Related Research Articles
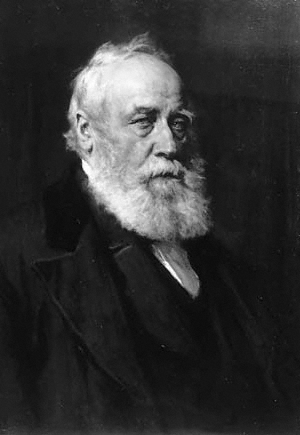
William Forbes Skene WS FRSE FSA(Scot) DCL LLD, was a Scottish lawyer, historian and antiquary.

Apple bobbing, also known as bobbing for apples, is a game often played on Halloween. The game is played by filling a tub or a large basin with water and putting apples in the water. Because apples are less dense than water, they will float at the surface. Players then try to catch one with their teeth. Use of arms is not allowed, and the hands are often tied behind the back to prevent cheating.

The Trinity College harp, also known as "Brian Boru's harp", is a medieval musical instrument on display in the long room at Trinity College Dublin in Ireland. It is an early Irish harp or wire-strung cláirseach. It is dated to the 14th or 15th century and, along with the Queen Mary Harp and the Lamont Harp, is the oldest of three surviving medieval harps from the region. The harp was used as a model for the coat of arms of Ireland and for the trade-mark of Guinness stout.

John Lesley was a Scottish Roman Catholic bishop and historian. His father was Gavin Lesley, rector of Kingussie, Badenoch.

Clan MacKinnon is a Highland Scottish clan from the islands of Mull and Skye, in the Inner Hebrides.

Clan MacIntyre is a Highland Scottish clan. The name MacIntyre, means "son of the carpenter.” It is most commonly said to descend from Maurice Mac Neil a nephew of Somerled, the great 12th century leader of the Scottish Gaels. Through an ingenious strategy, Maurice secured the marriage of Somerled to the daughter of the King of Mann and the Isles, thus greatly increasing Somerled's territories. At an unknown date the clan journeyed from the Hebrides to the Scottish mainland where the chiefs established their home at Glen Noe, in Ardchattan Parish, on the east side of Loch Etive.
Cailean Mór Caimbeul is one of the earliest attested members of Clan Campbell and an important ancestor figure of the later medieval Earls of Argyll.

Clan Maclachlan, also known as Clan Lachlan, Clann Lachainn (Argyll), and Clann Lachlainn, is a Highland Scottish clan that historically centred on the lands of Strathlachlan on Loch Fyne, Argyll on the west coast of Scotland. The clan claims descent from Lachlan Mor, who lived on Loch Fyne in the 13th century, and who has left his name upon the countryside he once controlled: places such as Strathlachlan, Castle Lachlan and Lachlan Bay. Tradition gives Lachlan Mor a descent from an Irish prince of the O'Neill dynasty, Ánrothán Ua Néill, son of Áed, son of Flaithbertach Ua Néill, King of Ailech and Cenél nEógain, died 1036. Clan Maclachlan has been associated with other clans, such as Clan Lamont, Clan Ewen of Otter, Clan MacNeil of Barra, and the MacSweens: as all claim descent from Anrothan O'Neill who left Ireland for Kintyre in the 11th century. From this descent the clan claims a further descent from the legendary Niall Noigíallach, High King of Ireland, who lived from the mid 4th century to the early 5th century.

Clan Macfie is a Highlands Scottish Clan.

Baynard Castle was a moated castle built in the 12th and 13th centuries in the village of Cottingham, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It was referred to by terms including the 'castle at Cottingham' or 'Stuteville's castle'; the term Baynard Castle is common in 19th-century references and later.

Ardcharnich is a crofting township in the parish of Loch Broom, Wester Ross in the Highland, within the Scottish council area of Highland. Scotland. The Gaelic name, Ard Charnaich means "High Cliff", and refers to a prominent inland cliff to the north east of the township which whilst clearly visible from the loch is out of sight of the settlement itself.
Clan Gillanders, also known in Scottish Gaelic as Clann Ghille Ainnriais, is a Scottish clan whose genealogy is preserved in the 15th-century manuscript MS 1467.

Dùn an Achaidh, sometimes Anglicised as Dun Acha, is a dun located near the village of Acha on the Inner Hebridean island of Coll. It is considered the best preserved dun on the island. The site of Dùn an Achaidh is located at grid reference NM18335456. According to local tradition, the dun was the stronghold of, and named after, the son of a Norse king. The early 20th century antiquary Erskine Beveridge considered it as one of the four most interesting fortifications on Coll.

MS 1467, earlier known as MS 1450, is a mediaeval Gaelic manuscript which contains numerous pedigrees for many prominent Scottish individuals and clans. Transcriptions of the genealogies within the text were first published in the early 19th century and have ever since been used by writers on the clan histories. The 19th century transcriptions and translations from the manuscript have long been considered inadequate; yet there is no modern, scholarly edition of the manuscript.
Paul Mactire, also known as Paul MacTyre, and Paul M'Tyre, was a 14th-century Scotsman who lived in the north of Scotland. He appears in several contemporary records, as well as in a 15th-century genealogy which records his supposed ancestry. He is known to have married a niece of the brother of the Earl of Ross. According to later tradition, he was a notorious robber, or freebooter in the north of Scotland; and, according to local tradition, he was the builder of a now ruinous fortress in Sutherland. He is said to be the ancestor of several Scottish families. According to some sources Paul Mactire's father was Leod Macgilleandrais.

Suibhne mac Duinnshléibhe was a late 12th-century, and early 13th-century, lord in Argyll. He does not appear in contemporary records, although his name appears in the patronymic names of two of his sons. Suibhne appears in the 16th century Leabhar Chlainne Suibhne, which documents the early history of Clann Suibhne. This account claims that he is the ancestor of Irish clan, and that he was the builder of Castle Sween in Knapdale, Argyll. However, other sources suggest the castle was built in the late 11th century by Suibhne MacAnrahan, brother of the High King of Ireland. Suibhne is said to be identical to the "Swineruo", or Suibhne Ruadh, recorded in the Ane Accompt of the Genealogie of the Campbells, a 17th-century Clan Campbell genealogy.
Donald Gregory (1803–1836) was a Scottish historian and antiquarian, who published a valuable history of the Western Highlands and Isles of Scotland.
Leod Macgilleandrais is purported to have been a 14th-century Scotsman, who lived in the north-west of Scotland. He is known from clan traditions, which date to the late 17th century. According to these traditions, Leod was a follower of the Earl of Ross, and that he was an enemy of the Mackenzies of Kintail. He is said to have captured one of the early Mackenzie chiefs, and was then later killed by the slain chief's son sometime in the 14th century. His memory is preserved in the place where he is said to have been slain. According to at least one version of the tradition, Leod was survived by a son named Paul. Several historians in 19th and early 20th centuries equated this son to Paul Mactire.
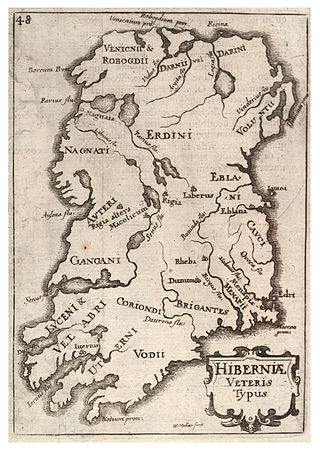
Dunum was a Latinized nameplace in ancient Ireland and the name of at least two recorded settlements there, one in the far north, one in the far south. The southerly settlement is attributed in ancient print as the original site or namesake of Rathdrum in County Wicklow. The northerly is attributed to the settlement of Downpatrick in County Down, which the Irish called Dunedh, and also Rath-keltar or Rath-Keltair, because it was the castle of Keltair, son of Duach – Rath- meaning castle – and was quoted as that in the Will of Saint Patrick.
Mary I of England died on 17 November 1558 at St James's Palace in London. She was 42 years old. Mary was buried in Westminster Abbey on 14 December.
References
- ↑ Gregg, William Henry (1910). Controversial Issues in Scottish History: A Contrast of the Early Chronicles with the Works of Modern Historians. G.P. Putnam's sons. pp. 380–406.