
The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought by the Delian League led by Athens against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. Historians have traditionally divided the war into three phases. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese and attempt to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. This period of the war was concluded in 421 BC, with the signing of the Peace of Nicias. That treaty, however, was soon undermined by renewed fighting in the Peloponnese. In 415 BC, Athens dispatched a massive expeditionary force to attack Syracuse, Sicily; the attack failed disastrously, with the destruction of the entire force in 413 BC. This ushered in the final phase of the war, generally referred to either as the Decelean War, or the Ionian War. In this phase, Sparta, now receiving support from the Achaemenid Empire, supported rebellions in Athens's subject states in the Aegean Sea and Ionia, undermining Athens's empire, and, eventually, depriving the city of naval supremacy. The destruction of Athens's fleet in the Battle of Aegospotami effectively ended the war, and Athens surrendered in the following year. Corinth and Thebes demanded that Athens should be destroyed and all its citizens should be enslaved, but Sparta refused.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.
This decade witnessed the continuing decline of the Achaemenid Empire, fierce warfare amongst the Greek city-states during the Peloponnesian War, the ongoing Warring States period in Zhou dynasty China, and the closing years of the Olmec civilization in modern-day Mexico.

This is a timeline of Ancient Greece from its emergence around 800 BC to its subjection to the Roman Empire in 146 BC.
Year 424 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Crassus, Fidenas, Rutilus and Iullus. The denomination 424 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Nicias, was an Athenian politician and general during the period of the Peloponnesian War. Nicias was a member of the Athenian aristocracy and had inherited a large fortune from his father, which was invested in the silver mines around Attica's Mt. Laurium. Following the death of Pericles in 429 BC, he became the principal rival of Cleon and the democrats in the struggle for the political leadership of the Athenian state. He was a moderate in his political views and opposed the aggressive imperialism of the democrats. His principal aim was to conclude a peace with Sparta as soon as it could be obtained on terms favourable to Athens.

The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between the Athenian empire on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat of the Athenian forces.

The History of the Peloponnesian War is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War, which was fought between the Peloponnesian League and the Delian League. It was written by Thucydides, an Athenian historian who also happened to serve as an Athenian general during the war. His account of the conflict is widely considered to be a classic and regarded as one of the earliest scholarly works of history. The History is divided into eight books.
Eurymedon was one of the Athenian generals (strategoi) during the Peloponnesian War.
Hagnon, son of Nikias was an Athenian general and statesman. In 437/6 BC, he led the settlers who founded the city of Amphipolis in Thrace; in the Peloponnesian War, he served as an Athenian general on several occasions, and was one of the signers of the Peace of Nicias and the alliance between Athens and Sparta. In 411 BC, during the oligarchic coup, he supported the oligarchy and was one of the ten commissioners (probouloi) appointed to draw up a new constitution.

The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between Ancient Carthage and the Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily, over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580–265 BC.
The Mytilenean revolt was an incident in the Peloponnesian War in which the city of Mytilene attempted to unify the island of Lesbos under its control and revolt from the Athenian Empire. In 428 BC, the Mytilenean government planned a rebellion in concert with Sparta, Boeotia, and certain other cities on the island, and began preparing to revolt by fortifying the city and laying in supplies for a prolonged war. These preparations were interrupted by the Athenian fleet, which had been notified of the plot, and the Mytileneans sent representatives to Athens to discuss a settlement, but simultaneously dispatched a secret embassy to Sparta to request support.
The Aetolian campaign, often referred to as "Demosthenes' Aetolian campaign", was a failed Athenian offensive in northwestern Greece during the Archidamian War. In 426 BCE, Demosthenes was dispatched from Athens to the Corinthian Gulf in command of a fleet of 30 ships. Arriving in the northwest, he quickly assembled a coalition force from Athens' allies in the region and besieging the city of Leucas. Before that siege reached a conclusion, however, he was persuaded to abandon it in favor of an attack on the tribal region of Aetolia. Leaving Leucas, he set out towards Aetolia, losing along the way several major contingents from his army, whose leaders were apparently unhappy with his change in strategy.
Athenagoras of Syracuse an elusive character who is only commented on in Thucydides (6.36–40). The context of his speech in Thucydides is 415 BC, during the Peloponnesian War, when Athens was about to invade Sicily. He denies the invasion, rudely retorting to Hermocrates' speech that no invasion was imminent. The basic outline of his speech is as follows:
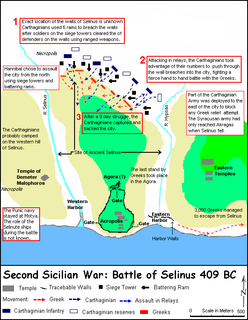
The Battle of Selinus, which took place early in 409 BC, is the opening battle of the so-called Second Sicilian War. The ten-day-long siege and battle was fought in Sicily between the Carthaginian forces under Hannibal Mago and the Dorian Greeks of Selinus. The city of Selinus had defeated the Elymian city of Segesta in 415, an event that led to the Athenian invasion of Sicily in 415 and ended in the defeat of Athenian forces in 413. When Selinus again worsted Segesta in 411, Carthage, responding to the appeal of Segesta, had besieged and sacked Selinus after the Carthaginian offer of negotiations had been refused by the Greeks. This was the first step towards Hannibal's campaign to avenge the Carthaginian defeat at the first battle of Himera in 480. The city of Selinus was later rebuilt, but never regained her former status.
The Battle of Gela took place in the summer of 405 BC in Sicily. The Carthaginian army under Himilco, which had spent the winter and spring in the captured city of Akragas, marched to confront the Greeks at Gela. The Syracuse government had deposed Daphnaeus, the unsuccessful general of the Greek army at Akragas, with Dionysius, another officer who had been a follower of Hermocrates. Dionysius schemed and gained full dictatorial powers. When the Carthaginians advanced on Gela and put the town under siege, Dionysius marched from Syracuse to confront the threat. He planned to use a complex three-pronged attack plan against the Carthaginians, which failed due to lack of proper coordination. Dionysius chose to evacuate Gela, as the defeat caused discontent in Syracuse and he did not wish to lose his power. Himilco sacked the abandoned city after the Greeks had fled to Camarina.
The Battle of Abacaenum took place between the Carthaginian forces under Mago and the Greek army under Dionysius in 393 BC near the Sicilian town on Abacaenum in north-eastern Sicily. Dionysius, tyrant of Syracuse, had been expanding his influence over Sicels' territories in Sicily. After Dionysius' unsuccessful siege in 394 BC of Tauromenium, a Carthaginian ally, Mago decided to attack Messana. However, the Carthaginian army was defeated by the Greeks near the town of Abacaenum and had to retire to the Carthaginian territories in Western Sicily. Dionysius did not attack the Carthaginians but continued to expand his influence in eastern Sicily.
The Siege of Segesta took place either in the summer of 398 BC or the spring of 397 BC. Dionysius the Elder, tyrant of Syracuse, after securing peace with Carthage in 405 BC, had steadily increased his military power and tightened his grip on Syracuse. He had fortified Syracuse against sieges and had created a large army of mercenaries and a large fleet, in addition to employing catapults and quinqueremes for the first time in history. In 398 BC he attacked and sacked the Phoenician city of Motya despite a Carthaginian relief effort led by Himilco II of Carthage. While Motya was under siege, Dionysius besieged and assaulted Segesta unsuccessfully. Following the sack of Motya, Segesta again came under siege by Greek forces, but the Elymian forces based in Segesta managed to inflict damage on the Greek camp in a daring night assault. When Himilco of Carthage arrived in Sicily with the Carthaginian army in the spring of 397 BC, Dionysius withdrew to Syracuse. The failure of Dionysius to secure a base in western Sicily meant the main events of the Second Sicilian war would be acted out mostly in eastern Sicily, sparing the Elymian and Phoenician cities the ravages of war until 368 BC.
The Sack of Camarina took place in the spring of 405 BC in Sicily. Hermocrates had plundered Carthaginian possessions in Sicily from Selinus after 408 BC, and in response Carthage sent and army to Sicily under Hannibal Mago and Himilco II of the Magonid family which faced a coalition of Sicilian Greeks under the leadership of Syracuse. The Greeks were forced to abandon Akragas in the winter of 406 BC after an 8-month siege. Hannibal Mago had perished at Akragas from the plague during the siege, the Carthaginians sacked Akragas and wintered there, then attacked Gela in the spring of 405 BC. Dionysius I had become supreme commander of Syracuse by this time, but his army was defeated at Gela. Although Greek casualties were light, Dionysius evacuated the city, which the Carthaginians plundered the following day. The Greek army had fallen back to Camarina after a forced march along with Gelan refugees the day after the sack of Gela. Dionysius ordered the citizens of Camarina to leave their city instead of organizing a defence. While retreating to Syracuse, part of the Greek army rebelled and occupied Syracuse, which Dionysius later managed to recapture. The Carthaginians sacked Camarina and encamped before Syracuse during the summer, and after a while a peace treaty was signed which confirmed Carthaginian control over Selinus, Akragas, Gela and Camarina, Greeks were allowed to settle in these cities while Dionysius was confirmed as the ruler of Syracuse. Carthage had reached the apex of her control in Sicily which she would not again reach until the death of Agathocles in 289 BC.














