Related Research Articles

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.

Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is effective for dracunculiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, and amebiasis. It is an option for a first episode of mild-to-moderate Clostridioides difficile colitis if vancomycin or fidaxomicin is unavailable. Metronidazole is available orally, as a cream or gel, and by slow intravenous infusion.

A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments.

Enteritis is inflammation of the small intestine. It is most commonly caused by food or drink contaminated with pathogenic microbes, such as Serratia, but may have other causes such as NSAIDs, radiation therapy as well as autoimmune conditions like coeliac disease. Symptoms include abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhoea, dehydration, and fever. Related diseases of the gastrointestinal system involve inflammation of the stomach and large intestine.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given that, approaching the examination of a person and planning of a differential diagnosis is extremely important.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas UC primarily affects the colon and the rectum.

Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), also known as Bridges–Good syndrome, chronic granulomatous disorder, and Quie syndrome, is a diverse group of hereditary diseases in which certain cells of the immune system have difficulty forming the reactive oxygen compounds used to kill certain ingested pathogens. This leads to the formation of granulomas in many organs. CGD affects about 1 in 200,000 people in the United States, with about 20 new cases diagnosed each year.

Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), also known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), after the German physician Friedrich Wegener, is a rare long-term systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis). It is an autoimmune disease and a form of vasculitis that affects small- and medium-size vessels in many organs but most commonly affects the upper respiratory tract, lungs and kidneys. The signs and symptoms of GPA are highly varied and reflect which organs are supplied by the affected blood vessels. Typical signs and symptoms include nosebleeds, stuffy nose and crustiness of nasal secretions, and inflammation of the uveal layer of the eye. Damage to the heart, lungs and kidneys can be fatal.
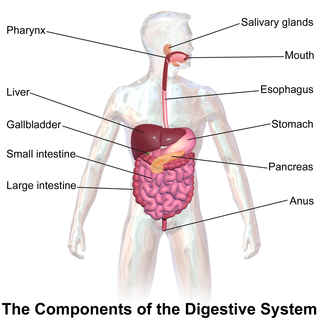
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

Neurosarcoidosis refers to a type of sarcoidosis, a condition of unknown cause featuring granulomas in various tissues, in this type involving the central nervous system. Neurosarcoidosis can have many manifestations, but abnormalities of the cranial nerves are the most common. It may develop acutely, subacutely, and chronically. Approximately 5–10 percent of people with sarcoidosis of other organs develop central nervous system involvement. Only 1 percent of people with sarcoidosis will have neurosarcoidosis alone without involvement of any other organs. Diagnosis can be difficult, with no test apart from biopsy achieving a high accuracy rate. Treatment is with immunosuppression. The first case of sarcoidosis involving the nervous system was reported in 1905.
Pouchitis is an umbrella term for inflammation of the ileal pouch, an artificial rectum surgically created out of ileum in patients who have undergone a proctocolectomy or total colectomy. The ileal pouch-anal anastomosis is created in the management of patients with ulcerative colitis, indeterminate colitis, familial adenomatous polyposis, cancer, or rarely, other colitides.

Biological therapy, the use of medications called biopharmaceuticals or biologics that are tailored to specifically target an immune or genetic mediator of disease, plays a major role in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Even for diseases of unknown cause, molecules that are involved in the disease process have been identified, and can be targeted for biological therapy. Many of these molecules, which are mainly cytokines, are directly involved in the immune system. Biological therapy has found a niche in the management of cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diseases of unknown cause that result in symptoms due to immune related mechanisms.
Orofacial granulomatosis (OFG) is a condition characterized by persistent enlargement of the soft tissues of the mouth, lips and the area around the mouth on the face, causing in most cases extreme pain. The mechanism of the enlargement is granulomatous inflammation. The underlying cause of the condition is not completely understood, and there is disagreement as to how it relates to Crohn's disease and sarcoidosis.
AA amyloidosis is a form of amyloidosis, a disease characterized by the abnormal deposition of fibers of insoluble protein in the extracellular space of various tissues and organs. In AA amyloidosis, the deposited protein is serum amyloid A protein (SAA), an acute-phase protein which is normally soluble and whose plasma concentration is highest during inflammation.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die, resulting in a stroke. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.

Blau syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic inflammatory disorder which affects the skin, eyes, and joints. It is caused by a mutation in the NOD2 (CARD15) gene. and is classified as an inborn error of immunity. Symptoms usually begin before the age of four, and the disease manifests as early onset cutaneous sarcoidosis, granulomatous arthritis, and uveitis.

Amoebiasis, or amoebic dysentery, is an infection of the intestines caused by a parasitic amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. Amoebiasis can be present with no, mild, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of weight, colonic ulcerations, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bloody diarrhea. Complications can include inflammation and ulceration of the colon with tissue death or perforation, which may result in peritonitis. Anemia may develop due to prolonged gastric bleeding.
Serum-derived bovine immunoglobulin/protein isolate (SBI) is a medical food product derived from bovine serum obtained from adult cows in the United States. It is sold under the name EnteraGam.
Crohn's disease (CD) of the vulva is a rare extra intestinal condition, with granulomatous cutaneous lesions affecting the female genitalia. Lesions connected to the affected gut via a healthy tissue are referred to as metastatic lesions.

Segmental colitis associated with diverticulosis (SCAD) is a condition characterized by localized inflammation in the colon, which spares the rectum and is associated with multiple sac-like protrusions or pouches in the wall of the colon (diverticulosis). Unlike diverticulitis, SCAD involves inflammation of the colon between diverticula, while sparing the diverticular orifices. SCAD may lead to abdominal pain, especially in the left lower quadrant, intermittent rectal bleeding and chronic diarrhea.
References
- ↑ Gupta, NK; Masia, R (July 2013). "Cord colitis syndrome: a cause of granulomatous inflammation in the upper and lower gastrointestinal tract". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 37 (7): 1109–13. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31828a827a. PMC 3687023 . PMID 23715165.
- 1 2 Bhatt, AS; Freeman, SS; Herrera, AF; Pedamallu, CS; Gevers, D; Duke, F; Jung, J; Michaud, M; Walker, BJ; Young, S; Earl, AM; Kostic, AD; Ojesina, AI; Hasserjian, R; Ballen, KK; Chen, YB; Hobbs, G; Antin, JH; Soiffer, RJ; Baden, LR; Garrett, WS; Hornick, JL; Marty, FM; Meyerson, M (Aug 8, 2013). "Sequence-based discovery of Bradyrhizobium enterica in cord colitis syndrome". The New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (6): 517–28. doi:10.1056/nejmoa1211115. PMC 3889161 . PMID 23924002.
- ↑ Yong, Ed. "Contaminomics: Why some Microbiome Studies may Be Wrong". Archived from the original on November 13, 2014. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ↑ Bhatt, Ami S; Freeman, Samuel S; Herrera, Alex F; Pedamallu, Chandra Sekhar; Gevers, Dirk; Duke, Fujiko; Jung, Joonil; Michaud, Monia; Walker, Bruce J (2013-08-08). "Sequence-Based Discovery of Novel Bacteria, Bradyrhizobium Enterica, in Cord Colitis Syndrome". New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (6): 517–528. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1211115. ISSN 1533-4406. PMC 3889161 . PMID 23924002.
- ↑ Gorkiewicz, G; Trajanoski, S; Högenauer, C (Nov 7, 2013). "Bradyrhizobium enterica in Cord Colitis Syndrome". The New England Journal of Medicine. 369 (19): 1866–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1311318. PMID 24195569.
- 1 2 Herrera, Alex F.; Soriano, Gabriela; Bellizzi, Andrew M.; Hornick, Jason L.; Ho, Vincent T.; Ballen, Karen K.; Baden, Lindsey R.; Cutler, Corey S.; Antin, Joseph H.; Soiffer, Robert J.; Marty, Francisco M. (2011). "Cord Colitis Syndrome in Cord-Blood Stem-Cell Transplantation". New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (9). Massachusetts Medical Society: 815–824. doi: 10.1056/nejmoa1104959 . ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 21879899.