A Consumer Price Index measures changes in the price level of market basket of consumer goods and services purchased by households.
In economics, the GDP deflator is a measure of the level of prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy in a year. GDP stands for gross domestic product, the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within the territory of a country over a particular period of time.
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is the price of a representative basket of wholesale goods. Some countries use WPI changes as a central measure of inflation. But now India has adopted new CPI to measure inflation. However, United States now report a producer price index instead.
A market basket or commodity bundle is a fixed list of items, in given proportions, used specifically to track the progress of inflation in an economy or specific market.
The personal consumption expenditure (PCE) measure is the component statistic for consumption in gross domestic product (GDP) collected by the United States Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). It consists of the actual and imputed expenditures of households and includes data pertaining to durable and non-durable goods and services. It is essentially a measure of goods and services targeted towards individuals and consumed by individuals.
The official measure of producer prices in the United States is called the Producer Price Index (PPI). It measures average changes in prices received by domestic producers for their output. The PPI was known as the Wholesale Price Index, or WPI, up to 1978. The PPI is one of the oldest continuous systems of statistical data published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, as well as one of the oldest economic time series compiled by the Federal Government. The origins of the index can be found in an 1891 U.S. Senate resolution authorizing the Senate Committee on Finance to investigate the effects of the tariff laws “upon the imports and exports, the growth, development, production, and prices of agricultural and manufactured articles at home and abroad.”
Substitution bias describes a possible bias in economic index numbers if they do not incorporate data on consumer expenditures switching from relatively more expensive products to cheaper ones as prices changed.
In the United Kingdom, the retail prices index or retail price index (RPI) is a measure of inflation published monthly by the Office for National Statistics. It measures the change in the cost of a representative sample of retail goods and services.
The Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP) is an indicator of inflation and price stability for the European Central Bank (ECB). It is a consumer price index which is compiled according to a methodology that has been harmonised across EU countries. The euro area HICP is a weighted average of price indices of member states who have adopted the euro. The primary goal of the ECB is to maintain price stability, defined as keeping the year on year increase HICP below but close to 2% for the medium term. In order to do that, the ECB can control the short-term interest rate through Eonia, the European overnight index average, which affects market expectations. The HICP is also used to assess the convergence criteria on inflation which countries must fulfill in order to adopt the euro. In the United Kingdom, the HICP is called the CPI and is used to set the inflation target of the Bank of England.
Core inflation represents the long run trend in the price level. In measuring long run inflation, transitory price changes should be excluded. One way of accomplishing this is by excluding items frequently subject to volatile prices, like food and energy.

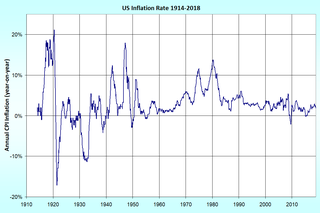
The United States Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a set of consumer price indices calculated by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). To be precise, the BLS routinely computes many different CPIs that are used for different purposes. Each is a time series measure of the price of consumer goods and services. The BLS publishes the CPI monthly.
RPIX is a measure of inflation in the United Kingdom, equivalent to the all items Retail Price Index (RPI) excluding mortgage interest payments.

The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the official measure of inflation of consumer prices of the United Kingdom. It is also called the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP).
The Higher Education Price Index (HEPI) is a measure of the inflation rate applicable to United States higher education. HEPI measures the average relative level in the prices of a fixed market basket of goods and services typically purchased by colleges and universities through current-fund educational and general expenditures, excluding expenditures for research. Educational and general expenditures include the functions of instruction and departmental research, extension and public services, educational programs such as workshops and instructional institutes supported by sponsors outside the institution, student services, general administration and expenses, staff benefits, libraries, and operation and maintenance of the physical plant. Sponsored research, sales and services of education departments, and auxiliary enterprises are not priced by HEPI. The index is calculated on a fiscal year basis ending each June 30, by the Commonfund Institute, a branch of Commonfund, a non-profit organization devoted to the management of college and university endowments.

The Christmas Price Index is a tongue-in-cheek economic indicator, maintained by the U.S. bank PNC Wealth Management, which tracks the cost of the items in the carol "The Twelve Days of Christmas".
This page lists details of the consumer price index by country
Inflation rate in India was 3.78% as of August 2015, as per the Indian Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. This represents a modest reduction from the previous annual figure of 9.6% for June 2011. Inflation rates in India are usually quoted as changes in the Wholesale Price Index (WPI), for all commodities
The National Consumer Price Index measures the price inflation of key consumer goods for Swiss private households. The average of the population is used as a reference to obtain a "truthful" value. The CPI measures the price trend based on a basket of commodities containing about 1050 goods and services. These are weighted according to their share of the household budget.
The United States Chained Consumer Price Index (C-CPI-U), also known as chain-weighted CPI or chain-linked CPI is a time series measure of price levels of consumer goods and services created by the Bureau of Labor Statistics as an alternative to the US Consumer Price Index. It is based on the idea that in an inflationary environment, consumers will choose less-expensive substitutes. This reduces the rate of cost of living increases through the reduction of the quality of consumed goods. The "fixed weight" CPI also takes such substitutions into account, but does so through a periodic adjustment of the "basket of goods" that it represents, rather than through a continuous estimation of the declining quality of goods consumed. Application of the chained CPI to federal benefits has been controversially proposed to reduce the federal deficit.