
A router is a computer and networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks, including internetworks such as the global Internet.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
Systems Network Architecture (SNA) is IBM's proprietary networking architecture, created in 1974. It is a complete protocol stack for interconnecting computers and their resources. SNA describes formats and protocols but, in itself, is not a piece of software. The implementation of SNA takes the form of various communications packages, most notably Virtual Telecommunications Access Method (VTAM), the mainframe software package for SNA communications.

A system on a chip or system-on-chip is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include on-chip central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, input/output devices and interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. SoCs may contain digital and also analog, mixed-signal and often radio frequency signal processing functions.
A virtual private network (VPN) is a mechanism for creating a secure connection between a computing device and a computer network, or between two networks, using an insecure communication medium such as the public Internet.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.

A cable modem termination system is a piece of equipment, typically located in a cable company's headend or hubsite, which is used to provide data services, such as cable Internet or Voice over IP, to cable subscribers. A CMTS provides many of the same functions provided by the DSLAM in a DSL system.

Catalyst is the brand for a variety of network switches, wireless controllers, and wireless access points sold by Cisco Systems. While commonly associated with Ethernet switches, a number of different types of network interfaces have been available throughout the history of the brand. Cisco acquired several different companies and rebranded their products as different versions of the Catalyst product line. The original Catalyst 5000 and 6000 series were based on technology acquired from Crescendo Communications. The 1700, 1900, and 2800 series Catalysts came from Grand Junction Networks, and the Catalyst 3000 series came from Kalpana in 1994.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.
Cisco Certifications are the list of the Certifications offered by Cisco Systems. There are four to five levels of certification: Associate (CCNA/CCDA), Professional (CCNP/CCDP), Expert (CCIE/CCDE) and recently, Architect, as well as nine different paths for the specific technical field; Routing & Switching, Design, Industrial Network, Network Security, Service Provider, Service Provider Operations, Storage Networking, Voice, Datacenter and Wireless.
There are also a number of specialist technicians, sales, Business, data center certifications and CCAI certified instructors.
The current portfolio of PowerConnect switches are now being offered as part of the Dell Networking brand: information on this page is an overview of all current and past PowerConnect switches as per August 2013, but any updates on current portfolio will be detailed on the Dell Networking page.

In routing, the data plane, sometimes called the forwarding plane or user plane, defines the part of the router architecture that decides what to do with packets arriving on an inbound interface. Most commonly, it refers to a table in which the router looks up the destination address of the incoming packet and retrieves the information necessary to determine the path from the receiving element, through the internal forwarding fabric of the router, and to the proper outgoing interface(s).
Internet 0 is a low-speed physical layer designed to route 'IP over anything'. It was developed at MIT's Center for Bits and Atoms by Neil Gershenfeld, Raffi Krikorian, and Danny Cohen. When it was invented, a number of other proposals were being labelled as "internet 2". The name was chosen to emphasize that this was designed to be a slow, but very inexpensive internetworking system, and forestall "high-performance" comparison questions such as "how fast is it?"
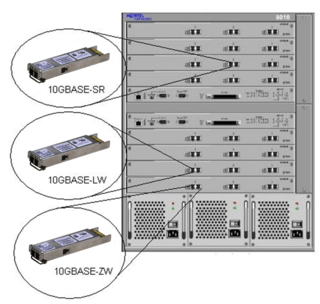
10 Gigabit Ethernet is a group of computer networking technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of 10 gigabits per second. It was first defined by the IEEE 802.3ae-2002 standard. Unlike previous Ethernet standards, 10GbE defines only full-duplex point-to-point links which are generally connected by network switches; shared-medium CSMA/CD operation has not been carried over from the previous generations of Ethernet standards so half-duplex operation and repeater hubs do not exist in 10GbE. The first standard for faster 100 Gigabit Ethernet links was approved in 2010.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Networking is the Networking Products division of Hewlett Packard Enterprise. HPE Networking and its predecessor entities have developed and sold networking products since 1979. Currently, it offers networking and switching products for small and medium sized businesses through its wholly owned subsidiary Aruba Networks. Prior to 2015, the entity within HP which offered networking products was called HP Networking.
Arista Networks, Inc. is an American computer networking company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. The company designs and sells multilayer network switches to deliver software-defined networking (SDN) for large datacenter, cloud computing, high-performance computing, and high-frequency trading environments. These products include 10/25/40/50/100/200/400/800 gigabit low-latency cut-through Ethernet switches. Arista's Linux-based network operating system, Extensible Operating System (EOS), runs on all Arista products.
Dell Networking is the name for the networking portfolio of Dell. In the first half of 2013, Dell started to rebrand their different existing networking product brands to Dell Networking. Dell Networking is the name for the networking equipment that was known as Dell PowerConnect, as well as the Force10 portfolio.
A data center is a pool of resources interconnected using a communication network. A data center network (DCN) holds a pivotal role in a data center, as it interconnects all of the data center resources together. DCNs need to be scalable and efficient to connect tens or even hundreds of thousands of servers to handle the growing demands of cloud computing. Today's data centers are constrained by the interconnection network.
Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface (CAPI), is a high-speed processor expansion bus standard for use in large data center computers, initially designed to be layered on top of PCI Express, for directly connecting central processing units (CPUs) to external accelerators like graphics processing units (GPUs), ASICs, FPGAs or fast storage. It offers low latency, high speed, direct memory access connectivity between devices of different instruction set architectures.
In computer networking, east-west traffic is network traffic among devices within a specific data center. The other direction of traffic flow is north-south traffic, data flowing from or to a system physically residing outside the data center.







