Related Research Articles

Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of permanent movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time. Often, symptoms include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, swallowing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time.

The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) is a part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH). It conducts and funds research on brain and nervous system disorders and has a budget of just over US$1.5 billion. The mission of NINDS is "to reduce the burden of neurological disease—a burden borne by every age group, every segment of society, and people all over the world". NINDS has established two major branches for research: an extramural branch that funds studies outside the NIH, and an intramural branch that funds research inside the NIH. Most of NINDS' budget goes to fund extramural research. NINDS' basic science research focuses on studies of the fundamental biology of the brain and nervous system, genetics, neurodegeneration, learning and memory, motor control, brain repair, and synapses. NINDS also funds clinical research related to diseases and disorders of the brain and nervous system, e.g. AIDS, Alzheimer disease, epilepsy, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, spinal cord injury, stroke, and traumatic brain injury.

CADASIL or CADASIL syndrome, involving cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, is the most common form of hereditary stroke disorder, and is thought to be caused by mutations of the Notch 3 gene on chromosome 19. The disease belongs to a family of disorders called the leukodystrophies. The most common clinical manifestations are migraine headaches and transient ischemic attacks or strokes, which usually occur between 40 and 50 years of age, although MRI is able to detect signs of the disease years prior to clinical manifestation of disease.
Perinatal asphyxia is the medical condition resulting from deprivation of oxygen to a newborn infant that lasts long enough during the birth process to cause physical harm, usually to the brain. It is also the inability to establish and sustain adequate or spontaneous respiration upon delivery of the newborn. It remains a serious condition which causes significant mortality and morbidity. It is an emergency condition and requires adequate and quick resuscitation measures.
Gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy which is taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using such a definition of gestational age is that menstrual periods are essentially always noticed, while there is usually a lack of a convenient way to discern when fertilization occurred.
Monoplegia is paralysis of a single limb, usually an arm. Common symptoms associated with monoplegic patients are weakness, numbness, and pain in the affected limb. Monoplegia is a type of paralysis that falls under hemiplegia. While hemiplegia is paralysis of half of the body, monoplegia is localized to a single limb or to a specific region of the body. Monoplegia of the upper limb is sometimes referred to as brachial monoplegia, and that of the lower limb is called crural monoplegia. Monoplegia in the lower extremities is not as common of an occurrence as in the upper extremities. Monoparesis is a similar, but less severe, condition because one limb is very weak, not paralyzed. For more information, see paresis.

Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) is a form of white-matter brain injury, characterized by the necrosis of white matter near the lateral ventricles. It can affect newborns and fetuses; premature infants are at the greatest risk of neonatal encephalopathy which may lead to this condition. Affected individuals generally exhibit motor control problems or other developmental delays, and they often develop cerebral palsy or epilepsy later in life.
Hypertonia is a term sometimes used synonymously with spasticity and rigidity in the literature surrounding damage to the central nervous system, namely upper motor neuron lesions. Impaired ability of damaged motor neurons to regulate descending pathways gives rise to disordered spinal reflexes, increased excitability of muscle spindles, and decreased synaptic inhibition. These consequences result in abnormally increased muscle tone of symptomatic muscles. Some authors suggest that the current definition for spasticity, the velocity-dependent over-activity of the stretch reflex, is not sufficient as it fails to take into account patients exhibiting increased muscle tone in the absence of stretch reflex over-activity. They instead suggest that "reversible hypertonia" is more appropriate and represents a treatable condition that is responsive to various therapy modalities like drug and/or physical therapy.

Intrauterine hypoxia occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system. This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders and cerebral palsy.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (anti-RhE) is caused by the anti-RhE antibody of the Rh blood group system. The anti-RhE antibody can be naturally occurring, or arise following immune sensitization after a blood transfusion or pregnancy.
Neonatal encephalopathy (NE), also known as neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, is defined by signs and symptoms of abnormal neurological function in the first few days of life in an infant born at term. In this condition there is difficulty initiating and maintaining respirations, a subnormal level of consciousness, and associated depression of tone, reflexes, and possibly seizures. Encephalopathy is a nonspecific response of the brain to injury which may occur via multiple methods, but is commonly caused by birth asphyxia, leading to cerebral hypoxia.
Birth injury refers to damage or injury to the child before, during, or just after the birthing process. "Birth trauma" refers specifically to mechanical damage sustained during delivery.

Tobacco smoking during pregnancy causes many detrimental effects on health and reproduction, in addition to the general health effects of tobacco. A number of studies have shown that tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, and that it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the foetus.

Over time, the approach to cerebral palsy management has shifted away from narrow attempts to fix individual physical problems – such as spasticity in a particular limb – to making such treatments part of a larger goal of maximizing the person's independence and community engagement. Much of childhood therapy is aimed at improving gait and walking. Approximately 60% of people with CP are able to walk independently or with aids at adulthood. However, the evidence base for the effectiveness of intervention programs reflecting the philosophy of independence has not yet caught up: effective interventions for body structures and functions have a strong evidence base, but evidence is lacking for effective interventions targeted toward participation, environment, or personal factors. There is also no good evidence to show that an intervention that is effective at the body-specific level will result in an improvement at the activity level, or vice versa. Although such cross-over benefit might happen, not enough high-quality studies have been done to demonstrate it.
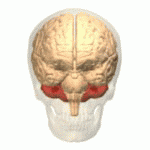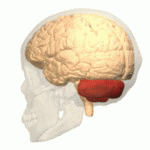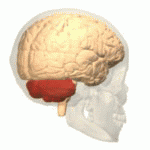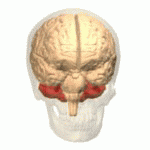
Ataxic cerebral palsy is clinically observed in approximately 5-10% of all cases of cerebral palsy, making it the least frequent form of cerebral palsy diagnosed. Ataxic cerebral palsy is caused by damage to cerebellar structures, differentiating it from the other two forms of cerebral palsy, which are spastic cerebral palsy and athetoid cerebral palsy.

Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblasts during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, either primarily or secondarily.
Neonatal Stroke, similar to a stroke which occurs in adults, is defined as a disturbance to the blood supply of the developing brain in the first 28 days of life. This description includes both ischemic events, which results from a blockage of vessels, and hypoxic events, which results from a lack of oxygen to the brain tissue, as well as some combination of the two. A neonatal stroke occurs in approximately 1 in 4000 births, but is likely much higher due to the lack of noticeable symptoms. One treatment with some proven benefits is hypothermia, but may be most beneficial in conjunction with pharmacological agents. Neonatal strokes may lead to cerebral palsy, learning difficulties, or other disabilities. Well-designed clinical trials for stroke treatment in neonates are lacking, but some current studies involve the transplantation of neural stem cells and umbilical cord stem cells; it is not yet known if this therapy is likely to be successful.
Antenatal depression, also known as prenatal or perinatal depression, is a form of clinical depression that can affect a woman during pregnancy, and can be a precursor to postpartum depression if not properly treated. It is estimated that 7% to 20% percent of pregnant women are affected by this condition. Any form of prenatal stress felt by the mother can have negative effects on various aspects of fetal development, which can cause harm to the mother and child. Even after birth, a child born from a depressed or stressed mother feels the affects. The child is less active and can also suffer from emotional distress. Antenatal depression can be caused by the stress and worry that pregnancy can bring, but at a more severe level. Other triggers include unplanned pregnancy, difficulty becoming pregnant, history of abuse, and economic or family situations.

Cannabis consumption in pregnancy might be associated with restrictions in growth of the fetus, miscarriage, and cognitive deficits. The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommended that cannabis use be stopped before and during pregnancy. Cannabis is the most commonly used illicit substance among pregnant women.
A neonatal seizure is a seizure in a baby younger than 4 weeks old. Seizures are abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. They are the most frequent neurological problem in the nursery, and often require evaluation and treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit. Seizures in the neonatal population can be categorized into acute symptomatic seizures and genetic or structural causes. Diagnosis relies on identification of the cause of the seizure, and verification of actual seizure activity by measuring of electrical activity with electroencephalography (EEG). Treatment depends on the cause of the seizure, but often includes pharmacologic treatment with anti-epileptic drugs.
References
- ↑ Baptiste-Roberts, Kesha; Nicholson, Wanda K.; Wang, Nae-Yuh; Brancati, Frederick L. (January 2012). "Gestational Diabetes and Subsequent Growth Patterns of Offspring: The National Collaborative Perinatal Project". Maternal and Child Health Journal. 16 (1): 125–132. doi:10.1007/s10995-011-0756-2. ISSN 1092-7875. PMC 3707279 . PMID 21327952.
- 1 2 Gesink Law, D. C.; Maclehose, R. F.; Longnecker, M. P. (February 2007). "Obesity and time to pregnancy". Human Reproduction. 22 (2): 414–420. doi:10.1093/humrep/del400. ISSN 0268-1161. PMC 1924918 . PMID 17095518.
- 1 2 3 Klebanoff, Mark A. (January 2009). "The Collaborative Perinatal Project: a 50-year retrospective". Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology. 23 (1): 2–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2008.00984.x. ISSN 1365-3016. PMC 2646177 . PMID 19228308.
- ↑ Hardy, Janet B. (May 2003). "The Collaborative Perinatal Project". Annals of Epidemiology. 13 (5): 303–311. doi:10.1016/S1047-2797(02)00479-9. PMID 12821268.
- ↑ Stroud, Laura R.; Solomon, Catherine; Shenassa, Edmond; Papandonatos, George; Niaura, Raymond; Lipsitt, Lewis P.; LeWinn, Kaja; Buka, Stephen L. (February 2007). "Long-term stability of maternal prenatal steroid hormones from the National Collaborative Perinatal Project: Still valid after all these years". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32 (2): 140–150. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2006.11.008. PMC 2693201 . PMID 17270355.
- ↑ Light, Irwin J. (1973-01-01). "The Collaborative Perinatal Study of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke: The Women and Their Pregnancies". Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 125 (1): 146. doi:10.1001/archpedi.1973.04160010106025. ISSN 1072-4710.
- ↑ Lubchenco, Lula O. (February 1972). "The women and their pregnancies. The collaborative study of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke". The Journal of Pediatrics. 82 (2): 340. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(73)80186-6.
- ↑ Taylor, Paul M. (1980-09-26). "The First Year of Life: The Collaborative Perinatal Project of the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 244 (13): 1503. doi:10.1001/jama.1980.03310130075046. ISSN 0098-7484.