
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives the creator of an original work, or another right holder, the exclusive and legally secured right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States.

Itar-Tass Russian News Agency v. Russian Kurier, Inc., 153 F.3d 82, was a copyright case about the Russian language weekly Russian Kurier in New York City that had copied and published various materials from Russian newspapers and news agency reports of Itar-TASS. The case was ultimately decided by the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit. The decision was widely commented upon and the case is considered a landmark case because the court defined rules applicable in the U.S. on the extent to which the copyright laws of the country of origin or those of the U.S. apply in international disputes over copyright. The court held that to determine whether a claimant actually held the copyright on a work, the laws of the country of origin usually applied, but that to decide whether a copyright infringement had occurred and for possible remedies, the laws of the country where the infringement was claimed applied.
The Public Domain Enhancement Act (PDEA) was a bill in the United States Congress, first introduced in the United States House of Representatives on June 25, 2003, which, if passed, would have added a tax for copyrighted works to retain their copyright status. The purpose of the bill was to make it easier to determine who holds a copyright, and to allow copyrighted works which have been abandoned by their owners, also known as orphan works, to pass into the public domain.

"All rights reserved" is a phrase that originated in copyright law as part of copyright notices. It indicates that the copyright holder reserves, or holds for their own use, all the rights provided by copyright law, such as distribution, performance, and creation of derivative works; that is, they have not waived any such right. Copyright law in most countries no longer requires such notices, but the phrase persists. The original understanding of the phrase as relating specifically to copyright may have been supplanted by common usage of the phrase to refer to any legal right, although it is probably understood to refer at least to copyright.
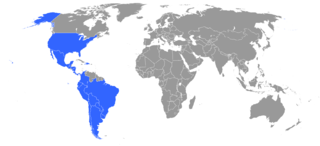
The Buenos Aires Convention is an international copyright treaty signed in Buenos Aires, Argentina, on 11 August 1910, providing mutual recognition of copyrights where the work carries a notice containing a statement of reservation of rights (Art. 3). This was commonly done with the phrase "All rights reserved" next to the copyright notice. This implementation varied as US law only required the author and year of publishing. Copyright protection under the convention is granted for the shorter of the terms of the protecting country and the source country of the work. The rather vague nature of the requirement for a statement of reservation led to the development of longer and more legalistic wordings, which have persisted despite the developments in international copyright law.
Copyright in the Netherlands is governed by the Dutch Copyright Law, copyright is the exclusive right of the author of a work of literature or artistic work to publish and copy such work.

The Uruguay Round Agreements Act is an Act of Congress in the United States that implemented in U.S. law the Marrakesh Agreement of 1994. The Marrakesh Agreement was part of the Uruguay Round of negotiations which transformed the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) into the World Trade Organization (WTO). One of its effects is to give United States copyright protection to foreign works that had previously been in the public domain in the United States.

The purpose of copyright registration is to place on record a verifiable account of the date and content of the work in question, so that in the event of a legal claim, or case of infringement or plagiarism, the copyright owner can produce a copy of the work from an official government source.
The copyright symbol, or copyright sign, ©, is the symbol used in copyright notices for works other than sound recordings. The use of the symbol is described by the Universal Copyright Convention. The symbol is widely recognized but, under the Berne Convention, is no longer required in most nations to assert a new copyright.

In United States copyright law, a copyright notice is a notice of statutorily prescribed form that informs users of the underlying claim to copyright ownership in a published work.

In copyright law, related rights are the rights of a creative work not connected with the work's actual author. It is used in opposition to the term "authors' rights". Neighbouring rights is a more literal translation of the original French droits voisins. Both authors' rights and related rights are copyrights in the sense of English or U.S. law.

Attribution, in copyright law, is acknowledgment as credit to the copyright holder or author of a work. If a work is under copyright, there is a long tradition of the author requiring attribution while directly quoting portions of work created by that author.
Copyright in Russia developed originally along the same lines as in Western European countries. A first copyright statute dated back to 1828, and in 1857, a general copyright term of fifty years was instituted. The copyright law of 1911 was inspired by Western laws of the continental European tradition. One noteworthy exception in Russian copyright law was the "freedom of translation"—any work could be freely translated into another language.
The rule of the shorter term, also called the comparison of terms, is a provision in international copyright treaties. The provision allows that signatory countries can limit the duration of copyright they grant to foreign works under national treatment to no more than the copyright term granted in the country of origin of the work.

While no creative work is automatically protected worldwide, there are international treaties which provide protection automatically for all creative works as soon as they are fixed in a medium.Two of the most important international copyright treaties include the Berne Convention and the Universal Copyright Convention (UCC).

The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, was an international assembly held in 1886 in the Swiss city of Bern by ten European countries with the goal of agreeing on a set of legal principles for the protection of original work. They drafted and adopted a multi-party contract containing agreements for a uniform, border-crossing system that became known under the same name. Its rules have been updated many times since then. The treaty provides authors, musicians, poets, painters, and other creators with the means to control how their works are used, by whom, and on what terms. In some jurisdictions these type of rights are referred to as copyright; on the European continent they are generally referred to as author' rights or makerright.

The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds the exclusive rights, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission.

Thorvald Solberg was the first Register of Copyrights (1897–1930) in the United States Copyright Office. He was a noted authority on copyright and played an instrumental role in shaping the Copyright Act of 1909.

Works are in the public domain if they are not covered by the intellectual property right known as copyright, or if the intellectual property rights to the works have expired. Works automatically enter the public domain when their copyright has expired. The United States Copyright Office is a federal agency tasked with maintaining copyright records.
The copyright law of the United States has a long and complicated history, dating back to colonial times. It was established as federal law with the Copyright Act of 1790. This act was updated many times, including a major revision in 1976.