Related Research Articles
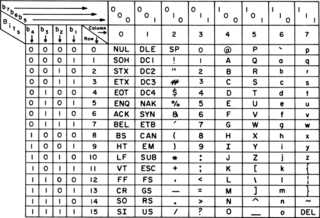
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Most modern character-encoding schemes are based on ASCII, although they support many additional characters.
Grid computing is the use of widely distributed computer resources to reach a common goal. A computing grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve many files. Grid computing is distinguished from conventional high-performance computing systems such as cluster computing in that grid computers have each node set to perform a different task/application. Grid computers also tend to be more heterogeneous and geographically dispersed than cluster computers. Although a single grid can be dedicated to a particular application, commonly a grid is used for a variety of purposes. Grids are often constructed with general-purpose grid middleware software libraries. Grid sizes can be quite large.
Identity management (IdM), also known as identity and access management, is a framework of policies and technologies for ensuring that the proper people in an enterprise have the appropriate access to technology resources. IdM systems fall under the overarching umbrellas of IT security and data management. Identity and access management systems not only identify, authenticate, and authorize individuals who will be utilizing IT resources, but also the hardware and applications employees need to access. Identity and access management solutions have become more prevalent and critical in recent years as regulatory compliance requirements have become increasingly more rigorous and complex.

JavaScript Object Notation is an open standard file format, and data interchange format, that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs and array data types. It is a very common data format, with a diverse range of applications, such as serving as a replacement for XML in AJAX systems.

Integrated Computer-Aided Manufacturing (ICAM) is a US Air Force program that develops tools, techniques, and processes to support manufacturing integration. It influenced the computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) project efforts of many companies. The ICAM program was founded in 1976 and initiative managed by the US Air Force at Wright-Patterson as a part of their technology modernization efforts. The program initiated the development a series of standards for modeling and analysis in management and business improvement, called Integrated Definitions, short IDEFs.
Common Logic (CL) is a framework for a family of logic languages, based on first-order logic, intended to facilitate the exchange and transmission of knowledge in computer-based systems.
Mass spectrometry is a scientific technique for measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It is often coupled to chromatographic techniques such as gas- or liquid chromatography and has found widespread adoption in the fields of analytical chemistry and biochemistry where it can be used to identify and characterize small molecules and proteins (proteomics). The large volume of data produced in a typical mass spectrometry experiment requires that computers be used for data storage and processing. Over the years, different manufacturers of mass spectrometers have developed various proprietary data formats for handling such data which makes it difficult for academic scientists to directly manipulate their data. To address this limitation, several open, XML-based data formats have recently been developed by the Trans-Proteomic Pipeline at the Institute for Systems Biology to facilitate data manipulation and innovation in the public sector. These data formats are described here.
CIMI may refer to:
The Museum Computer Network (MCN) is a US-based non-profit organization for professionals with an interest in the use of computer technology for museums.
Spectra may refer to:
Cary Karp, is a museum curator based in Sweden, has been instrumental in developing online facilities for museums in the context of the International Council of Museums (ICOM). In particular, he was central in promoting and establishing the .museum top-level domain as President of the international Museum Domain Management Association (MuseDoma). He has also been a principal contributor to establishment of standards for registration of internationalized domain names.

Metadata is "data that provides information about other data". In other words, it is "data about data." Many distinct types of metadata exist, including descriptive metadata, structural metadata, administrative metadata, reference metadata and statistical metadata.
The Getty Vocabulary Program is a department within the Getty Research Institute at the Getty Center in Los Angeles, California. It produces and maintains the Getty controlled vocabulary databases, Art and Architecture Thesaurus, Union List of Artist Names, and Getty Thesaurus of Geographic Names. They are compliant with ISO and NISO standards for thesaurus construction. The Getty vocabularies are the premiere references for categorizing works of art, architecture, material culture, and the names of artists, architects, and geographic names. They have been the life work of many people and continue to be critical contributions to cultural heritage information management and documentation. They contain terms, names, and other information about people, places, things, and concepts relating to art, architecture, and material culture. They can be accessed online free of charge on the Getty website.

Europeana is a web portal created by the European Union containing digitalised museum collections of more than 3,000 institutions across Europe. It includes records of over 10 million cultural and scientific artefacts, brought together on a single platform and presented in a variety of ways relevant to modern users. The prototype for Europeana was the European Digital Library Network (EDLnet), launched in 2008.
Categories for the Description of Works of Art (CDWA) describes the content of art databases by articulating a conceptual framework for describing and accessing information about works of art, architecture, other material culture, groups and collections of works, and related images. The CDWA includes 532 categories and subcategories. A small subset of categories are considered core in that they represent the minimum information necessary to identify and describe a work. The CDWA includes discussions, basic guidelines for cataloging, and examples.
Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC) is the combination of cloud computing and mobile computing to bring rich computational resources to mobile users, network operators, as well as cloud computing providers. The ultimate goal of MCC is to enable execution of rich mobile applications on a plethora of mobile devices, with a rich user experience. MCC provides business opportunities for mobile network operators as well as cloud providers. More comprehensively, MCC can be defined as "a rich mobile computing technology that leverages unified elastic resources of varied clouds and network technologies toward unrestricted functionality, storage, and mobility to serve a multitude of mobile devices anywhere, anytime through the channel of Ethernet or Internet regardless of heterogeneous environments and platforms based on the pay-as-you-use principle."

FUJITSU Cloud IaaS Trusted Public S5 is a Fujitsu cloud computing platform that aims to deliver standardized enterprise-class public cloud services globally. It offers Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) from Fujitsu's data centers to provide computing resources that can be employed on-demand and suited to customers' needs. The service ensures a high level of reliability that is sufficient for deployment in mission-critical systems.
The Public Services Network (PSN) is the UK government's high-performance network, which helps public sector organisations work together, reduce duplication and share resources. It unified the provision of network infrastructure across the United Kingdom public sector into an interconnected "network of networks" to increase efficiency and reduce overall public expenditure.
Cloud Infrastructure Management Interface (CIMI) is an open standard API specification for managing cloud infrastructure.
A Collections Management System (CMS), sometimes called a Collections Information System, is software used by the collections staff of a collecting institution or by individual private collectors and collecting hobbyists or enthusiasts. Collecting institutions are primarily museums and archives and cover a very broad range from huge, international institutions, to very small or niche-specialty institutions such as local historical museums and preservation societies. Secondarily, libraries and galleries are also collecting institutions. Collections Management Systems (CMSs) allow individuals or collecting institutions to organize, control, and manage their collections' objects by “tracking all information related to and about” those objects. In larger institutions, the CMS may be used by collections staff such as registrars, collections managers, and curators to record information such as object locations, provenance, curatorial information, conservation reports, professional appraisals, and exhibition histories. All of this recorded information is then also accessed and used by other institutional departments such as “education, membership, accounting, and administration."
References
- ↑ "Computer Interchange of Museum Information (CIMI)". Museum and cultural heritage information standards and organisations. ICOM . Retrieved May 7, 2012.
- ↑ CIMI. "Standards Framework". Spectra . Museum Computer Network. 20 (2–3). Archived from the original on 2012-04-23. Retrieved 2012-05-07.