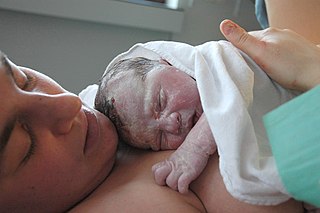
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in developing countries most are home births.

A doula is a non-medical professional who provides guidance for the service of others and who supports another person through a significant health-related experience, such as childbirth, miscarriage, induced abortion or stillbirth, as well as non-reproductive experiences such as dying. A doula might also provide support to the client's partner, family, and friends.

House arrest is a legal measure where a person is required to remain at their residence under supervision, typically as an alternative to imprisonment. The person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted and may require prior approval.

Solitary confinement is a form of imprisonment in which an incarcerated person lives in a single cell with little or no contact with other people. It is a punitive tool used within the prison system to discipline or separate incarcerated individuals who are considered to be security risks to other incarcerated individuals or prison staff, as well as those who violate facility rules or are deemed disruptive. However, it can also be used as protective custody for incarcerated individuals whose safety is threatened by other prisoners. This is employed to separate them from the general prison population and prevent injury or death.
Solitary is the state of being alone or in solitude. The term may refer to:

A nanny is a person who provides child care. Typically, this care is given within the children's family setting. Throughout history, nannies were usually servants in large households and reported directly to the lady of the house. Today, modern nannies, like other domestic workers, may live in or out of the house, depending on their circumstances and those of their employers. Some employment agencies specialize in providing nannies, as there are families that specifically seek them and may make them a part of the household.

The postpartum period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to last for six weeks. There are three distinct phases of the postnatal period; the acute phase, lasting for six to twelve hours after birth; the subacute phase, lasting six weeks; and the delayed phase, lasting up to six months. During the delayed phase, some changes to the genitourinary system take much longer to resolve and may result in conditions such as urinary incontinence. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and newborn deaths occur during this period.
Isolation is the near or complete lack of social contact by an individual.
The Four Seasons, originally referring to the traditional seasons of spring, summer, autumn, and winter, may refer to:
In the field of obstetrics, lochia is the vaginal discharge after giving birth, containing blood, mucus, and uterine tissue. Lochia discharge typically continues for four to eight weeks after childbirth, a time known as the postpartum period or puerperium. A 2016 review ties this "lochial period" to worldwide customs of postpartum confinement, a time for the new mother and baby to bond.
POC most commonly refers to:
Birth or parturition is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring.

In Christian tradition the churching of women, also known as thanksgiving for the birth or adoption of a child, is the ceremony wherein a blessing is given to mothers after recovery from childbirth. The ceremony includes thanksgiving for the woman's survival of childbirth, and is performed even when the child is stillborn, or has died unbaptized.

Convalescence is the gradual recovery of health and strength after illness or injury.
A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, physician, obstetrician, or nurse, is trained to be present at ("attend") childbirth, whether the delivery takes place in a health care institution or at home, to recognize and respond appropriately to medical complications, and to implement interventions to help prevent them in the first place, including through prenatal care. Different birth attendants are able to provide different levels of care.

Lying-in is the term given to the European forms of postpartum confinement, the traditional practice involving long bed rest before and after giving birth. The term and the practice it describes are old-fashioned or archaic, but lying-in used to be considered an essential component of the postpartum period, even if there were no medical complications during childbirth.

A maternity hospital specializes in caring for women during pregnancy and childbirth. It also provides care for newborn infants, and may act as a centre for clinical training in midwifery and obstetrics. Formerly known as lying-in hospitals, most of them, like cottage hospitals, have been absorbed into larger general hospitals, where they operate as the maternity department.
Solitary confinement is a punishment or special form of imprisonment in which a prisoner is denied contact with any other persons.

Postpartum confinement is a traditional practice following childbirth. Those who follow these customs typically begin immediately after the birth, and the seclusion or special treatment lasts for a culturally variable length: typically for one month or 30 days, 26 days, up to 40 days, two months, or 100 days. This postnatal recuperation can include care practices in regards of "traditional health beliefs, taboos, rituals, and proscriptions." The practice used to be known as "lying-in", which, as the term suggests, centres on bed rest. In some cultures, it may be connected to taboos concerning impurity after childbirth.
Abuse during childbirth is generally defined as interactions or conditions deemed humiliating or undignified by local consensus and interactions or conditions experienced as or intended to be humiliating or undignifying. Bowser and Hill's 2010 landscape analysis defined seven categories of abusive or disrespectful care, including physical abuse, non-consented clinical care, non-confidential care, non-dignified care, discrimination, abandonment, and detention in health facilities.










