
The Napoleonic Code, officially the Civil Code of the French, is the French civil code established during the French Consulate in 1804 and still in force in France, although heavily and frequently amended since its inception. Although Napoleon himself was not directly involved in the drafting of the Code, as it was drafted by a commission of four eminent jurists, he chaired many of the commission's plenary sessions, and his support was crucial to its passage into law.

Commercial law, which is also known by other names such as mercantile law or trade law depending on jurisdiction; is the body of law that applies to the rights, relations, and conduct of persons and organizations engaged in commercial and business activities. It is often considered to be a branch of civil law and deals with issues of both private law and public law.
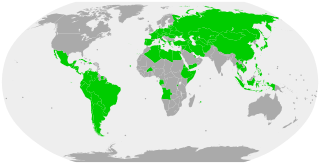
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property, family, and obligations.
In law, codification is the process of collecting and restating the law of a jurisdiction in certain areas, usually by subject, forming a legal code, i.e. a codex (book) of law.

Legal history or the history of law is the study of how law has evolved and why it has changed. Legal history is closely connected to the development of civilisations and operates in the wider context of social history. Certain jurists and historians of legal process have seen legal history as the recording of the evolution of laws and the technical explanation of how these laws have evolved with the view of better understanding the origins of various legal concepts; some consider legal history a branch of intellectual history. Twentieth-century historians viewed legal history in a more contextualised manner – more in line with the thinking of social historians. They have looked at legal institutions as complex systems of rules, players and symbols and have seen these elements interact with society to change, adapt, resist or promote certain aspects of civil society. Such legal historians have tended to analyse case histories from the parameters of social-science inquiry, using statistical methods, analysing class distinctions among litigants, petitioners and other players in various legal processes. By analyzing case outcomes, transaction costs, and numbers of settled cases, they have begun an analysis of legal institutions, practices, procedures and briefs that gives a more complex picture of law and society than the study of jurisprudence, case law and civil codes can achieve.
The Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch, abbreviated BGB, is the civil code of Germany, codifying most generally-applicably private law. In development since 1881, it became effective on 1 January 1900, and was considered a massive and groundbreaking project.
In the United States, state law refers to the law of each separate U.S. state.

Civil law is a legal system originating in Italy and France that has been adopted in large parts of the world. Modern civil law stems mainly from the Napoleonic Code of the early 19th century, and it is a continuation of ancient Roman law. Its core principles are codified into a referable system, which serves as the primary source of law.

Macau law is broadly based on Portuguese law, and therefore part of the civil law tradition of continental European legal systems. Portuguese law is itself highly influenced by German law. However, many other influences are present, including Chinese law, Italian law, and some narrow aspects of common law.
The Egyptian Civil Code is the primary source of civil law for Egypt.

A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the code was enacted, by a process of codification. Though the process and motivations for codification are similar in different common law and civil law systems, their usage is different.
The Polish law or legal system in Poland has been developing since the first centuries of Polish history, over 1,000 years ago. The public and private laws of Poland are codified.
Lithuanian law is a part of the legal system of Lithuania. It belongs to the civil law legal system, as opposed to the common law legal system. The legal system of Lithuania is based on epitomes of the French and German systems. The Lithuanian legal system is grounded on the principles laid out in the Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania and safeguarded by the Constitutional Court of the Republic of Lithuania.
Codification of laws is a common practice in the Philippines. Many general areas of substantive law, such as criminal law, civil law and labor law are governed by codes of law.
The Burgerlijk Wetboek is the Civil Code of the Netherlands. Early versions were largely based on the Napoleonic Code. The Dutch Civil Code was substantively reformed in 1992. The Code deals with the rights of natural persons, legal persons, patrimony and succession. It also sets out the law of property, obligations and contracts, and conflict of laws. Proposed amendments will add a Book on intellectual property.

The Civil Code of California is a collection of statutes for the State of California. The code is made up of statutes which govern the general obligations and rights of persons within the jurisdiction of California. It was based on a civil code originally prepared by David Dudley Field II in 1865 for the state of New York. It is one of the 29 California Codes and was among the first four enacted in 1872.

The legal system of Belgium is based on the Napoleonic code. The Napoleonic code is the French civil code which was issued between 1804 and 1810. It clearly presents the French legal system. Belgium’s constitution is influenced by earlier constitutions of the French and the Netherlands. Belgium is one of a few countries in the world where defendants are often denied the right to defend themselves. Belgium became an independent state in 1830 with the help of British government and there were restrictions on the parliamentary system of Belgium government. The language differences in Belgium have caused governmental and constitutional problems. Official languages are French, Dutch and German, which has official status in one district only. Parliamentary democracy usually ends up becoming a coalition government. Belgium is a federal state and has a civil law system.

The law of Sweden is a civil law system, whose essence is manifested in its dependence on statutory law. Sweden's civil law tradition, as in the rest of Europe, is founded upon Roman law as codified in the Corpus Juris Civilis, but as developed within German law, rather than upon the Napoleonic Code. But, over time Sweden along with the other Scandinavian countries have deviated significantly from their classical Roman and German models. Instead, the Scandinavian countries together with Finland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Åland (self-governing) and Iceland may be said to have a special "Nordic" version of jurisprudence that is neither a truly civil law system nor a part of the British-derived common law legal system.
The law of Ohio consists of several levels, including constitutional, statutory, and regulatory, local and common law. The Ohio Revised Code forms the general statutory law.









