The General Conference on Weights and Measures is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established in 1875 under the terms of the Metre Convention through which member states act together on matters related to measurement science and measurement standards. The CGPM is made up of delegates of the governments of the member states and observers from the Associates of the CGPM. It elects the International Committee for Weights and Measures as the supervisory board of the BIPM to direct and supervise it.
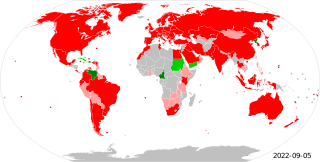
The Metre Convention, also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations: Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazil, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Peru, Portugal, Russia, Spain, Sweden and Norway, Switzerland, Ottoman Empire, United States of America, and Venezuela.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.

A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition, is a large global exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specific site for a period of time, typically between three and six months.

The Convention for the Unification of certain rules relating to international carriage by air, commonly known as the Warsaw Convention, is an international convention which regulates liability for international carriage of persons, luggage, or goods performed by aircraft for reward.

Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960.

The Bureau International des Expositions is an intergovernmental organization created to supervise international exhibitions falling under the jurisdiction of the Convention Relating to International Exhibitions.

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, Sudan, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.

The Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH) is an intergovernmental organisation in the area of private international law, that administers several international conventions, protocols and soft law instruments.

The Brussels Regime is a set of rules regulating which courts have jurisdiction in legal disputes of a civil or commercial nature between individuals resident in different member states of the European Union (EU) and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). It has detailed rules assigning jurisdiction for the dispute to be heard and governs the recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments.

A garden festival is a festival and exposition held to celebrate the arts of gardening, garden design, landscaping and landscape architecture. There are local garden festivals, regional garden festivals, national garden festivals and international garden festivals. The idea probably originated with Germany's Bundesgartenschau. The UK held five garden festivals in the period 1984–1992.

The Brussels International Exposition of 1935 was a world's fair held between 27 April and 6 November 1935 on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Belgium.

Expo '90 or The International Garden and Greenery Exposition, organized as a part of the International Expositions Convention, was the first large-scale international gardening exposition in Asia and focused on the theme of the "Harmonious Coexistence of Nature and Mankind." The exposition was held in Tsurumi Ryokuchi, Osaka for 183 days, from Sunday, April 1 to Sunday, September 30, 1990. The convention included participation from 83 countries and 55 international organizations and attracted over 23,126,934 visitors.
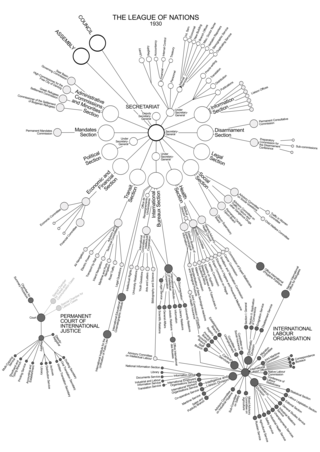
The League of Nations was established with three main constitutional organs: the Assembly; the Council; the Permanent Secretariat. The two essential wings of the League were the Permanent Court of International Justice and the International Labour Organization.
The Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes, also known as the Water Convention, is an international environmental agreement and one of five UNECE's negotiated environmental treaties. The purpose of this convention is to improve national attempts and measures for protection and management of transboundary surface waters and groundwaters. On the international level, Parties are obliged to cooperate and create joint bodies. The Convention includes provisions on: monitoring, research, development, consultations, warning and alarm systems, mutual assistance and access as well as exchange of information.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.
Expo 1985 Plovdiv was an international exposition that took place from November 4–30, 1985 in Plovdiv, Bulgaria. The exhibition had the theme "The Achievements of Young Inventors". The specialized exhibition was the 24th held by the Bureau International des Expositions and the second held in Plovdiv. Another specialized exposition, Expo '85 in Tsukuba, Japan occurred the same year.
The International Exhibition on Urbanism and Housing was a specialized exhibition recognised by the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), which held in Paris, France, from 10 July to 15 August 1947. It focused on housing estate projects in the context of post-war reconstruction and attracted 14 participating countries including Mexico, Poland and South Africa.

2023 International Horticultural Exposition or Expo 2023 is an International Horticultural Expo hosted by Doha, Qatar. The Horticultural Expo 2023 Doha is being held from October 2, 2023 until March 28, 2024. Spanning 1.7 million square meters, the event takes place in Al Bidda Park, one of the biggest parks in Doha which overlooks the Persian Gulf. Originally scheduled to be held from 14 October 2021 to 17 March 2022, but it was rescheduled to 2023 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Bureau International des Expositions (BIE) general assembly in Paris formally recognised it on 22 November 2018 as an International Horticultural Exhibition. The Expo was organized under the theme "Green Desert, Better Environment". An 80-hectare (200-acre) site has been identified.














