
In certain Christian denominations, holy orders are the ordained ministries of bishop, priest (presbyter), and deacon, and the sacrament or rite by which candidates are ordained to those orders. Churches recognizing these orders include the Catholic Church, the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Anglican, Assyrian, Old Catholic, Independent Catholic and some Lutheran churches. Except for Lutherans and some Anglicans, these churches regard ordination as a sacrament.

Ecumenism – also called interdenominationalism, or ecumenicalism – is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjective ecumenical is thus applied to any non-denominational initiative that encourages greater cooperation and union among Christian denominations and churches.
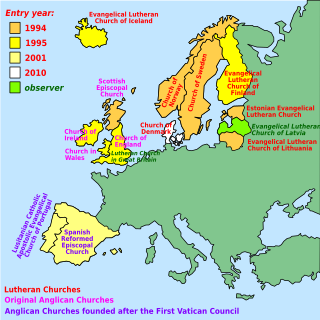
The Porvoo Communion is a communion of 15 predominantly northern European Anglican and Evangelical Lutheran churches, with a couple of far-southwestern European church bodies of the same denomination. It was established in 1992 by a theological agreement entitled the Porvoo Common Statement which establishes full communion between and among these churches. The agreement was negotiated in the town of Järvenpää in Finland, but the communion's name comes from the nearby city of Porvoo, where a joint Eucharist was celebrated in Porvoo Cathedral after the formal signing in Järvenpää.
The Continuing Anglican movement, also known as the Anglican Continuum, encompasses a number of Christian churches, principally based in North America, that have an Anglican identity and tradition but are not part of the Anglican Communion.

John Henry Hobart was the third Episcopal bishop of New York (1816–1830). He vigorously promoted the extension of the Episcopal Church in upstate New York, as well as founded both the General Theological Seminary in New York City and Geneva College in Geneva in the Finger Lakes area. He was the beloved pastor of Elizabeth Seton before her conversion to Catholicism.
The Pastoral Provision is a set of practices and norms in the Catholic Church in the United States, by which bishops are authorized to provide spiritual care for Catholics converting from the Anglican tradition, by establishing parishes for them and ordaining priests from among them. The provision provides a way for individuals to become priests in territorial dioceses, even after Pope Benedict XVI's Anglicanorum Coetibus proclamation established the Personal Ordinariates, a non-diocesan mechanism for former Anglicans to join the Church.

The Reformed Episcopal Church (REC) is an Anglican church of evangelical Episcopalian heritage. It was founded in 1873 in New York City by George David Cummins, a former bishop of the Protestant Episcopal Church.
In Christianity, the term secular clergy refers to deacons and priests who are not monastics or otherwise members of religious life. Secular priests are priests who commit themselves to a certain geographical area and are ordained into the service of the residents of a diocese or equivalent church administrative region. That includes serving the everyday needs of the people in parishes, but their activities are not limited to that of their parish.

High church Lutheranism is a movement that began in 20th-century Europe and emphasizes worship practices and doctrines that are similar to those found within Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy and Anglo-Catholicism. In the more general usage of the term, it describes the general high church characteristics of Lutheranism in Nordic and Baltic countries such as Sweden, Finland, Estonia and Latvia. The mentioned countries, once a part of the Swedish Empire, have more markedly preserved Catholic traditions.

The Episcopal Diocese of Tennessee is the diocese of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America that covers roughly Middle Tennessee. A single diocese spanned the entire state until 1982, when the Episcopal Diocese of West Tennessee was created; the Diocese of Tennessee was again split in 1985 when the Episcopal Diocese of East Tennessee was formed. It is headquartered in Nashville, Tennessee.

Frederick Joseph Kinsman was an American Roman Catholic church historian who had formerly been a bishop of the Protestant Episcopal Church. From 1908 to 1919 he was Episcopal Bishop of Delaware.

Anglican interest in ecumenical dialogue can be traced back to the time of the Reformation and dialogues with both Orthodox and Lutheran churches in the sixteenth century. In the nineteenth century, with the rise of the Oxford Movement, there arose greater concern for reunion of the churches of "Catholic confession". This desire to work towards full communion with other denominations led to the development of the Chicago-Lambeth Quadrilateral, approved by the Third Lambeth Conference of 1888. The four points were stipulated as the basis for church unity, "a basis on which approach may be by God's blessing made towards Home Reunion":

The Episcopal Church (TEC), based in the United States with additional dioceses elsewhere, is a member church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. It is a mainline Protestant denomination and is divided into nine provinces. The presiding bishop of the Episcopal Church is Michael Bruce Curry, the first African American bishop to serve in that position.
The ordination of lesbian, gay, bisexual and/or transgender (LGBT) clergy who are open about their sexuality or gender identity; are sexually active if lesbian, gay, or bisexual; or are in committed same-sex relationships is a debated practice within some contemporary Christian denominations.

Robert Josias "Raphael" Morgan was a Jamaican-American who is believed to be the first Black Eastern Orthodox priest in the United States. After being active in other denominations, including the AME Church, Church of England, and the Episcopal Church, Morgan converted to Orthodoxy. He was ordained as an Orthodox priest of the Ecumenical Patriarchate. He was designated as "Missionary to America and the West Indies." He claimed to have founded the "Order of Golgotha", but the Orthodox Church is not organized into orders.
William McGarvey (1861–1924) was a Catholic priest and former Episcopal priest who served as rector of St. Elizabeth's Church in Philadelphia. In 1896 he became the leader of a group known as the Congregation of the Companions of the Holy Saviour (CSSS), which was associated with St. Elisabeth's.

Mount Calvary Church is a Catholic parish located in the Seton Hill neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. The church was founded in 1842 as a mission congregation within the Episcopal Church and is now a community within the Personal Ordinariate of the Chair of Saint Peter of the Catholic Church.
Charles Philip Augustus Burnett was a major American Anglo-Catholic priest, liturgist, and author in the Episcopal Church. Born in Skaneateles, New York, he was graduated from the General Theological Seminary in 1878, and ordained to the priesthood "with full literary qualifications" in 1879 by Bishop Horatio Potter of the Episcopal Diocese of New York. Burnett was associated closely with William McGarvey of Philadelphia, but remained within the Protestant Episcopal Church after McGarvey and many of his followers became Roman Catholics in the Open Pulpit Controversy of 1907-1909.

The Church of the Annunciation, also called the Church of the Annunciation of the Blessed Virgin Mary, is a North Philadelphia Episcopal church in the Episcopal Diocese of Pennsylvania. It has an historic Anglo-Catholic liturgical identity. Its original name as a mission congregation beginning in 1870 was the Church of Our Merciful Saviour until 1882. Founded formally in 1880, it had 580 active members in 1960, and reported average attendance of 15 in 2022.
American Church Union (ACU) is the name of several distinct Anglican organizations in the American Episcopal Church and the Anglican Continuum. The groups have had an Anglo-Catholic orientation. It is named in imitation of the English Church Union.












