Related Research Articles

Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as MF4.
A personal communications service (PCS) is set of communications capabilities that provide a combination of terminal mobility, personal mobility, and service profile management. This class of services comprises several types of wireless voice or wireless data communications systems, typically incorporating digital technology, providing services similar to advanced cellular mobile or paging services. In addition, PCS can also be used to provide other wireless communications services, including services that allow people to place and receive communications while away from their home or office, as well as wireless communications to homes, office buildings and other fixed locations. Described in more commercial terms, PCS is a generation of wireless cellular-phone technology, that combines a range of features and services surpassing those available in analogue- and first-generation (2G) digital-cellular phone systems, providing a user with an all-in-one wireless phone, paging, messaging, and data service.

Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of signals, whether communications between people or from electronic signals not directly used in communication. As classified and sensitive information is usually encrypted, signals intelligence may necessarily involve cryptanalysis. Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling to whom and in what quantity—is also used to integrate information, and it may complement cryptanalysis.

MIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
Data communication, including data transmission and data reception, is the transfer of data, transmitted and received over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication using radio spectrum, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth, or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

The UL enterprise is a global private safety company headquartered in Northbrook, Illinois, composed of three organizations, UL Research Institutes, UL Standards & Engagement and UL Solutions.

A safety-critical system or life-critical system is a system whose failure or malfunction may result in one of the following outcomes:

Diver communications are the methods used by divers to communicate with each other or with surface members of the dive team. In professional diving, diver communication is usually between a single working diver and the diving supervisor at the surface control point. This is considered important both for managing the diving work, and as a safety measure for monitoring the condition of the diver. The traditional method of communication was by line signals, but this has been superseded by voice communication, and line signals are now used in emergencies when voice communications have failed. Surface supplied divers often carry a closed circuit video camera on the helmet which allows the surface team to see what the diver is doing and to be involved in inspection tasks. This can also be used to transmit hand signals to the surface if voice communications fails. Underwater slates may be used to write text messages which can be shown to other divers, and there are some dive computers which allow a limited number of pre-programmed text messages to be sent through-water to other divers or surface personnel with compatible equipment.
In telecommunications, trunking is a technology for providing network access to multiple clients simultaneously by sharing a set of circuits, carriers, channels, or frequencies, instead of providing individual circuits or channels for each client. This is reminiscent to the structure of a tree with one trunk and many branches. Trunking in telecommunication originated in telegraphy, and later in telephone systems where a trunk line is a communications channel between telephone exchanges.

A two-way radio is a radio transceiver, which is used for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication with other users with similar radios, in contrast to a broadcast receiver, which only receives transmissions.
Virtual Telecommunications Access Method (VTAM) is the IBM subsystem that implements Systems Network Architecture (SNA) for mainframe environments. VTAM provides an application programming interface (API) for communication applications, and controls communication equipment such as adapters and controllers. In modern terminology, VTAM provides a communication stack and device drivers.

Military communications or military signals involve all aspects of communications, or conveyance of information, by armed forces. Examples from Jane's Military Communications include text, audio, facsimile, tactical ground-based communications, naval signalling, terrestrial microwave, tropospheric scatter, satellite communications systems and equipment, surveillance and signal analysis, security, direction finding and jamming. The most urgent purposes are to communicate information to commanders and orders from them.

In aviation, ACARS is a digital datalink system for transmission of short messages between aircraft and ground stations via airband radio or satellite. The protocol was designed by ARINC and deployed in 1978, using the Telex format. More ACARS radio stations were added subsequently by SITA.
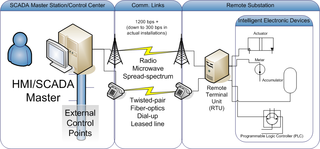
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
Cobham Limited is a British aerospace manufacturing company based in Bournemouth, England.

Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments. A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching system, and other plain old telephone service facilities, optical fiber cabling, IP networks, and microwave transmission systems. Telecommunications engineering also overlaps with broadcast engineering.
Unified communications (UC) is a business and marketing concept describing the integration of enterprise communication services such as instant messaging (chat), presence information, voice, mobility features, audio, web & video conferencing, fixed-mobile convergence (FMC), desktop sharing, data sharing, call control and speech recognition with non-real-time communication services such as unified messaging. UC is not necessarily a single product, but a set of products that provides a consistent unified user interface and user experience across multiple devices and media types.

Telex is a telecommunication service that provides text-based message exchange over the circuits of the public switched telephone network or by private lines. The technology operates on switched station-to-station basis with teleprinter devices at the receiving and sending locations. Telex was a major method of sending text messages electronically between businesses in the post–World War II period. Its usage went into decline as the fax machine grew in popularity in the 1980s.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.