In computing, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts the packets of data sent over an internet protocol network. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs).
Trusted Computing (TC) is a technology developed and promoted by the Trusted Computing Group. The term is taken from the field of trusted systems and has a specialized meaning. With Trusted Computing, the computer will consistently behave in expected ways, and those behaviors will be enforced by computer hardware and software. Enforcing this behavior is achieved by loading the hardware with a unique encryption key inaccessible to the rest of the system.
An open standard is a standard that is publicly available and has various rights to use associated with it, and may also have various properties of how it was designed. There is no single definition and interpretations vary with usage.
A broadcast flag is a set of status bits sent in the data stream of a digital television program that indicates whether or not the data stream can be recorded, or if there are any restrictions on recorded content. Possible restrictions include the inability to save an unencrypted digital program to a hard disk or other non-volatile storage, inability to make secondary copies of recorded content, forceful reduction of quality when recording, and inability to skip over commercials.
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of digital copy protection developed by Intel Corporation to prevent copying of digital audio & video content as it travels across connections. Types of connections include DisplayPort (DP), Digital Visual Interface (DVI), and High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), as well as less popular or now deprecated protocols like Gigabit Video Interface (GVIF) and Unified Display Interface (UDI).
The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards body which develops open standards for the mobile phone industry. It is not a formal government-sponsored standards organization like the ITU, but a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.
Digital Transmission Content Protection (DTCP) is a digital rights management (DRM) technology that restrict digital home technologies including DVD players and televisions by encrypting interconnections between devices. This permits the distribution of content through other devices such as personal computers or portable media players, if they also implement the DTCP standards. DTCP has also been referred to as "5C" content protection, a reference to the five companies that created DTCP; Hitachi, Intel, Matsushita, Sony, and Toshiba.
Content Protection for Recordable Media and Pre-Recorded Media (CPRM/CPPM) is a mechanism for controlling the copying, moving and deletion of digital media on a host device, such as a personal computer, or other player. It is a form of digital rights management (DRM) developed by The 4C Entity, LLC.
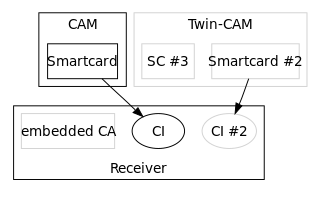
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.
The Broadcast Protection Discussion Group (BPDG) is a working group of content providers, television broadcasters, consumer electronics manufacturers, information technology companies, interested individuals and consumer activists. The group was formed specifically for the purpose of evaluating the suitability of the broadcast flag for preventing unauthorized redistribution and to determine whether there was substantial support for the broadcast flag. The group completed its mission with the release of the BPDG Report.
DVB Content Protection & Copy Management often abbreviated to DVB-CPCM or CPCM is a digital rights management standard being developed by the DVB Project. Its main application is interoperable rights management of European digital television, though other countries may also adopt the standard.
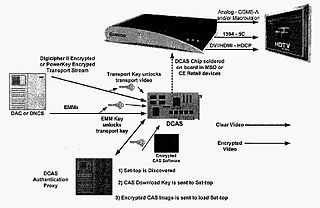
Downloadable Conditional Access System or DCAS was a proposal advanced by CableLabs for secure software download of a specific Conditional Access client which controls digital rights management (DRM) into an OCAP-compliant host consumer media device. The National Cable & Telecommunications Association (NCTA) proposed that DCAS be used as a substitute for physical CableCARDs, a standard also created by CableLabs for which products began appearing in August 2004 as part of industry compliance to the FCC mandate, which in turn is pursuant to the Telecommunications Act of 1996. DCAS is growing in popularity as a less expensive alternative for CableCARD, with major North American operator deployments from Cablevision and Charter. DCAS deployments can be expected to grow in the coming years, thanks to favorable regulatory view from the STELA Reauthorization Act of 2014 and FCC appointing a Downloadable Security Technical Advisory Committee, and wider support for key ladder (K-LAD) functionality from system-on-chip (SoC) vendors and set-top box manufacturers.
ISO 13485Medical devices -- Quality management systems -- Requirements for regulatory purposes is an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard published for the first time in 1996; it represents the requirements for a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. This standard supersedes earlier documents such as EN 46001 and EN 46002, the previously published ISO 13485, and ISO 13488. ISO 13485:2016 Certificates meets the requirement of IEC 60601-2-25 : 1993 + A1: 1999 safety of Electrocardiograms.
Teletext was introduced in the analogue television in the 80's, leading to a limited interaction with television sets to obtain information about things like the schedule and weather. But nowadays this concept goes even far away and a new and improved way of interaction with the user has been developed. The early private broadcasters, as Canal+, were the pioneers in adopting this new form and today are preceded by their digital formats.
A hardware restriction is content protection enforced by electronic components. The hardware restriction scheme may complement a digital rights management system implemented in software. Some examples of hardware restriction information appliances are video game consoles, smartphones, tablet computers, Macintosh computers and personal computers that implement secure boot.

Cinavia, originally called Verance Copy Management System for Audiovisual Content (VCMS/AV), is an analog watermarking and steganography system under development by Verance since 1999, and released in 2010. In conjunction with the existing Advanced Access Content System (AACS) digital rights management (DRM) inclusion of Cinavia watermarking detection support became mandatory for all consumer Blu-ray Disc players from 2012.
IEC 62455 is an International Electrotechnical Commission terminal specification standard, prepared by the IEC 100 Technical Committee (TC), for a service purchase and protection system for digital broadcasts. Its full title is Internet protocol (IP) and transport stream (TS) based service access. This 18Crypt technology aimed to compete the Open Security Framework (OSF) has never been successful in the market where less than 10 000 deployed devices were using it. On the opposite, the OSF aimed as an open approach enabling wider competition has been widely deployed in a large number of devices and re-used in many standards like in the USA or in China...

SAT>IP specifies a IP-based Client-Server communication protocol for a TV gateway in which SAT>IP servers, connected to one or more DVB broadcast sources, send the program selected and requested by an SAT>IP client over an IP based local area network in either unicast for the one requesting client or multicast in one datastream for several SAT>IP clients.
A trusted execution environment (TEE) is a secure area of a main processor. It guarantees code and data loaded inside to be protected with respect to confidentiality and integrity. A TEE as an isolated execution environment provides security features such as isolated execution, integrity of applications executing with the TEE, along with confidentiality of their assets. In general terms, the TEE offers an execution space that provides a higher level of security than a rich mobile operating system open and more functionality than a 'secure element' (SE).