Related Research Articles

Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.

A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
Teleradiology is the transmission of radiological patient images from procedures such as x-rays photographs, Computed tomography (CT), and MRI imaging, from one location to another for the purposes of sharing studies with other radiologists and physicians. Teleradiology allows radiologists to provide services without actually having to be at the location of the patient. This is particularly important when a sub-specialist such as an MRI radiologist, neuroradiologist, pediatric radiologist, or musculoskeletal radiologist is needed, since these professionals are generally only located in large metropolitan areas working during daytime hours. Teleradiology allows for specialists to be available at all times.
Sir Peter James Kerley KCVO CBE (1900–1979) was an Irish radiologist famous for his role in the lung surgery of King George VI and the naming of the radiological sign in heart failure, Kerley lines.
Kerley lines are a sign seen on chest radiographs with interstitial pulmonary edema. They are thin linear pulmonary opacities caused by fluid or cellular infiltration into the interstitium of the lungs. They are named after Irish neurologist and radiologist Peter Kerley.
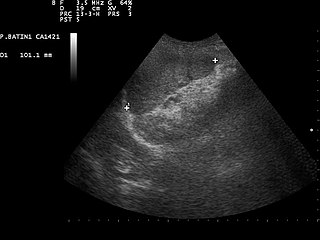
Focused assessment with sonography in trauma is a rapid bedside ultrasound examination performed by surgeons, emergency physicians, and paramedics as a screening test for blood around the heart or abdominal organs (hemoperitoneum) after trauma. There is also the extended FAST (eFAST) which includes some additional ultrasound views to assess for pneumothorax.
In chest radiography, the Westermark sign is a sign that represents a focus of oligemia (hypovolemia) seen distal to a pulmonary embolism (PE). While the chest x-ray is normal in the majority of PE cases, the Westermark sign is seen in 2% of patients.

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.

A lung nodule or pulmonary nodule is a relatively small focal density in the lung. A solitary pulmonary nodule (SPN) or coin lesion, is a mass in the lung smaller than three centimeters in diameter. A pulmonary micronodule has a diameter of less than three millimetres. There may also be multiple nodules.
Physician self-referral is a term describing the practice of a physician ordering tests on a patient that are performed by either the referring physician himself or a fellow faculty member from whom he receives financial compensation in return for the referral. Examples of self-referral include an internist performing an EKG, a surgeon suggesting an operation that he himself would perform, and a physician ordering imaging tests that would be done at a facility he owns or leases.
The Fleischner Society is an international, multidisciplinary medical society for thoracic radiology, dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the chest. Founded in 1969 by eight radiologists whose predominant professional interests were imaging of chest diseases, the Society was named in memory of Felix Fleischner, an inspiring educator, clinician, and researcher who made many contributions to the field of chest radiology. The Society has had an active membership of approximately 65 members throughout its existence as well as approximately 35 senior members, who have retired from active medical practice or work in medical science after years of active membership in the Society.
In medicine, the Golden S sign is a sign seen on imaging of the chest that suggests a central lung mass or lung collapse. It was first described by Dr. Ross Golden (1889-1975) in 1925 in association with bronchial carcinoma, but it is also seen in metastatic cancer, enlarged lymph nodes, and collapse of the right upper lobe of the lung.
Paediatric radiology is a subspecialty of radiology involving the imaging of fetuses, infants, children, adolescents and young adults. Many paediatric radiologists practice at children's hospitals.
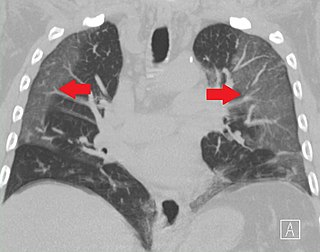
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.

Paleoradiology is the study of archaeological remains through the use of radiographic techniques, such as X-ray, CT and micro-CT scans. It is predominately used by archaeologists and anthropologists to examine mummified remains due to its non-invasive nature. Paleoradiologists can discover post-mortem damage to the body, or any artefacts buried with them, while still keeping the remains intact. Radiological images can also contribute evidence about the person's life, such as their age and cause of death. The first recorded use of paleoradiology was in 1896, just a year after the Rōntgen radiograph was first produced. Although this method of viewing ancient remains is advantageous due to its non-invasive manner, many radiologists lack expertise in archeology and very few radiologists can identify ancient diseases which may be present.
Fleischner sign is a radiological sign that aids the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. The sign indicates the dilatation of the proximal pulmonary arteries due to pulmonary embolism. It was named after Felix Fleischner, who first described it. The Fleishner sign is seen both on X-ray and CT scan of chest/thorax.
Knuckle sign is a radiologic sign used for diagnosing pulmonary embolism. The presence of a blood clot in the branch of a pulmonary artery can resemble a knuckle in CT and X-ray images, which is why it is called knuckle sign. It is frequently seen along with other signs of pulmonary embolism, such as the Fleischner sign and Westermark sign.
Dr. Morris Simon, MB, BCH, (1926–2005) was a South African-born American radiologist, professor, and inventor. His medical practice was based primarily at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, where he specialized in chest radiology. He is also credited with a number of medical inventions, including a flexible filter for dissolving blood clots, and innovations that streamlined patient care and records holding.
The "Honda sign" (H-pattern) is a radiologic sign seen in case of sacral insufficiency fracture in bilateral sacral insufficiency fractures on a radioisotope bone scan. It gets its name because the shape observed resembles the logo of the Honda motor company, resembling the alphabet "H".
References
- ↑ Chiarenza, Alessandra; Esposto Ultimo, Luca; Falsaperla, Daniele; Travali, Mario; Foti, Pietro Valerio; Torrisi, Sebastiano Emanuele; Schisano, Matteo; Mauro, Letizia Antonella; Sambataro, Gianluca; Basile, Antonio; Vancheri, Carlo; Palmucci, Stefano (4 December 2019). "Chest imaging using signs, symbols, and naturalistic images: a practical guide for radiologists and non-radiologists". Insights into Imaging. 10 (1): 114. Retrieved 15 November 2023.
- ↑ Partap, Vince A. (November 1999). "The Comet Tail Sign 1". Radiology. 213 (2): 553–554. doi:10.1148/radiology.213.2.r99nv08553.