Related Research Articles

The Gold Coast was a British Crown Colony on the Gulf of Guinea in West Africa from 1821 to its independence as part of the nation of Ghana in 1957. The term Gold Coast is also often used to describe all of the four separate jurisdictions that were under the administration of the Governor of the Gold Coast. These were the Gold Coast itself, Ashanti, the Northern Territories Protectorate and the British Togoland trust territory.
The Fante Confederacy refers either to the alliance of the Fante states in existence at least since the sixteenth century, or it can also refer to the modern Confederation formed in 1868. The Confederation is seen as one of the first and most prominent self-rule movements in Ghana and the entirety of Africa. Its mission was to shake of Colonialism and establish a modern free democratic state.

Danish overseas colonies and Dano-Norwegian colonies are the colonies that Denmark–Norway possessed from 1536 until 1953. At its apex the colonies spanned four continents: Europe, North America, Africa and Asia.

Elmina Castle was erected by the Portuguese in 1482 as Castelo de São Jorge da Mina, also known as Castelo da Mina or simply Mina, in present-day Elmina, Ghana. It was the first trading post built on the Gulf of Guinea, and the oldest European building in existence south of the Sahara. First established as a trade settlement, the castle later became one of the most important stops on the route of the Atlantic slave trade. The Dutch seized the fort from the Portuguese in 1637, after an unsuccessful attempt to the same extent in 1596, and took over all of the Portuguese Gold Coast in 1642. The slave trade continued under the Dutch until 1814. In 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast, including the fort, became a possession of Great Britain.

Cape Coast Castle is one of about forty "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast of West Africa by European traders. It was originally a Portuguese "feitoria" or trading post, established in 1555, which they named Cabo Corso. However, in 1653 the Swedish Africa Company constructed a timber fort there. It originally was a centre for the trade in timber and gold. It was later used in the trans-Atlantic slave trade. Other Ghanaian slave castles include Elmina Castle and Fort Christiansborg. They were used to hold slaves before they were loaded onto ships and sold in the Americas, especially the Caribbean. This "gate of no return" was the last stop before crossing the Atlantic Ocean.

Sweden possessed overseas colonies from 1638 to 1663, in 1733 and from 1784 to 1878. Sweden possessed five colonies, four of which were short lived. The colonies spanned three continents: Africa, Asia and North America.

The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. The Dutch began trading in the area around 1598, joining the Portuguese which had a trading post there since the late 1400s. Eventually, the Dutch Gold Coast became the most important Dutch colony in West Africa after Fort Elmina was captured from the Portuguese in 1637, but fell into disarray after the abolition of the slave trade in the early 19th century. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–71, ceded to the United Kingdom.

The Danish Gold Coast comprised the colonies that Denmark–Norway controlled in Africa as a part of the Gold Coast, which is on the Gulf of Guinea. It was colonized by the Dano-Norwegian fleet, first under indirect rule by the Danish West India Company, later as a crown colony of the kingdom of Denmark-Norway.

The Swedish Gold Coast was a Swedish colony founded in 1650 by Hendrik Carloff on the Gulf of Guinea in present-day Ghana in Africa. It lasted until April 1663 when the whole Swedish Gold Coast was seized by Denmark, and integrated in the Danish Gold Coast.

Fort Prinzenstein is a fort located at Keta, Ghana which was used in the slave trade. Many such forts were built in Africa, but Prinzenstein is one of the few that lie east of the Volta River. Keta served as an open port until the Tema Harbour commenced its operation to the west in 1962. The fort has been designated a World Heritage property.
Osu Castle, also known as Fort Christiansborg or simply the Castle, is a castle located in Osu, Accra, Ghana on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean's Gulf of Guinea. The first substantial fort was built by Denmark-Norway in the 1660s, though the castle has changed hands between Denmark-Norway, Portugal, the Akwamu, Britain, and finally post-Independence Ghana, and was rebuilt numerous times. For most of the castle's history, it has been the seat of government in Ghana with some interruptions, the latest when the John Kufuor administration moved the seat of government to Golden Jubilee House after 6 January 2009, which was quickly reversed by the incoming John Atta Mills administration. It also serves as the place where the late president of Ghana John Atta Mills is buried; in a bird sanctuary, overlooking the Atlantic Ocean.

The Treaty of Butre between the Netherlands and Ahanta was signed at Butre, Dutch Gold Coast on 27 August 1656. The treaty regulated the jurisdiction of the Netherlands and the Dutch West India Company over the town of Butre and the surrounding country of Upper Ahanta, creating a Dutch protectorate over the area. The treaty lasted until the Dutch departure from the Gold Coast in April 1872.

The Treaty of Axim was concluded between the Netherlands and the chiefs of Axim in the western region of the Gold Coast and signed at Fort St. Anthony near Axim on 17 February 1642. The treaty regulated the jurisdiction of the Netherlands and the Dutch West India Company in the town and polity of Axim after the Dutch West India Company had successfully attacked the Portuguese who were the occupants of Fort St. Anthony in the town. Over time, the agreement was in part superseded and replaced by new contracts and agreements. The treaty did remain the basis for Dutch jurisdiction and political relations between Axim and the Dutch until the latter left the Gold Coast in 1872.
Christian Tychsen was the first head of the Danish Gold Coast to be given the title of Governor on a regular basis. Prior to his governorship, only Bartholomaus von Gronstein, Conrad Crull, and Magnus Prang had served as governors. He served as governor from 20 October 1766 until his death in 1768, governing from the capital of the colony, Fort Christiansborg.
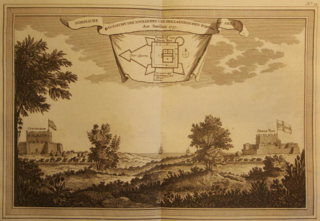
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is a day's march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the region during the middle of the 17th century. Fort Crèvecœur was part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty (1867), which defined areas of influence on the Gold Coast, transferred it to the British in 1868.

Hendrik Carloff was an adventurer active in the 17th century. Carloff began his career as a cabin boy, but rose to become the Commander and Director of the Dutch West India Company. He later joined the Swedish Africa Company and the Danish Africa Company on the Gold Coast, during which time he was involved in the slave trade. Between 1676 and 1677, he was the Governor of Tobago.

The Swedish Africa Company was a Swedish trading company, founded in 1649 on the initiative of the Walloon-Dutch merchant Louis De Geer and his son Laurens, for whom Sweden had become a second home. The primary interest of the company was the trade on the Swedish Gold Coast. The establishment of the pseudo Swedish Africa Company caused much astonishment in the Amsterdam city council.
Erik Tylleman was an Opperhoved of the Danish Gold Coast, a Danish Crown Colony. He governed from the colony's capital, Fort Christiansborg. Tylleman was the first Danish Governor who reigned in the United Gold Coast in 1698. The Danish Gold Coast was established on the eastern Gold Coast.

The Ebenezer Presbyterian Church, formerly known as the Basel Mission Church, Christiansborg, is a historic Protestant church located in the suburb of Osu in Accra, Ghana. The church was founded by the Basel Evangelical Missionary Society in 1847. Previously near the Christiansborg Castle at a hamlet called Osu Amanfong, where a commemorative monument now stands, the church relocated northwards to its present location near the Salem School when a new chapel was constructed and consecrated in 1902. The church is affiliated to the Presbyterian Church of Ghana. Liturgical services are conducted in English and the Ga language.
References
- ↑ Ole Jutesen, ed. Danish Sources for the History of Ghana, Vol.1 (1657-1753). Copenhagen: The Royal Danish Academy of Sciences and Letters, 2005. p. 48 ISBN 87-7304-312-5 ; also Liste der Gouverneure von Ghana (in German) and List of colonial heads of the Danish Gold Coast.
- ↑ which meant "Station Chief"; also Factor meant the same thing