
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift, while moving through air or some other fluid. As such, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as an airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expressed as its lift-to-drag ratio. The lift a wing generates at a given speed and angle of attack can be one to two orders of magnitude greater than the total drag on the wing. A high lift-to-drag ratio requires a significantly smaller thrust to propel the wings through the air at sufficient lift.

A submersible pump is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped. The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface as opposed to jet pumps having to pull fluids. Submersibles are more efficient than jet pumps.

A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backhoes, hydraulic brakes, power steering systems, transmissions, garbage trucks, aircraft flight control systems, lifts, and industrial machinery.

A check valve, clack valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction.

Gas lift or bubble pumps use the artificial lift technique of raising a fluid such as water or oil by introducing bubbles of compressed air, water vapor or other vaporous bubbles into the outlet tube. This has the effect of reducing the hydrostatic pressure in the outlet tube vs. the hydrostatic pressure at the inlet side of the tube.

A steam injector is typically used to deliver cold water to a boiler against its own pressure using its own live or exhaust steam, replacing any mechanical pump. This was the purpose for which it was originally invented in 1858 by Henri Giffard. Its operation was from the start intriguing since it seemed paradoxical, almost like perpetual motion, but its operation was later explained using thermodynamics. Other types of injector may use other pressurised motive fluids such as air.

A lift table is a device that employs a scissors mechanism to raise or lower goods and/or persons. Typically lift tables are used to raise large, heavy loads through relatively small distances. Common applications include pallet handling, vehicle loading and work positioning. Lift tables are a recommended way to help reduce incidents of musculoskeletal disorders by correctly re-positioning work at a suitable height for operators. Lift tables lend themselves to being easily adapted to a specific use. They can work in hostile environments, be manufactured in stainless steel and have equipment like conveyors, turn-tables, barriers and gates easily added to their deckplates.

The term drafting water refers to the use of suction to move a liquid such as water from a vessel or body of water below the intake of a suction pump. A rural fire department or farmer might draft water from a pond as the first step in moving the water elsewhere. A suction pump creates a partial vacuum and the atmospheric pressure on the water's surface forces the water into the pump, usually via a rigid pipe or a semi-rigid hard suction hose.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.

The pumping of water is a basic and practical technique, far more practical than scooping it up with one's hands or lifting it in a hand-held bucket. This is true whether the water is drawn from a fresh source, moved to a needed location, purified, or used for irrigation, washing, or sewage treatment, or for evacuating water from an undesirable location. Regardless of the outcome, the energy required to pump water is an extremely demanding component of water consumption. All other processes depend or benefit either from water descending from a higher elevation or some pressurized plumbing system.

Centrifugal pumps are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from where it exits.

A tube well is a type of water well in which a long, 100–200 millimetres (3.9–7.9 in)-wide, stainless steel tube or pipe is bored into an underground aquifer. The lower end is fitted with a strainer, and a pump lifts water for irrigation. The required depth of the well depends on the depth of the water table.

A photobioreactor is a bioreactor that utilizes a light source to cultivate phototrophic microorganisms. These organisms use photosynthesis to generate biomass from light and carbon dioxide and include plants, mosses, macroalgae, microalgae, cyanobacteria and purple bacteria. Within the artificial environment of a photobioreactor, specific conditions are carefully controlled for respective species. Thus, a photobioreactor allows much higher growth rates and purity levels than anywhere in nature or habitats similar to nature. Hypothetically, phototropic biomass could be derived from nutrient-rich wastewater and flue gas carbon dioxide in a photobioreactor.
Artificial lift refers to the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.
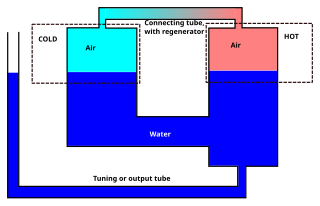
A Fluidyne engine is an alpha or gamma type Stirling engine with one or more liquidpistons. It contains a working gas, and either two liquid pistons or one liquid piston and a displacer.

A sprayer is a device used to spray a liquid, where sprayers are commonly used for projection of water, weed killers, crop performance materials, pest maintenance chemicals, as well as manufacturing and production line ingredients. In agriculture, a sprayer is a piece of equipment that is used to apply herbicides, pesticides, and fertilizers on agricultural crops. Sprayers range in size from man-portable units to trailed sprayers that are connected to a tractor, to self-propelled units similar to tractors, with boom mounts of 4-30 feet up to 60–151 feet in length depending on engineering design for tractor and land size.

A river rapids ride is an amusement ride that simulates whitewater rafting.

Lift irrigation is a method of irrigation in which water is not transported by natural flow, but is lifted with pumps or surge pools etc.
A rotodynamic pump is a kinetic machine in which energy is continuously imparted to the pumped fluid by means of a rotating impeller, propeller, or rotor, in contrast to a positive displacement pump in which a fluid is moved by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing the trapped volume into the pump's discharge. Examples of rotodynamic pumps include adding kinetic energy to a fluid such as by using a centrifugal pump to increase fluid velocity or pressure.
















