint limiting morphological diversification.

Gravitropism is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general feature of all higher and many lower plants as well as other organisms. Charles Darwin was one of the first to scientifically document that roots show positive gravitropism and stems show negative gravitropism. That is, roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull and stems grow in the opposite direction. This behavior can be easily demonstrated with any potted plant. When laid onto its side, the growing parts of the stem begin to display negative gravitropism, growing upwards. Herbaceous (non-woody) stems are capable of a degree of actual bending, but most of the redirected movement occurs as a consequence of root or stem growth outside. The mechanism is based on the Cholodny–Went model which was proposed in 1927, and has since been modified. Although the model has been criticized and continues to be refined, it has largely stood the test of time.

A seedling is a young sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle, the hypocotyl, and the cotyledons. The two classes of flowering plants (angiosperms) are distinguished by their numbers of seed leaves: monocotyledons (monocots) have one blade-shaped cotyledon, whereas dicotyledons (dicots) possess two round cotyledons. Gymnosperms are more varied. For example, pine seedlings have up to eight cotyledons. The seedlings of some flowering plants have no cotyledons at all. These are said to be acotyledons.
Imbibition is a special type of diffusion that takes place when liquid is absorbed by solids-colloids causing an increase in volume. Water surface potential movement takes place along a concentration gradient; some dry materials absorb water. A gradient between the absorbent and the liquid is essential for imbibition. For a substance to imbibe a liquid, there must first be some attraction between them. Imbibition occurs when a wetting fluid displaces a non-wetting fluid, the opposite of drainage in which a non-wetting phase displaces the wetting fluid. The two processes are governed by different mechanisms. Imbibition is also a type of diffusion since water movement is along the concentration gradient. Seeds and other such materials have almost no water hence they absorb water easily. Water potential gradient between the absorbent and liquid imbibed is essential for imbibition.
An epicotyl is important for the beginning stages of a plant's life. It is the region of a seedling stem above the stalks of the seed leaves of an embryo plant. It grows rapidly, showing hypogeal germination, and extends the stem above the soil surface. A common misconception is that the epicotyl, being closer to the apex of the plant, is the first part to emerge after germination - rather, the hypocotyl, the region of the stem between the point of attachment of the cotyledons and the root - forms a hook during hypogeal germination and pushes out of the soil, allowing the more delicate tissues of the plumules and apical meristem to avoid damage from pushing through the soil. The epicotyl will expand and form the point of attachment of the shoot apex and leaf primordia or "first true leaves". Cotyledons may remain belowground or be pushed up aboveground with the growing stem depending on the plant species in question.
Seed dormancy is an evolutionary adaptation that prevents seeds from germinating during unsuitable ecological conditions that would typically lead to a low probability of seedling survival. Dormant seeds do not germinate in a specified period of time under a combination of environmental factors that are normally conducive to the germination of non-dormant seeds.
Scald is common disease of barley in temperate regions. It is caused by the fungus Rhynchosporium commune and can cause significant yield losses in cooler, wet seasons.

Macrophomina phaseolina is a Botryosphaeriaceae plant pathogen fungus that causes damping off, seedling blight, collar rot, stem rot, charcoal rot, basal stem rot, and root rot on many plant species.
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names.

Grey leaf spot (GLS) is a foliar fungal disease that affects maize, also known as corn. GLS is considered one of the most significant yield-limiting diseases of corn worldwide. There are two fungal pathogens that cause GLS: Cercospora zeae-maydis and Cercospora zeina. Symptoms seen on corn include leaf lesions, discoloration (chlorosis), and foliar blight. Distinct symptoms of GLS are rectangular, brown to gray necrotic lesions that run parallel to the leaf, spanning the spaces between the secondary leaf veins. The fungus survives in the debris of topsoil and infects healthy crops via asexual spores called conidia. Environmental conditions that best suit infection and growth include moist, humid, and warm climates. Poor airflow, low sunlight, overcrowding, improper soil nutrient and irrigation management, and poor soil drainage can all contribute to the propagation of the disease. Management techniques include crop resistance, crop rotation, residue management, use of fungicides, and weed control. The purpose of disease management is to prevent the amount of secondary disease cycles as well as to protect leaf area from damage prior to grain formation. Corn grey leaf spot is an important disease of corn production in the United States, economically significant throughout the Midwest and Mid-Atlantic regions. However, it is also prevalent in Africa, Central America, China, Europe, India, Mexico, the Philippines, northern South America, and Southeast Asia. The teleomorph of Cercospora zeae-maydis is assumed to be Mycosphaerella sp.
















