Related Research Articles

Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. This could happen through direct absorption, a merger, a tender offer or a hostile takeover. As an aspect of strategic management, M&A can allow enterprises to grow or downsize, and change the nature of their business or competitive position.

A conglomerate is a type of multi-industry company that consists of several different and unrelated business entities that operate in various industries under one corporate group. A conglomerate usually has a parent company that owns and controls many subsidiaries, which are legally independent but financially and strategically dependent on the parent company. Conglomerates are often large and multinational corporations that have a global presence and a diversified portfolio of products and services. Conglomerates can be formed by merger and acquisitions, spin-offs, or joint ventures.
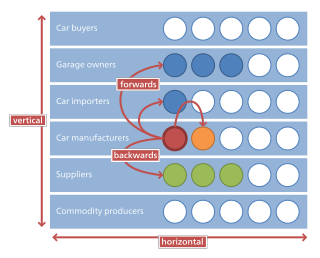
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same level of the value chain, in the same industry. A company may do this via internal expansion, acquisition or merger.

In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It contrasts with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation.
Economies of scope are "efficiencies formed by variety, not volume". In economics, "economies" is synonymous with cost savings and "scope" is synonymous with broadening production/services through diversified products. Economies of scope is an economic theory stating that average total cost of production decrease as a result of increasing the number of different goods produced. For example, a gas station that sells gasoline can sell soda, milk, baked goods, etc. through their customer service representatives and thus gasoline companies achieve economies of scope. The business historian Alfred Chandler argued that economies of scope contributed to the rise of American business corporations during the 20th century.
In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates. Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning.

Financial services are economic services tied to finance provided by financial institutions. Financial services encompass a broad range of service sector activities, especially as concerns financial management and consumer finance.
A strategic alliance is an agreement between two or more parties to pursue a set of agreed upon objectives needed while remaining independent organizations.
A strategic partnership is a relationship between two commercial enterprises, usually formalized by one or more business contracts. A strategic partnership will usually fall short of a legal partnership entity, agency, or corporate affiliate relationship. Strategic partnerships can take on various forms from shake hand agreements, contractual cooperation's all the way to equity alliances, either the formation of a joint venture or cross-holdings in each other.

Alfred A. Knopf, Inc. is an American publishing house that was founded by Blanche Knopf and Alfred A. Knopf Sr. in 1915. Blanche and Alfred traveled abroad regularly and were known for publishing European, Asian, and Latin American writers in addition to leading American literary trends. It was acquired by Random House in 1960, and is now part of the Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group division of Penguin Random House which is owned by the German conglomerate Bertelsmann.
A private equity fund is a collective investment scheme used for making investments in various equity securities according to one of the investment strategies associated with private equity. Private equity funds are typically limited partnerships with a fixed term of 10 years. At inception, institutional investors make an unfunded commitment to the limited partnership, which is then drawn over the term of the fund. From the investors' point of view, funds can be traditional or asymmetric.
Merger control refers to the procedure of reviewing mergers and acquisitions under antitrust / competition law. Over 130 nations worldwide have adopted a regime providing for merger control. National or supernational competition agencies such as the EU European Commission, the UK Competition and Markets Authority, or the US Department of Justice or Federal Trade Commission are normally entrusted with the role of reviewing mergers.
A corporate group, company group or business group, also formally known as a group of companies, is a collection of parent and subsidiary corporations that function as a single economic entity through a common source of control. These types of groups are often managed by an account manager. The concept of a group is frequently used in tax law, accounting and company law to attribute the rights and duties of one member of the group to another or the whole. If the corporations are engaged in entirely different businesses, the group is called a conglomerate. The forming of corporate groups usually involves consolidation via mergers and acquisitions, although the group concept focuses on the instances in which the merged and acquired corporate entities remain in existence rather than the instances in which they are dissolved by the parent. The group may be owned by a holding company which may have no actual operations.
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) is an American imprint of the American Dutch publishing conglomerate Wolters Kluwer. It was established by the acquisition of Williams & Wilkins and its merger with J.B. Lippincott Company in 1998. Under the LWW brand, Wolters Kluwer, through its Health Division, publishes scientific, technical, and medical content such as textbooks, reference works, and over 275 scientific journals. Publications are aimed at physicians, nurses, clinicians, and students.
Diversification is a corporate strategy to enter into or start new products or product lines, new services or new markets, involving substantially different skills, technology and knowledge.
Lear Siegler Incorporated (LSI) is a diverse American corporation established in 1962. Its products range from car seats and brakes to weapons control systems for military fighter planes. The company's more than $2 billion-a-year annual sales comes from three major areas: aerospace-technology, automotive parts, and industrial-commercial. The company, however, is basically anonymous, since its products are either unmarked or bear only the label "LSI". Lear Siegler went private in 1987.
National champions are corporations which are technically private businesses but due to governmental policy are ceded a dominant position in a national economy. In this system, these large organizations are expected not only to seek profit but also to "advance the interests of the nation"; the government sets policies which favor these organizations. The policy is practiced by many governments, in some sectors more than others, but by giving an unfair advantage against market competition, the policy promotes economic nationalism domestically and global pre-eminence abroad contrary to the free market. The policy also deters or prevents venture capitalism.
Strategic fit expresses the degree to which an organization is matching its resources and capabilities with the opportunities in the external environment. The matching takes place through strategy and it is therefore vital that the company has the actual resources and capabilities to execute and support the strategy. Strategic fit can be used actively to evaluate the current strategic situation of a company as well as opportunities such as mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and divestitures of organizational divisions. Strategic fit is related to the resource-based view of the firm which suggests that the key to profitability is not only through positioning and industry selection but rather through an internal focus which seeks to utilize the unique characteristics of the company's portfolio of resources and capabilities. A unique combination of resources and capabilities can eventually be developed into a competitive advantage which the company can profit from. However, it is important to differentiate between resources and capabilities. Resources relate to the inputs to production owned by the company, whereas capabilities describe the accumulation of learning the company possesses.
In international trade, foreign market entry modes are the ways in which a company can expand its services into a non-domestic market.

The Ansoff matrix is a strategic planning tool that provides a framework to help executives, senior managers, and marketers devise strategies for future business growth. It is named after Russian American Igor Ansoff, an applied mathematician and business manager, who created the concept.
References
- ↑ Campbell R. McConnell and Stanley L. Brue (2005). Economics. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 603. ISBN 9780072819359.
- ↑ John Leslie Livingstone and Theodore Grossman (2001). The Portable MBA in Finance and Accounting. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 563–564. ISBN 9780471168560.
- ↑ Jay B. Barney and William S. Hesterly (2008). Strategic Management and Competitive Advantages. Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 313–314. ISBN 978-0-13-613520-3.