
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software—typically a suite of integrated applications—that an organization can use to collect, store, manage, and interpret data from many business activities. ERP Systems can be local based or Cloud-based. Cloud-based applications have grown in recent years due to information being readily available from any location with internet access.
Software engineering is the systematic application of engineering approaches to the development of software.
In telecommunication, provisioning involves the process of preparing and equipping a network to allow it to provide new services to its users. In National Security/Emergency Preparedness telecommunications services, "provisioning" equates to "initiation" and includes altering the state of an existing priority service or capability.
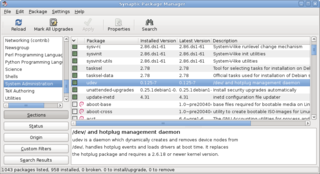
A package manager or package-management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer's operating system in a consistent manner.

A system administrator, or sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems; especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to ensure that the uptime, performance, resources, and security of the computers they manage meet the needs of the users, without exceeding a set budget when doing so.
Rational ClearCase is a family of computer software tools that supports software configuration management (SCM) of source code and other software development assets. It also supports design-data management of electronic design artifacts, thus enabling hardware and software co-development. ClearCase includes revision control and forms the basis for configuration management at large and medium-sized businesses, accommodating projects with hundreds or thousands of developers. It is developed by IBM.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure.
FCAPS is the ISO Telecommunications Management Network model and framework for network management. FCAPS is an acronym for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security, the management categories into which the ISO model defines network management tasks. In non-billing organizations accounting is sometimes replaced with administration.
Requirements engineering (RE) is the process of defining, documenting, and maintaining requirements in the engineering design process. It is a common role in systems engineering and software engineering.
Software deployment is all of the activities that make a software system available for use.
Commercial off-the-shelf or commercially available off-the-shelf (COTS) products are packaged or canned (ready-made) hardware or software, which are adapted aftermarket to the needs of the purchasing organization, rather than the commissioning of custom-made, or bespoke, solutions. A related term, Mil-COTS, refers to COTS products for use by the U.S. military.
A software factory is a structured collection of related software assets that aids in producing computer software applications or software components according to specific, externally defined end-user requirements through an assembly process. A software factory applies manufacturing techniques and principles to software development to mimic the benefits of traditional manufacturing. Software factories are generally involved with outsourced software creation.
Coding best practices are a set of informal rules that the software development community employs to help improve software quality.
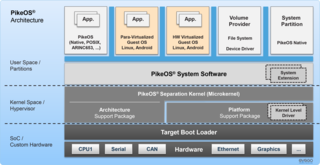
PikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple logical partition types for many other operating systems (OS), each called a GuestOS, and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of things (IoT) according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries.
Ian F. Sommerville, is a British academic. He is the author of a popular student textbook on software engineering, as well as a number of other books and papers. He worked as a professor of software engineering at the University of St Andrews in Scotland until 2014 and is a prominent researcher in the field of systems engineering, system dependability and social informatics, being an early advocate of an interdisciplinary approach to system dependability.
A software system is a system of intercommunicating components based on software forming part of a computer system. It "consists of a number of separate programs, configuration files, which are used to set up these programs, system documentation, which describes the structure of the system, and user documentation, which explains how to use the system".
In requirements engineering, requirements elicitation is the practice of researching and discovering the requirements of a system from users, customers, and other stakeholders. The practice is also sometimes referred to as "requirement gathering".

A Definitive Media Library is a secure Information Technology repository in which an organisation's definitive, authorised versions of software media are stored and protected. Before an organisation releases any new or changed application software into its operational environment, any such software should be fully tested and quality assured. The Definitive Media Library provides the storage area for software objects ready for deployment and should only contain master copies of controlled software media configuration items (CIs) that have passed appropriate quality assurance checks, typically including both procured and bespoke application and gold build source code and executables. In the context of the ITIL best practice framework, the term Definitive Media Library supersedes the term definitive software library referred to prior to version ITIL v3.
Knowledge-based configuration, or also referred to as product configuration or product customization, is an activity of customising a product to meet the needs of a particular customer. The product in question may consist of mechanical parts, services, and software. Knowledge-based configuration is a major application area for artificial intelligence (AI), and it is based on modelling of the configurations in a manner that allows the utilisation of AI techniques for searching for a valid configuration to meet the needs of a particular customer.
A DevOps toolchain is a set or combination of tools that aid in the delivery, development, and management of software applications throughout the systems development life cycle, as coordinated by an organisation that uses DevOps practices.




