
NEXRAD or Nexrad is a network of 160 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United States Department of Commerce, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) within the Department of Transportation, and the U.S. Air Force within the Department of Defense. Its technical name is WSR-88D.

A contour line of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function parallel to the -plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value.

Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type. Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the intensity of the precipitation. Both types of data can be analyzed to determine the structure of storms and their potential to cause severe weather.
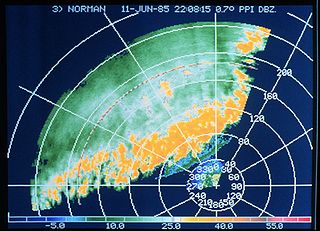
A plan position indicator (PPI) is a type of radar display that represents the radar antenna in the center of the display, with the distance from it and height above ground drawn as concentric circles. As the radar antenna rotates, a radial trace on the PPI sweeps in unison with it about the center point. It is the most common type of radar display.

3D radar provides for radar ranging and direction in three dimensions. In addition to range, the more common two-dimensional radar provides only azimuth for direction, whereas the 3D radar also provides elevation. Applications include weather monitoring, air defense, and surveillance.

Terrain-following radar (TFR) is a military aerospace technology that allows a very-low-flying aircraft to automatically maintain a relatively constant altitude above ground level and therefore make detection by enemy radar more difficult. It is sometimes referred to as ground hugging or terrain hugging flight. The term nap-of-the-earth flight may also apply but is more commonly used in relation to low-flying military helicopters, which typically do not use terrain-following radar.

A wind profiler is a type of weather observing equipment that uses radar or sound waves (SODAR) to detect the wind speed and direction at various elevations above the ground. Readings are made at each kilometer above sea level, up to the extent of the troposphere. Above this level there is inadequate water vapor present to produce a radar "bounce." The data synthesized from wind direction and speed is very useful to meteorological forecasting and timely reporting for flight planning. A twelve-hour history of data is available through NOAA websites.
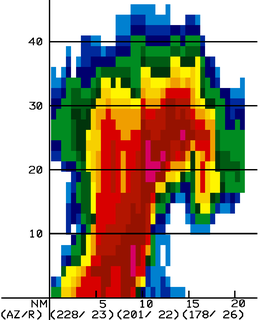
The bounded weak echo region, also known as a BWER or a vault, is a radar signature within a thunderstorm characterized by a local minimum in radar reflectivity at low levels which extends upward into, and is surrounded by, higher reflectivities aloft. This feature is associated with a strong updraft and is almost always found in the inflow region of a thunderstorm. It cannot be seen visually. The BWER has been noted on radar imagery of severe thunderstorms since 1973 and has a lightning detection system equivalent known as a lightning hole.

The cloud top is the highest altitude of the visible portion of the cloud. It is traditionally expressed either in metres above the Earth surface, or as the corresponding pressure level in hectopascal.
The J.S. Marshall Radar Observatory is a McGill University facility in Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue, Quebec, Canada housing several weather radars and other meteorological sensors, many of them running around the clock. It is one of the components of the McGill Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences department where students in remote sensing perform their research. Furthermore, the main radar is part of the Canadian weather radar network, was on a contract with the Meteorological Service of Canada, as well as a research device, up to October 3, 2018.

The Canadian weather radar network consists of 31 weather radars spanning Canada's most populated regions. Their primary purpose is the early detection of precipitation, its motion and the threat it poses to life and property.

A radar display is an electronic device to present radar data to the operator. The radar system transmits pulses or continuous waves of electromagnetic radiation, a small portion of which backscatter off targets and return to the radar system. The receiver converts all received electromagnetic radiation into a continuous electronic analog signal of varying voltage that can be converted then to a screen display.
Radar envelope is a critical Measure of Performance (MOP) identified in the Test and Evaluation Master Plan (TEMP). This is the volume of space where a radar system is required to reliably detect an object with a specific size and speed. This is one of the requirements that must be evaluated as part of the acceptance testing process.
Kosmos 156 was a Soviet weather satellite launched on 27 April 1967, one of eleven weather satellites launched by the Soviet Union between 1964 and 1969. It formed part of the experimental "Meteor" weather satellite system. In 1969, the Kosmos satellite series was scrapped for the more modern and updated Meteor satellite.

Multiple Elevation Scan Option for Supplemental Adaptive Intra-Volume Low-Level Scan, is a dynamic scanning option for the WSR-88D, controllable by the operator of the radar, when in VCP mode 12 and 212, and additionally 35 and 215 with the Build 18 update scheduled for October 2017. When active, anywhere from one to three supplemental low-level scans can be added to any volume, increasing overall low-level data availability and improves general severe weather detection, as needed. When active, per the National Weather Service, low-level updates will be available "every 75 to 90 seconds".

Multifunction Phased Array Radar (MPAR) was an experimental Doppler radar system that utilized phased array technology. MPAR could scan at angles as high as 60 degrees in elevation, and simultaneously track meteorological phenomena, biological flyers, non-cooperative aircraft, and air traffic. From 2003 through 2016, there was one operational MPAR within the mainland United States—a repurposed AN/SPY-1A radar set loaned to NOAA by the U.S. Navy. The MPAR was decommissioned and removed in 2016.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.

A cosecant squared antenna, sometimes known as a constant height pattern, is a modified form of parabolic reflector used in some radar systems. It is shaped to send more radio energy in certain directions in order to smooth out the reception pattern of objects as their range changes in relation to the radar. The name refers to the fact that the amount of energy returned from a target drops off with the square of the cosecant of the angle between the radar and the target.
John Stewart Marshall (1911-1992) was a Canadian physicist and meteorologist. Researcher for the Canadian government during the Second World war and then professor at McGill University from 1945 until his retirement in 1979, he was renowned for his research in cloud physics and precipitation, but especially for being a pioneer of weather radar.
The HF200 is a height finder radar designed and first built by Decca Radar in 1957, and continuing sales into the 1970s after the division was purchased by Plessey in 1965. It was one of the company's successful heavy radar projects, winning the contract for many of the ROTOR stations in the UK and additional sales around the world with a total production run of about 40 examples. These served into the 1980s, and in one case, 1993, before 3D radars removed the need for separate height-finders.
















