
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of the nine official regions of England in the United Kingdom. Additionally, it is one of four regions that altogether make up Southern England. South West England consists of the counties of Cornwall, Dorset, Devon, Bristol, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and large towns in the region include Bath, Bristol, Bournemouth, Cheltenham, Exeter, Gloucester, Plymouth and Swindon. It is geographically the largest of the nine regions of England with a land area of 9,203 square miles (23,836 km2), but the third-least populous, with an estimated 5,764,881 residents in 2022.

The West Somerset Railway (WSR) is a 22.75-mile (36.6 km) heritage railway line in Somerset, England. The freehold of the line and stations is owned by Somerset Council. The railway is leased to and operated by West Somerset Railway plc, which is supported and minority-owned by the West Somerset Railway Association (WSRA) charitable trust and the West Somerset Railway Heritage Trust (WSRHT). WSR operates services using both heritage steam and diesel trains.

The Avon Valley Railway (AVR) is a standard gauge heritage railway in South Gloucestershire, England, operated by a local group, the Avon Valley Railway Company Ltd. The 3-mile (5 km) heritage line runs from Oldland Common to Avon Riverside. It follows the Avon Valley southeast from Oldland Common to Bitton and then it runs alongside the River Avon from Bitton towards Saltford.

The Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway, was an English railway line jointly owned by the Midland Railway (MR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) that grew to connect Bath and Bournemouth, with a branch in Somerset from Evercreech Junction to Burnham-on-Sea and Bridgwater. Strictly speaking, its main line only ran from Bath Junction to Broadstone, as the Bath to Bath Junction section was wholly owned by the MR and the Broadstone to Bournemouth section was owned by the LSWR.

Taunton railway station is a junction station on the route from London to Penzance, 163 miles 12 chains (263 km) west of London Paddington station, measured via Box. It is situated in Taunton, Somerset, and is operated by Great Western Railway. The station is also served by CrossCountry trains and by the West Somerset Railway on special event days and by mainline steam excursions.
The Bristol and Gloucester Railway was a railway company opened in 1844 to run services between Bristol and Gloucester. It was built on the 7 ftBrunel gauge, but it was acquired in 1845 by the 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge Midland Railway, which also acquired the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway at the same time.

Bridgwater railway station serves the town of Bridgwater in Somerset, England. It is on the Bristol to Taunton Line and is operated by Great Western Railway. It is 151 miles 47 chains from the zero point at London Paddington via Box.

The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied with the Great Western Railway (GWR), which built its main line between London and Bristol, and in time formed part of a through route between London and Cornwall.

Washford railway station is a station on the West Somerset Railway, a heritage railway in England. The station is situated in the village of Washford, which is itself within the civil parish of Old Cleeve in the county of Somerset.

Bishops Lydeard railway station is a heritage railway station in the village of Bishops Lydeard, Somerset, England. It is the southern terminus for regular trains on the West Somerset Railway.

Norton Fitzwarren railway station is an untimetabled station on the West Somerset Railway in Somerset, England. It was built in 2009 about 1⁄4 mile (0.4 km) north of the site of the old station that served the village of Norton Fitzwarren from 1873 until 1961. There were fatal railway accidents in the vicinity in 1890, 1940 and 1978.
The Bristol and North Somerset Railway was a railway line in the West of England that connected Bristol with Radstock, through Pensford and further into northern Somerset, to allow access to the Somerset Coalfield. The line ran almost due south from Bristol and was 16 miles (26 km) long.
The Mangotsfield and Bath branch line was a railway line opened by the Midland Railway Company in 1869 to connect Bath to its network at Mangotsfield, on its line between Bristol and Birmingham. It was usually referred to as "the Bath branch" of the Midland Railway.
Stroud railway station served the town of Stroud, in Gloucestershire, England. The station was on a short 1.25 mi-long branch from Dudbridge on the Stonehouse and Nailsworth Railway, part of the Midland Railway. It was not connected to the earlier and still used Stroud railway station on the Great Western Railway.
The Dursley and Midland Junction Railway was a company formed to build a railway branch line to connect the town of Dursley in Gloucestershire, England, to the nearby main line between Bristol and Gloucester, at Coaley. The line was opened in 1856, but was immediately loss-making, and the company soon had to sell its line to the Midland Railway.
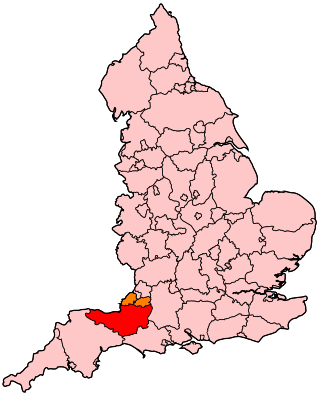
The earliest known infrastructure for transport in Somerset is a series of wooden trackways laid across the Somerset Levels, an area of low-lying marshy ground. To the west of this district lies the Bristol Channel, while the other boundaries of the county of Somerset are along chains of hills that were once exploited for their mineral deposits. These natural features have all influenced the evolution of the transport network. Roads and railways either followed the hills, or needed causeways to cross the Levels. Harbours were developed, rivers improved, and linked to sources of traffic by canals. Railways were constructed throughout the area, influenced by the needs of the city of Bristol, which lies just to the north of Somerset, and to link the ports of the far south-west with the rest of England.

The Bristol to Exeter line is a major branch of the Great Western Main Line in the West of England and runs from Bristol, to Exeter, from where it continues as the Exeter to Plymouth line. It was one of the principal routes of the pre-1948 Great Western Railway which were subsequently taken over by the Western Region of British Railways and are now part of the Network Rail system.
The Bristol and Gloucestershire Railway was an early mineral railway, opened in two stages in 1832 and 1834, which connected collieries near Coalpit Heath with Bristol, at the river Avon. Horse traction was used. It was later taken over by the Bristol and Gloucester Railway, and much of the route became part of the main line between Birmingham and Bristol, though that was later by-passed and closed. Part of it now forms the Bristol and Bath Railway Path.











