
The contraction of cardiac muscle in all animals is initiated by electrical impulses known as action potentials. The rate at which these impulses fire, controls the rate of cardiac contraction, that is, the heart rate. The cells that create these rhythmic impulses, setting the pace for blood pumping, are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate. They make up the cardiac pacemaker, that is, the natural pacemaker of the heart. In most humans, the concentration of pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial (SA) node is the natural pacemaker, and the resultant rhythm is a sinus rhythm.

Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two subgroups; the single-unit (unitary) and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit cells, the whole bundle or sheet contracts as a syncytium.

In cell biology, the cleavage furrow is the indentation of the cell's surface that begins the progression of cleavage, by which animal and some algal cells undergo cytokinesis, the final splitting of the membrane, in the process of cell division. The same proteins responsible for muscle contraction, actin and myosin, begin the process of forming the cleavage furrow, creating an actomyosin ring. Other cytoskeletal proteins and actin binding proteins are involved in the procedure.

A sarcomere is the complicated unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells which are formed in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma.
Weakness is a symptom of a number of different conditions. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis.
A uterine contraction is a muscle contraction of the uterine smooth muscle.

The endocardium is the innermost layer of tissue that lines the chambers of the heart. Its cells are embryologically and biologically similar to the endothelial cells that line blood vessels. The endocardium also provides protection to the valves and heart chambers.
An inotrope is an agent that alters the force or energy of muscular contractions. Negatively inotropic agents weaken the force of muscular contractions. Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular contraction.
Muscle fatigue is the decline in ability of a muscle to generate force. It can be a result of vigorous exercise but abnormal fatigue may be caused by barriers to or interference with the different stages of muscle contraction. There are two main causes of muscle fatigue: the limitations of a nerve’s ability to generate a sustained signal ; and the reduced ability of the muscle fiber to contract.

Sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm of a myocyte. It is comparable to the cytoplasm of other cells, but it contains unusually large amounts of glycosomes and significant amounts of myoglobin, an oxygen-binding protein. The calcium ion concentration in sarcoplasma is also a special element of the muscle fiber; it is the means by which muscle contractions take place and are regulated.

Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle fibers. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding a heavy book or a dumbbell at the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state.

The myometrium is the middle layer of the uterine wall, consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells but also of supporting stromal and vascular tissue. Its main function is to induce uterine contractions.
Myocardial contractility represents the innate ability of the heart muscle (cardiac muscle or myocardium) to contract. The ability to produce changes in force during contraction result from incremental degrees of binding between different types of tissue, that is, between filaments of myosin (thick) and actin (thin) tissue. The degree of binding depends upon the concentration of calcium ions in the cell. Within an in vivo intact heart, the action/response of the sympathetic nervous system is driven by precisely timed releases of a catecholamine, which is a process that determines the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol of cardiac muscle cells. The factors causing an increase in contractility work by causing an increase in intracellular calcium ions (Ca++) during contraction.
Muscle weakness is a lack of muscle strength. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have either true or perceived muscle weakness. True muscle weakness is a primary symptom of a variety of skeletal muscle diseases, including muscular dystrophy and inflammatory myopathy. It occurs in neuromuscular junction disorders, such as myasthenia gravis. Muscle weakness can also be caused by low levels of potassium and other electrolytes within muscle cells. It can be temporary or long-lasting. The term myasthenia is from my- from Greek μυο meaning "muscle" + -asthenia ἀσθένεια meaning "weakness".

Myofilaments are the filaments of myofibrils, constructed from proteins, principally myosin or actin. Types of muscle are striated muscle, obliquely striated muscle, and smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered. Smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments.
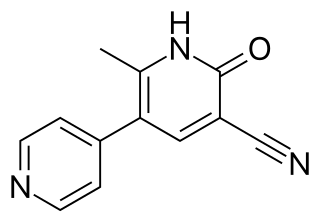
Milrinone, commonly known and marketed under the brand name Primacor, is a medication used in patients who have heart failure. It is a phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor that works to increase the heart's contractility and decrease pulmonary vascular resistance. Milrinone also works to vasodilate which helps alleviate increased pressures (afterload) on the heart, thus improving its pumping action. While it has been used in people with heart failure for many years, studies suggest that milrinone may exhibit some negative side effects that have caused some debate about its use clinically.

Intraglomerular mesangial cells are located among the glomerular capillaries within a renal corpuscle of a kidney.

Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. This is opposed to other components or tissues in muscle such as tendons or perimysium. It is formed during embryonic development through a process known as myogenesis. Muscle tissue consists of elongated cells also called as muscle fibres. This tissue is responsible for movements in our body. Muscles contain special proteins called contractile protein which contract and relax to cause movement.

Contraction band necrosis is a type of uncontrolled cell death (necrosis) unique to cardiac myocytes and thought to arise in reperfusion from hypercontraction, which results in sarcolemmal rupture.
Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.












