Collidine is the trivial name used to describe the chemical compounds which are trimethyl derivatives of pyridine. Their chemical properties resemble those of pyridine, although the presence of the methyl groups may prohibit some of the more straightforward reactions. Collidine comes in several isomers:
- 2,3,4-Collidine (2,3,4-trimethylpyridine)
- 2,3,5-Collidine (2,3,5-trimethylpyridine)
- 2,3,6-Collidine (2,3,6-trimethylpyridine)
- 2,4,5-Collidine (2,4,5-trimethylpyridine)
- 2,4,6-Collidine (2,4,6-trimethylpyridine)
- 3,4,5-Collidine (3,4,5-trimethylpyridine)
| Collidines | ||||||
| Name | 2,3,4-Collidine | 2,3,5-Collidine | 2,3,6-Collidine | 2,4,5-Collidine | 2,4,6-Collidine | 3,4,5-Collidine |
| Systematic Name | 2,3,4-Trimethylpyridine | 2,3,5-Trimethylpyridine | 2,3,6-Trimethylpyridine | 2,4,5-Trimethylpyridine | 2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine | 3,4,5-Trimethylpyridine |
| Structural formula |  |  |  |  |  | 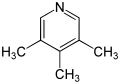 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2233-29-6 | 695-98-7 | 1462-84-6 | 1122-39-0 | 108-75-8 | 20579-43-5 |
All isomers share the molecular weight 121.18 g/mol and the chemical formula C8H11N.