The International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) is one of the three Sectors (branches) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It is responsible for coordinating standards for telecommunications and Information Communication Technology, such as X.509 for cybersecurity, Y.3172 and Y.3173 for machine learning, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC for video compression, between its Member States, Private Sector Members, and Academia Members.

The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, significantly predating the UN and making it the oldest UN agency. Doreen Bogdan-Martin is the Secretary-General of ITU, the first woman to serve as its head.
International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be classified into two broad categories: declarations, adopted by bodies such as the United Nations General Assembly, which are by nature declaratory, so not legally-binding although they may be politically authoritative and very well-respected soft law;, and often express guiding principles; and conventions that are multi-party treaties that are designed to become legally binding, usually include prescriptive and very specific language, and usually are concluded by a long procedure that frequently requires ratification by each states' legislature. Lesser known are some "recommendations" which are similar to conventions in being multilaterally agreed, yet cannot be ratified, and serve to set common standards. There may also be administrative guidelines that are agreed multilaterally by states, as well as the statutes of tribunals or other institutions. A specific prescription or principle from any of these various international instruments can, over time, attain the status of customary international law whether it is specifically accepted by a state or not, just because it is well-recognized and followed over a sufficiently long time.

A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement concluded by sovereign states in international law. International organizations can also be party to an international treaty. A treaty is binding under international law.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

The International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) is a multilateral treaty that commits nations to respect the civil and political rights of individuals, including the right to life, freedom of religion, freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, electoral rights and rights to due process and a fair trial. It was adopted by United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2200A (XXI) on 16 December 1966 and entered into force on 23 March 1976 after its thirty-fifth ratification or accession. As of June 2024, the Covenant has 174 parties and six more signatories without ratification, most notably the People's Republic of China and Cuba; North Korea is the only state that has tried to withdraw.
The ITU Radio Regulations (RR) is a basic document of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that regulates on law of nations scale radiocommunication services and the utilisation of radio frequencies. It is the supplementation to the ITU Constitution and Convention and in line with the ITU International Telecommunication Regulations (ITR). The ITU RR comprise and regulate the part of the allocated electromagnetic spectrum from 9 kHz to 300 GHz.

The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European Union (EU). It would have replaced the existing European Union treaties with a single text, given legal force to the Charter of Fundamental Rights, and expanded qualified majority voting into policy areas which had previously been decided by unanimity among member states.

The American Convention on Human Rights (ACHR), also known as the Pact of San José or by its Spanish name used in most of the signatory nations, Convención Americana sobre Derechos Humanos, is an international human rights instrument. It was adopted by many countries in the Western Hemisphere in San José, Costa Rica, on 22 November 1969. It came into force after the eleventh instrument of ratification was deposited on 18 July 1978.
Ratification is a principal's legal confirmation of an act of its agent. In international law, ratification is the process by which a state declares its consent to be bound to a treaty. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usually accomplished by exchanging the requisite instruments, and in the case of multilateral treaties, the usual procedure is for the depositary to collect the ratifications of all states, keeping all parties informed of the situation.
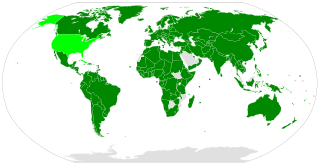
The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) is a multilateral treaty adopted by the United Nations General Assembly (GA) on 16 December 1966 through GA. Resolution 2200A (XXI), and came into force on 3 January 1976. It commits its parties to work toward the granting of economic, social, and cultural rights (ESCR) to all individuals including those living in Non-Self-Governing and Trust Territories. The rights include labour rights, the right to health, the right to education, and the right to an adequate standard of living. As of February 2024, the Covenant has 172 parties. A further four countries, including the United States, have signed but not ratified the Covenant.
Economic, social and cultural rights (ESCR) are socio-economic human rights, such as the right to education, right to housing, right to an adequate standard of living, right to health, victims' rights and the right to science and culture. Economic, social and cultural rights are recognised and protected in international and regional human rights instruments. Member states have a legal obligation to respect, protect and fulfil economic, social and cultural rights and are expected to take "progressive action" towards their fulfilment.

Spectrum management is the process of regulating the use of radio frequencies to promote efficient use and gain a net social benefit. The term radio spectrum typically refers to the full frequency range from 1 Hz to 3000 GHz that may be used for wireless communication. Increasing demand for services such as mobile telephones and many others has required changes in the philosophy of spectrum management. Demand for wireless broadband has soared due to technological innovation, such as 3G and 4G mobile services, and the rapid expansion of wireless internet services.

Human rights are largely respected in Switzerland, one of Europe's oldest democracies. Switzerland is often at or near the top in international rankings of civil liberties and political rights observance. Switzerland places human rights at the core of the nation's value system, as represented in its Federal Constitution. As described in its FDFA's Foreign Policy Strategy 2016-2019, the promotion of peace, mutual respect, equality and non-discrimination are central to the country's foreign relations.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by persons with disabilities and ensure that persons with disabilities enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention serves as a major catalyst in the global disability rights movement enabling a shift from viewing persons with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. The convention was the first U.N. human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.

An international organization, also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is an organization that is established by a treaty or other type of instrument governed by international law and possesses its own legal personality, such as the United Nations, the World Health Organization, International Union for Conservation of Nature, and BRICS. International organizations are composed of primarily member states, but may also include other entities, such as other international organizations, firms, and nongovernmental organizations. Additionally, entities may hold observer status.

The Asia Pacific Telecommunity (APT) was founded on the joint initiatives of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.
Armenian law, that being the modern Legal system of Armenia, is a system of law acted in Armenia.













