Related Research Articles

Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore in order to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil fuel source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures due to the lower potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide. Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron, which is converted into steel.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.

The Hayle Estuary and Carrack Gladden SSSI is a Site of Special Scientific Interest, noted for its biological interest, in west Cornwall, England, UK. It consists of three distinct parts, each of which is covered in a separate article: the Hayle Estuary, the sand-dune system of Porth Kidney Sands and the coastal headland at Carrack Gladden.

Hayle is a port town and civil parish in west Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is situated at the mouth of the Hayle River and is approximately seven miles (11 km) northeast of Penzance.

Angarrack is a village in west Cornwall, England, UK. It is in the parish of Gwinear-Gwithian a mile to the east of Hayle. Immediately south of the village Angarrack viaduct carries the Cornish mainline railway over the Angarrack River. The name comes from An Garrek which means "The Rock" in the Cornish language. According to the Ordnance Survey the spelling is Angarrack but on signs near the village, it is variously spelled Angarrack, Angharrack, or Angarrick.

Portreath is a civil parish, village and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is about three miles (5 km) northwest of Redruth. The village extends along both sides of a stream valley and is centred on the harbour and beach. West of the harbour entrance and breakwater are two sandy beaches that are popular with holidaymakers, surfers and naturists.
The West Cornwall Railway was a railway company in Cornwall, Great Britain, formed in 1846 to construct a railway between Penzance and Truro. It purchased the existing Hayle Railway, and improved its main line, and built new sections between Penzance and Hayle, and between Redruth and Truro, and opened throughout in 1852.

The Hayle Estuary is an estuary in west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is one of the few natural harbours on the north coast of south-west England and during the prehistoric and early medieval periods was important for trade and the movement of people and ideas.
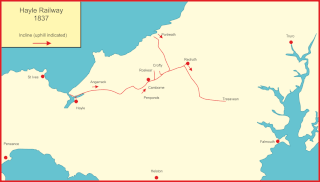
The Hayle Railway was an early railway in West Cornwall, constructed to convey copper and tin ore from the Redruth and Camborne areas to sea ports at Hayle and Portreath. It was opened in 1837, and carried passengers on its main line from 1843.
There are seventeen disused railway stations on the Cornish Main Line between Plymouth in Devon and Penzance in Cornwall, England. The remains of nine of these can be seen from passing trains. While a number of these were closed following the so-called "Beeching Axe" in the 1960s, many of them had been closed much earlier, the traffic for which they had been built failing to materialise.
The Port of Hayle is an important mining port, harbour and former industrial centre located in the town of Hayle, on the north coast of Cornwall. The Port is within the area of the Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape World Heritage site.

Warrington Town Hall is in the town of Warrington, Cheshire, England. It consists of a house, originally called Bank Hall, flanked by two detached service wings at right angles to the house, one on each side. The house and the service wings are each recorded in the National Heritage List for England as designated Grade I listed buildings. Being in that part of the town north of the River Mersey, the house falls within the historic county of Lancashire. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner declared it to be "the finest house of its date in south Lancashire".
Sir Christopher Hawkins, 1st Baronet FRS was a Cornish landowner, mine-owner, Tory Member of Parliament, and patron of steam power. He was Recorder of Grampound, of Tregony, and of St Ives, Cornwall.

The Quincy Smelter, also known as the Quincy Smelting Works, is a former copper smelter located on the north side of the Keweenaw Waterway in Ripley, Michigan. It is a contributing property of the Quincy Mining Company Historic District, a National Historic Landmark District. The smelter was built in 1898 by the Quincy Mining Company, operating from 1898 to 1931 and again from 1948 to 1971. The smelter was part of a Superfund site from 1986 to 2013.

Amazon is a 102-foot (31 m) long screw schooner ex-steam yacht built in 1885 at the private Arrow Yard of Tankerville Chamberlayne in Southampton.

Copperhouse is an eastern suburb of Hayle in west Cornwall, England. It grew up around the Copperhouse Foundry, which was run by Sandys, Carne and Vivian.
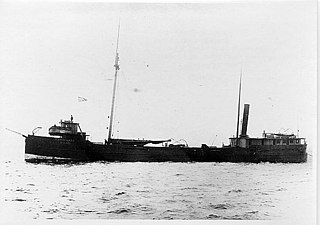
R. J. Hackett was a steamer built in 1869. When first launched, the ship's wide cross-section and long midships hold were unconventional, but the design's advantages in moving cargo through the inland lakes spawned many imitators. The Hackett is recognized as the first Great Lakes freighter, a vessel type that has dominated Great Lakes shipping for over 100 years. In 1905, the Hackett caught fire and sank on Whaleback Shoal in Green Bay, 9.5 miles (15.3 km) southeast of the Cedar River in Menominee County, Michigan. The wreck site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.

Plants for the production of lead are generally referred to as lead smelters. Primary lead production begins with sintering. Concentrated lead ore is fed into a sintering machine with iron, silica, limestone fluxes, coke, soda ash, pyrite, zinc, caustics or pollution control particulates. Smelting uses suitable reducing substances that will combine with those oxidizing elements to free the metal. Reduction is the final, high-temperature step in smelting. It is here that the oxide becomes the elemental metal. A reducing environment pulls the final oxygen atoms from the raw metal.

SS Selah Chamberlain was a wooden hulled Great Lakes freighter that sank in Lake Michigan in 1886, 6 miles (10 km) off the coast of Sheboygan, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, United States after being rammed by the steamer John Pridgeon Jr. with the loss of five lives. On January 7, 2019, the wreck of Selah Chamberlain was listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and was given the reference number 100003288. She was the first shipwreck listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2019.
References
- ↑ AECOM Infrastructure & Environment UK Limited (2016). Hayle Heritage and Character Assessment (PDF). Hayle: Hayle Town Council.
- ↑ "Copperhouse Dock, Hayle – 1327613 | Historic England". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England.