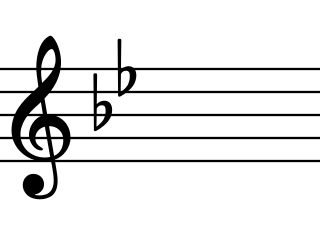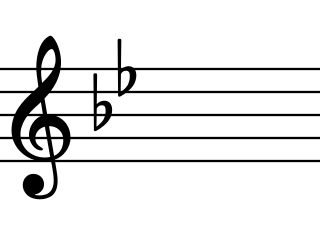
In musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp, flat, and rarely, natural symbols placed together on the staff. Key signatures are generally written immediately after the clef at the beginning of a line of musical notation, although they can appear in other parts of a score, notably after a double barline.

Lisp is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation. Originally specified in 1958, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language in widespread use today. Only Fortran is older, by one year. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Racket, Common Lisp, Scheme and Clojure.

Music notation or musical notation is any system used to visually represent aurally perceived music played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of written, printed, or otherwise-produced symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests.
Polish notation (PN), also known as normal Polish notation (NPN), Łukasiewicz notation, Warsaw notation, Polish prefix notation or simply prefix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators precede their operands, in contrast to the more common infix notation, in which operators are placed between operands, as well as reverse Polish notation (RPN), in which operators follow their operands. It does not need any parentheses as long as each operator has a fixed number of operands. The description "Polish" refers to the nationality of logician Jan Łukasiewicz, who invented Polish notation in 1924.
Staccato is a form of musical articulation. In modern notation, it signifies a note of shortened duration, separated from the note that may follow by silence. It has been described by theorists and has appeared in music since at least 1676.

A clef is a musical symbol used to indicate the pitch of written notes. Placed on a stave, it indicates the name and pitch of the notes on one of the lines. This line serves as a reference point by which the names of the notes on any other line or space of the stave may be determined.
In Western musical notation, the staff (US) or stave (UK) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pitch, percussion notes are placed by instrument, and rests and other symbols are placed by convention.
Sheet music is a handwritten or printed form of musical notation that uses musical symbols to indicate the pitches, rhythms, or chords of a song or instrumental musical piece. Like its analogs – printed books or pamphlets in English, Arabic, or other languages – the medium of sheet music typically is paper, although the access to musical notation since the 1980s has included the presentation of musical notation on computer screens and the development of scorewriter computer programs that can notate a song or piece electronically, and, in some cases, "play back" the notated music using a synthesizer or virtual instruments.

LilyPond is a computer program and file format for music engraving. One of LilyPond's major goals is to produce scores that are engraved with traditional layout rules, reflecting the era when scores were engraved by hand.
This is a list of musical terms that are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special musical meanings of these phrases differ from the original or current Italian meanings. Most of the other terms are taken from French and German, indicated by "Fr." and "Ger.", respectively.
A rest is a musical notation sign that indicates the absence of a sound.

Braille music is a Braille code that allows music to be notated using Braille cells so music can be read by visually impaired musicians. The Braille music system was originally developed by Louis Braille.
In music, an accent is an emphasis, stress, or stronger attack placed on a particular note or set of notes, or chord, either as a result of its context or specifically indicated by an accent mark. Accents contribute to the articulation and prosody of a performance of a musical phrase. Accents may be written into a score or part by a composer or added by the performer as part of his or her interpretation of a musical piece.
The numbered musical notation, is a musical notation system widely used in music publications in China. It dates back to the system designed by Pierre Galin, known as Galin-Paris-Chevé system. It is comparable to the Gongche notation from the Tang Dynasty.

A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation.
Articulation is a fundamental musical parameter that determines how a single note or other discrete event is sounded. Articulations primarily structure an event's start and end, determining the length of its sound and the shape of its attack and decay. They can also modify an event's timbre, dynamics, and pitch. Musical articulation is analogous to the articulation of speech, and during the Baroque and Classical periods it was taught by comparison to oratory.
Percussion notation is a type of musical notation indicating notes to be played by percussion instruments. As with other forms of musical notation, sounds are represented by symbols which are usually written onto a musical staff.
Portato, also mezzo-staccato, French notes portées, in music denotes a smooth, pulsing articulation and is often notated by adding dots under slur markings.
MusicEase is a proprietary WYSIWYG scorewriter created by Gary Rader and produced by MusicEase Software. It enables computers using Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X to produce musical notation and listen to them in MIDI.