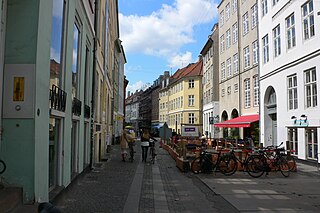The Copenhagen Fire of 1728 was the largest fire in the history of Copenhagen, Denmark. It began on the evening of 20 October 1728 and continued to burn until the morning of the 23rd of October 1728. It destroyed approximately 28% of the city and left 20% of the population homeless. The reconstruction lasted until 1737. No less than 47% of the section of the city, which dates back to the Middle Ages, was completely lost, and along with the Copenhagen Fire of 1795, it is the main reason that few traces of medieval Copenhagen can be found in the modern city.

The Copenhagen Fire of 1795 started on Friday, 5 June 1795, at or around 3 pm by the Navy's old base south east of Kongens Nytorv on Gammelholm, in the Navy's magazine for coal and timber, the so-called Dellehave. As the workers had already gone home, a considerable length of time passed before efforts to combat the fire started, and out of fear of theft, the fire hydrants had been removed. The people of Holmen also blocked the civilian fire brigade, possibly in the belief that since it was a military area, the military should take care of it.

Copenhagen City Hall is the headquarters of the Copenhagen City Council as well as the Lord mayor of the Copenhagen Municipality, Denmark. The building is situated on City Hall Square in central Copenhagen.

Gammeltorv is the oldest square in Copenhagen, Denmark. With adjoining Nytorv it forms a common space along the Strøget pedestrian zone. While the square dates back to the foundation of the city in the 12th century, most of its buildings were constructed after the Great Fire of 1795 in Neoclassical style. Another dominating feature is the Caritas Well, a Renaissance fountain erected by King Christian IV in 1610.

Nytorv is a public square in the centre of Copenhagen, Denmark. Together with the adjoining Gammeltorv it forms a common space, today part of the Strøget pedestrian zone. The square is dominated by the imposing Neoclassical façade of the Copenhagen Court House, which from 1815-1905 also served as the City Hall.

The Copenhagen Court House is a historic building located on Nytorv in Copenhagen, Denmark. Originally built as a combined city hall and courthouse, it now serves as the seat of the District Court of Copenhagen. Inaugurated in 1815, it was built to the design of Christian Frederik Hansen in Neoclassical style.

Amagertorv is a public square in the district of Indre By in central Copenhagen, Denmark. Today it forms part of the Strøget pedestrian zone, and is often described as the most central square in Copenhagen. Second only to Gammeltorv, it is also one of the oldest, taking its name from the Amager farmers who in the Middle Ages came into town to sell their produce at the site.

The Copenhagen University Library in Copenhagen, Denmark, is the main research library of the University of Copenhagen. Founded in 1482, it is the oldest library in Denmark.

Højbro Plads is a rectangular public square located between the adjoining Amagertorv and Slotsholmen Canal in the City Centre of Copenhagen, Denmark. It takes its name from the Højbro Bridge which connects it to the Slotsholmen island on the other side of the canal while Gammel Strand extends along the near side of the canal.

A new, third City Hall in Copenhagen, Denmark, was built at Gammeltorv in 1479. Rebuilt by King Christian IV into the Renaissance style in 1610, it was in use until 1728 when it was destroyed in the first Great Fire of Copenhagen. It was replaced by a new city hall which was built on its foundations the same year.

The Old City Hall at Gammeltorv Aalborg, Denmark, was built in 1762 and served as city hall until 1912. It is located at Gammeltorv and is now only used for ceremonial and representative purposes.

Store Kannikestræde is a street in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark, connecting Frue Plads to Købmagergade. Its history is closely associated with the University of Copenhagen and some of Copenhagen's oldest halls of residence are located in the street. It has been pedestrianized since 1973.
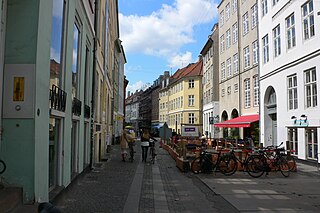
Strædet is the colloquial name of a popular shopping and café street in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark, linking Højbro Plads on Strøget at its eastern end with Regnbuepladsen next to City Hall to the west. The official street names are Læderstræde, Kompagnistræde and Farvergade. The shops along the street are generally smaller and more eclectic than the flagship stores on neighbouring Strøget. It is dominated by art galleries and antique shops. It is known for its rich gay culture with LGBT citizens, shops, bars, restaurants and coffeehouses.

Brolæggerstræde is a street in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark, linking Nytorv in the west with Badstuestræde in the east. Most of the buildings in the street date from the years after the Copenhagen Fire of 1795. The Carlsberg Foundation is headquartered at No. 5.

Åbenrå is a street in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark. It runs from Landemærket in the southeast to Rosenborggade in the northwest, linking Vognmagergade with Tornebuskgade. The last part of the street passes the rear side of the grounds of the Reformed Church in Gothersgade. The former rectory associated with the church is located at No. 32-36. It is now houses the Danish Association of Architects.

Admiralgade is a street in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark. It runs from Nikolaj Plads in the north to Holmens Kanal in the south.

Lavendelstræde is a street in the old town of Copenhagen, Denmark). It runs from Kattesundet-Hestemøllestræde in the northeast to Vester Voldgade in the west, linking Slutterigade and Nytorv and at Regnbuepladsen and Copenhagen City Hall in the southwest.

Valkendorfsgade 36, situated opposite the House of the Holy Ghost, off the shopping street Strøget is a Baroque style townhouse in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark. The building was listed on the Danish registry of protected buildings and places in 1918.

Brolæggerstræde 12 is a Neoclassical property situated in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark. It was like most of the other buildings in the street constructed as part of the rebuilding of the city following the Copenhagen Fire of 1795. It was listed on the Danish registry of protected buildings and places in 1950.

Brolæggerstræde 4 is a Neoclassical property situated in the Old Town of Copenhagen, Denmark. Like most of the other buildings in the area, it was constructed as part of the rebuilding of the city following the Copenhagen Fire of 1795. The three-winged complex was listed in the Danish registry of protected buildings and places in 1950.