
A rangefinder camera is a camera fitted with a rangefinder, typically a split-image rangefinder: a range-finding focusing mechanism allowing the photographer to measure the subject distance and take photographs that are in sharp focus. Most varieties of rangefinder show two images of the same subject, one of which moves when a calibrated wheel is turned; when the two images coincide and fuse into one, the distance can be read off the wheel. Older, non-coupled rangefinder cameras display the focusing distance and require the photographer to transfer the value to the lens focus ring; cameras without built-in rangefinders could have an external rangefinder fitted into the accessory shoe. Earlier cameras of this type had separate viewfinder and rangefinder windows; later the rangefinder was incorporated into the viewfinder. More modern designs have rangefinders coupled to the focusing mechanism so that the lens is focused correctly when the rangefinder images fuse; compare with the focusing screen in non-autofocus SLRs.

135 film, more popularly referred to as 35 mm film or 35 mm, is a format of photographic film with a film gauge of 35 mm (1.4 in) loaded into a standardized type of magazine for use in 135 film cameras.

Leica Camera AG is a German company that manufactures cameras, optical lenses, photographic lenses, binoculars, and rifle scopes. The company was founded by Ernst Leitz in 1869, in Wetzlar, Germany. The name Leica is derived from the first three letters of the founder's surname (Leitz) and the first two of the word camera: lei-ca.

Carl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multinational company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.

Zorki is the name of a series of 35mm rangefinder cameras manufactured in the Soviet Union between 1948 and 1978.

Cosina Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer of high-end optical glass, optical precision equipment, cameras, video and electronic related equipment, based in Nakano, Nagano Prefecture, Japan.
Kiev is a Soviet and Ukrainian brand of photographic equipment including cameras manufactured by the Arsenal Factory in Kyiv, Ukraine. The camera nameplates show the name "KIEV", with older cameras using "КИЕВ" or "КИЇВ" in Cyrillic.

Contax began as a German camera model in the Zeiss Ikon line in 1932, and later became a brand name. The early cameras were among the finest in the world, typically featuring high quality Zeiss interchangeable lenses. The final products under the Contax name were a line of 35 mm, medium format, and digital cameras engineered and manufactured by Japanese multinational Kyocera, and featuring modern Zeiss optics. In 2005, Kyocera announced that it would no longer produce Contax cameras. The rights to the brand are currently part of Carl Zeiss AG, but no Contax cameras are currently in production, and the brand is considered dormant.

The Leica M3 is a 35 mm rangefinder camera by Ernst Leitz GmbH, introduced in 1954. It was a new starting point for Leitz, which until then had only produced screw-mount Leica cameras that were incremental improvements to its original Leica (Ur-Leica). The M3 introduced several features to the Leica, among them the combination of viewfinder and rangefinder in one bright window, like on the Contax II, a bayonet lens mount, and rapid film advance lever. It was the most successful model of the M series, with over 220,000 units sold by the time production of the M3 model ended in 1966.

Bronica also Zenza Bronica was a Japanese manufacturer of classic medium-format roll film cameras and photographic equipment based in Tokyo, Japan. Their single-lens reflex (SLR) system-cameras competed with Pentax, Hasselblad, Mamiya and others in the medium-format camera market.

The M39 lens mount is a screw thread mounting system for attaching lenses to 35 mm cameras, primarily rangefinder (RF) Leicas. It is also the most common mount for Photographic enlarger lenses.

Retina was the brand-name of a long-running series of German-built Kodak 35mm cameras, produced from 1934 until 1969. Kodak Retina cameras were manufactured in Stuttgart-Wangen by the Kodak AG Dr. Nagel Werk which Kodak had acquired in December 1931.

The Contax G camera line consists of two cameras, the G1 and G2, interchangeable-lens cameras sold by Kyocera under the Contax brand in competition with the Leica M7, Cosina Voigtländer Bessa-R, and Konica Hexar RF. The G1 was introduced in 1994 with the G2 joining it in 1996. In 2005, Kyocera retreated from the camera business and announced it would cease all activity related to the manufacture of Contax cameras at the end of the year, effectively spelling the end of the G system.

The Konica Hexar RF is a 35 mm rangefinder camera which was sold by Konica. It was introduced to the market on 13 October 1999. and subsequently discontinued some time before the end of 2003. The camera used the "Bayonet Konica KM-mount", a copy of the Leica M-mount, thus sharing interchangeable lenses with those designed for Leica cameras and others compatible with them. The Hexar RF has a combined rangefinder/viewfinder modeled on that of Leica cameras, a similar body shape and size - and so is similar to Leica M-mount cameras in many aspects of operation.

The Bessa family of cameras was manufactured in Japan by Cosina as a revival of the Voigtländer brand name between 1999 and 2015.

The Contax I, or Original Contax, is a 35 mm rangefinder camera made between 1932 and 1936 by Zeiss Ikon. The Contax I had six identifiable variants, but fundamentally identical; every aspect was designed to outperform the Leica. For instance, the removable back was for faster loading and reloading, the bayonet lens mount was designed for rapid lens interchangeability, the long-base rangefinder allowed more accurate focusing, and the vertical metal shutter not only gave a faster maximum speed but also banished the problem of shutter blinds burning.
The Jupiter series of lenses are Russian camera lenses made by various manufacturers in the former Soviet Union. They were made to fit many camera types of the time, from pre-WWII rangefinders to almost modern SLRs. They are copied from Zeiss pre-WWII designs with incremental improvements, such as coatings, introduced during production. The majority of them are based on Zeiss Sonnar optical scheme, but that's not a rule.

The Leica copies originate from the Leica camera that was launched by Ernst Leitz, Wetzlar in 1925, using the Leica 39mm screw mount of 26 threads per inch, and the standard 35mm film. The design was carried out by Oskar Barnack, beginning in 1913 by building a camera for 24×36 mm negatives that by now is called the Ur-Leica, or Barnack Leica; but Ernst Leitz did not decide to manufacture it until 1924. Once started, the Leica production volume doubled each year; in 1929, some 16.000 cameras were produced. In 1930, an improved model with interchangeable lens was introduced, followed a year later by the fully developed Leica II with standardized film to lens flange distance, and in 1932 the basic Leica Standard; the Leica concept was established. This camera's features are the basis for defining a Leica copy.
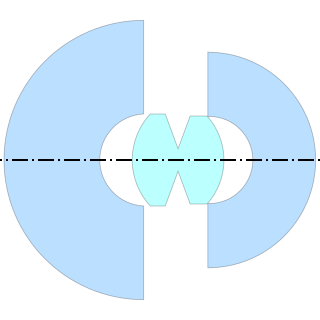
The Zeiss Hologon is an ultra wide-angle f=15mm f/8 triplet lens, providing a 110° angle of view for 35mm format cameras. The Hologon was originally fitted to a dedicated camera, the Zeiss Ikon Contarex Hologon in the late 1960s; as sales of that camera were poor and the Zeiss Ikon company itself was going bankrupt, an additional 225 lenses were made in Leica M mount and released for sale in 1972 as the only Zeiss-branded lenses for Leica rangefinders until the ZM line was released in 2005. The Hologon name was revived in 1994 for a recomputed f=16mm f/8 lens fitted to the Contax G series of rangefinder cameras.
The Contax T camera line consists of a number of compact cameras sold by Kyocera under the Contax brand. They were introduced between 1984 and 2002. The T, T2, and T3 use 35mm film and have a fixed 35 mm wide-angle lens. The T-VS, T-VS II, and T-VS III also use 35 mm film but have a 28–56 mm lens. The Tix uses APS film and has a fixed 28 mm wide-angle lens. The TVS Digital is a 5 MP digital camera with a 35–105 mm (equivalent) lens.

















