
Asteraceae or Compositae is a very large and widespread family of flowering plants (Angiospermae).

In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Vernation is the formation of new leaves or fronds. In plant anatomy, it is the arrangement of leaves in a bud.

Cupressaceae is a conifer family, the cypress family, with worldwide distribution. The family includes 27–30 genera, which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130–140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or (rarely) dioecious trees and shrubs up to 116 m (381 ft) tall. The bark of mature trees is commonly orange- to red- brown and of stringy texture, often flaking or peeling in vertical strips, but smooth, scaly or hard and square-cracked in some species.

A blunt is a cigar which is wider than a cigarillo and not quite as wide as a Corona, generally equivalent to a petit corona while short panatellas are sometimes classified as mini-blunts. These cigars typically consist of two main parts; the inner leaf, which is similar to a cigarette rolling paper, except it is made of tobacco, and a thicker outer leaf which is rolled around the inner leaf in a spiral. In most commercially available blunts, the "leaves" are not actual tobacco leaves but rather paper made from tobacco pulp.

In botany, phyllotaxis or phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves on a plant stem. Phyllotactic spirals form a distinctive class of patterns in nature.

Cathaya is a genus in the pine family, Pinaceae, with one known living species, Cathaya argyrophylla. Cathaya is a member of the subfamily Laricoideae, most closely related to Pseudotsuga and Larix. A second species, C. nanchuanensis, is now treated as a synonym, as it does not differ from C. argyrophylla in any characters.

Afrocarpus is a genus of conifers belonging to the family Podocarpaceae. Two to six species are recognized. They are evergreen trees native to Africa. Afrocarpus was designated a genus in 1989, when several species formerly classified in Podocarpus and Nageia were reclassified.

Cunninghamia is a genus of one or two living species of evergreen coniferous trees in the cypress family Cupressaceae. They are native to China, northern Vietnam and Laos, and perhaps also Cambodia. They may reach 50 m (160 ft) in height. In vernacular use, it is most often known as Cunninghamia, but is also sometimes called "China-fir". The genus name Cunninghamia honours Dr. James Cunningham, a British doctor who introduced this species into cultivation in 1702 and botanist Allan Cunningham.
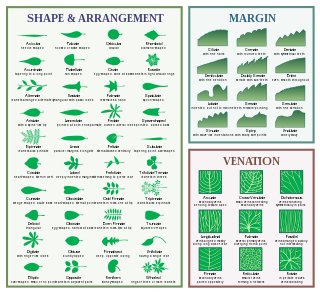
The following is a defined list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple or compound. The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.

Commelinaceae is a family of flowering plants. In less formal contexts, the group is referred to as the dayflower family or spiderwort family. It is one of five families in the order Commelinales and by far the largest of these with about 731 known species in 41 genera. Well known genera include Commelina (dayflowers) and Tradescantia (spiderworts). The family is diverse in both the Old World tropics and the New World tropics, with some genera present in both. The variation in morphology, especially that of the flower and inflorescence, is considered to be exceptionally high amongst the angiosperms.

The operculum, meaning little lid, is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor which exists in many groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails; the structure is found in some marine and freshwater gastropods, and in a minority of terrestrial gastropods, including the families Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc.
The following is a glossary of figure skating terms, sorted alphabetically.
Sideroxylon salicifolium, commonly called white bully or willow bustic, is a species of flowering plant native to Florida, the West Indies and Central America. It has also been considered a member of the genus Dipholis, with the binomial Dipholis salicifolia. Its specific epithet is derived from the Latin salix 'willow' and folia 'leaf'.
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of terms relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the related Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. See also List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. You can help by adding illustrations that assist an understanding of the terms.

Persoonia cornifolia is a plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a shrub with elliptic to egg-shaped leaves and hairy yellow flowers, and grows in northern New South Wales and south-eastern Queensland.

In botany, a whorl or verticil is an arrangement of sepals, petals, leaves, stipules or branches that radiate from a single point and surround or wrap around the stem. A whorl consists of at least three elements; a pair of opposite leaves is not called a whorl.

Pterostylis hamata, commonly known as the southern hooked rustyhood, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It has a rosette of leaves and between two and twelve transparent flowers with green and brown markings, a thick, brown, insect-like labellum and dished lateral sepals.
Pterostylis ferruginea, commonly known as the Bangham rustyhood, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to the border area between South Australia and Victoria. It has a rosette of leaves and when flowering, up to ten upright, dark green and translucent white flowers which have an insect-like labellum.

Spiranthes australis, commonly known as austral ladies tresses, is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to about ten leaves at the base of a flowering stem with up to sixty small pink and white flowers spirally arranged around it.



















