Sociologists of religion have stated that religious behaviour may have a concrete impact on a person's life. These consequences of religiosity are thought to include emotional and physical health, spiritual well-being, personal, marital, and family happiness. [1] Although a simple correlation between religiosity and well-being is repeatedly reported in the research literature, recent multivariate research (which controls for other predictors of well-being) suggests religiosity's contribution to happiness is minuscule and sometimes negative. [2]
This term consequences as the result of one's religiosity first appeared in Charles Y. Glock's five-dimensional religiosity measure. In the 1960s, Glock attempted to categorize the components of religiosity. In his five-dimensional scheme "consequences" are listed as the final dimension of religiosity. Glock theorized that certain consequences in a person's life can be attributed to religious living. Consequences of religiosity may include emotional and physical health, spiritual well-being, personal, marital, and family happiness. This, however, does not preclude the possibility of these factors working in the reverse as health, happiness and the like may interact with and have an influence on one's level of religiosity. [3]
Glock's consequential dimension of religiosity was criticized by some sociologists as they saw Glock's final dimension as consequence of religiosity and not a dimension of it. [4]

Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of quantitative methods and of qualitative approaches.
The meaning of spirituality has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape of man", oriented at "the image of God" as exemplified by the founders and sacred texts of the religions of the world. The term was used within early Christianity to refer to a life oriented toward the Holy Spirit and broadened during the Late Middle Ages to include mental aspects of life.
Civil religion, also referred to as a civic religion, is the implicit religious values of a nation, as expressed through public rituals, symbols, and ceremonies on sacred days and at sacred places. It is distinct from churches, although church officials and ceremonies are sometimes incorporated into the practice of civil religion. Countries described as having a civil religion include France, South Korea, the former Soviet Union, and the United States. As a concept, it originated in French political thought and became a major topic for U.S. sociologists since its use by Robert Bellah in 1960.
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and antitheism. Social scientists tend to define irreligion as a purely naturalist worldview that excludes a belief in anything supernatural. The broadest and loosest definition, serving as an upper limit, is the lack of religious identification, though many non-identifiers express metaphysical and even religious beliefs. The narrowest and strictest is subscribing to positive atheism.
In sociology, secularization is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The secularization thesis expresses the idea that as societies progress, particularly through modernization, rationalization, and advances in science and technology, religious authority diminishes in all aspects of social life and governance. In recent years, the secularization thesis has been challenged due to some global studies indicating that the irreligious population of the world may be in decline as a percentage of the world population due to irreligious countries having subreplacement fertility rates and religious countries having higher birth rates in general. Christian sociologist Peter L. Berger coined the term desecularization to describe this phenomenon. In addition, secularization rates are stalling or reversing in some countries/regions such as the countries in the former Soviet Union or large cities in the Western world with significant amounts of religious immigrants.
In sociology, the concept of religiosity has proven difficult to define. The Oxford English Dictionary suggests: "Religiousness; religious feeling or belief. [...] Affected or excessive religiousness". Different scholars have seen this concept as broadly about religious orientations and degrees of involvement or commitment. Religiosity, measured at the levels of individuals or of groups, includes experiential, ritualistic, ideological, intellectual, consequential, creedal, communal, doctrinal, moral, and cultural dimensions. Sociologists of religion have observed that an individual's experience, beliefs, sense of belonging, and behavior often are not congruent with their actual religious behavior, since there is much diversity in how one can be religious or not. Multiple problems exist in measuring religiosity. For instance, measures of variables such as church attendance produce different results when different methods are used - such as traditional surveys vs time-use surveys.

Psychology of religion consists of the application of psychological methods and interpretive frameworks to the diverse contents of religious traditions as well as to both religious and irreligious individuals. The various methods and frameworks can be summarized regarding the classic distinction between the natural-scientific and human-scientific approaches. The first cluster amounts to objective, quantitative, and preferably experimental procedures for testing hypotheses for causal connections among the objects of one's study. In contrast, the human-scientific approach accesses the human world of experience using qualitative, phenomenological, and interpretive methods. The goal of this approach is to discern meaningful, rather than causal, connections among the phenomena one seeks to understand.
Robert John Wuthnow is an American sociologist who is widely known for his work in the sociology of religion. He is the Gerhard R. Andlinger Professor of Sociology at Princeton University, where he is also the former Chair of the Department of Sociology and Director of the Princeton University Center for the Study of Religion.
Religious disaffiliation is the act of leaving a faith, or a religious group or community. It is in many respects the reverse of religious conversion. Several other terms are used for this process, though each of these terms may have slightly different meanings and connotations.

Various sociological classifications of religious movements have been proposed by scholars. In the sociology of religion, the most widely used classification is the church-sect typology. The typology is differently construed by different sociologists, and various distinctive features have been proposed to characterise churches and sects. On most accounts, the following features are deemed relevant:

The sociology of emotion applies sociological theorems and techniques to the study of human emotions. As sociology emerged primarily as a reaction to the negative effects of modernity, many normative theories deal in some sense with emotion without forming a part of any specific subdiscipline: Karl Marx described capitalism as detrimental to personal 'species-being', Georg Simmel wrote of the deindividualizing tendencies of 'the metropolis', and Max Weber's work dealt with the rationalizing effect of modernity in general.
Secular morality is the aspect of philosophy that deals with morality outside of religious traditions. Modern examples include humanism, freethinking, and most versions of consequentialism. Additional philosophies with ancient roots include those such as skepticism and virtue ethics. Greg M. Epstein also states that, "much of ancient Far Eastern thought is deeply concerned with human goodness without placing much if any stock in the importance of gods or spirits." An example is the Kural text of Valluvar, an ancient Indian theistic poet-philosopher whose work remains secular and non-denominational. Other philosophers have proposed various ideas about how to determine right and wrong actions. An example is Immanuel Kant's categorical imperative.
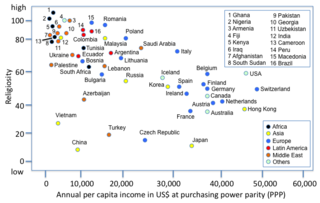
The correlation between wealth and religion has been subject to academic research. Wealth is the status of being the beneficiary or proprietor of a large accumulation of capital and economic power. Religion is a cultural system that often involves belief in supernatural forces and may intend to provide a moral system or a meaning of life. Jews typically rank as the highest income groups in the United States, with Hindus and Episcopalians behind them.
Doctrine is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief system. The etymological Greek analogue is "catechism".
The Society for the Scientific Study of Religion was formed to advance research in the social scientific perspective on religious institutions and experiences. The Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion is published by the society to provide a forum for empirical papers in the topic area.
Humanity is a virtue linked with basic ethics of altruism derived from the human condition. It also symbolises human love and compassion towards each other. Humanity differs from mere justice in that there is a level of altruism towards individuals included in humanity more so than the fairness found in justice. That is, humanity, and the acts of love, altruism, and social intelligence are typically individual strengths while fairness is generally expanded to all. Humanity can be classed as one of six virtues that are consistent across all cultures.
Scholarly studies have investigated the effects of religion on health. The World Health Organization (WHO) discerns four dimensions of health, namely physical, social, mental, and spiritual health. Having a religious belief may have both positive and negative impacts on health and morbidity.
Mervin Feldman Verbit is an American sociologist whose work focuses on sociology of religion, American Jews and the American Jewish community. He is currently the chair of the Sociology Department at Touro College.
Charles Young Glock was an American sociologist whose work focuses on sociology of religion and survey research.
Well-being is a topic studied in psychology, especially positive psychology. Related concepts are eudaimonia, happiness, flourishing, quality of life, contentment, and meaningful life.