Forest & Bird, also known by its formal name as the Royal Forest and Bird Protection Society of New Zealand, is an environmental organisation specialising in the protection and conservation of New Zealand's indigenous flora and fauna and unique wild places and natural ecosystems. Forest & Bird consists of 47 branches located in urban and rural centres throughout New Zealand. Branches are actively engaged in conservation projects and advocacy on a community, regional and national basis. Forest & Bird has offices and staff located in Auckland, Christchurch, Wellington, Nelson and Dunedin. Forest & Bird publishes a quarterly magazine Forest & Bird, one of New Zealand's definitive natural history and conservation publications.

Waihi is a town in Hauraki District in the North Island of New Zealand, especially notable for its history as a gold mine town.

Hauraki District is a territorial authority within the Hauraki region of New Zealand. The seat of the council is at Paeroa.
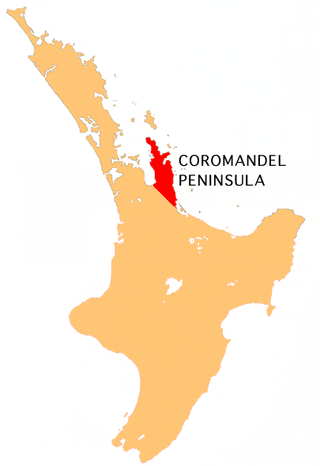
The Coromandel Peninsula on the North Island of New Zealand extends 85 kilometres (53 mi) north from the western end of the Bay of Plenty, forming a natural barrier protecting the Hauraki Gulf and the Firth of Thames in the west from the Pacific Ocean to the east. It is 40 kilometres (25 mi) wide at its broadest point. Almost its entire population lives on the narrow coastal strips fronting the Hauraki Gulf and the Bay of Plenty. In clear weather the peninsula is clearly visible from Auckland, the country's biggest city, which lies on the far shore of the Hauraki Gulf, 55 kilometres (34 mi) to the west. The peninsula is part of the Thames-Coromandel District and the Waikato Region.

The Otago Gold Rush was a gold rush that occurred during the 1860s in Central Otago, New Zealand. This was the country's biggest gold strike, and led to a rapid influx of foreign miners to the area – many of them veterans of other hunts for the precious metal in California and Victoria, Australia.

The Karangahake Gorge lies between the Coromandel and Kaimai ranges, at the southern end of the Coromandel Peninsula in New Zealand's North Island. A sharply winding canyon, it was formed by the Ohinemuri River. State Highway 2 passes through this gorge between the towns of Paeroa, Waikino and Waihi. This road is the main link between the Waikato region and the Bay of Plenty.

Waihi Beach is a coastal town at the western end of the Bay of Plenty in New Zealand's North Island. It lies 10 kilometres to the east of the town of Waihi, at the foot of the Coromandel Peninsula. The main beach is 10 kilometres long. The town had a permanent population of 2,780 as of June 2023.

The Ohinemuri River is located in the northern half of New Zealand's North Island, at the base of the Coromandel Peninsula.

Whitianga is a town on the Coromandel Peninsula, in the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. The town is located on Mercury Bay, on the northeastern coast of the peninsula. The town has a permanent population of 6,440 as of June 2023, making it the second-largest town on the Coromandel Peninsula behind Thames.

Whiritoa is a small beach town on the Coromandel Peninsula, New Zealand between Whangamatā and Waihi Beach. It has a permanent population in the low hundreds, which swells to over a thousand during the New Year holiday period.

Waikino is a small settlement at the eastern end of a gorge in the North Island of New Zealand alongside the Ohinemuri River, between Waihi and the Karangahake Gorge. The Waikino district lies at the base of the ecologically sensitive Coromandel Peninsula with its subtropical rainforests, steep ravines and fast moving rivers and streams. The cascades of the Owharoa Falls lie just to the south west of the settlement.

OceanaGold Corporation (OceanaGold) is a gold mining and exploration company based in Vancouver, Canada and Brisbane, Australia.

Mining in New Zealand began when the Māori quarried rock such as argillite in times prior to European colonisation. Mining by Europeans began in the latter half of the 19th century.

The Martha Mine is a gold mine in the New Zealand town of Waihi. Since July 2015 it has been owned by Australian-based OceanaGold.

The Waitawheta River is a river of the Waikato Region of New Zealand's North Island. It flows from a point south-east of Mount Te Aroha in the Kaimai Range to the Karangahake Gorge at the foot of the Coromandel Peninsula to reach the Ohinemuri River at Karangahake, five kilometres east of Paeroa.

The Crown Minerals Act is an Act of Parliament passed in 1991 in New Zealand. It controls the management of Crown owned minerals. Potential changes to Schedule 4 of the Act created controversy and opposition in 2010. The definition of minerals under the Act is very broad - it includes gravel, industrial rocks, building stone, coal and petroleum.

Eugenie Meryl Sage is a environmentalist and former New Zealand politician. Since the 2011 election, she has been a Green Party list MP in the House of Representatives and served as the Minister of Conservation and Land Information and the Associate Minister for the Environment from 2017 to 2020. She concluded her parliamentary term following the 2023 New Zealand general election.
The Coromandel Gold Rushes on the Coromandel Peninsula and around the nearby towns of Thames and Waihi in New Zealand in the nineteenth century were moderately successful. Traces of gold were found about 1842. A small find was made near Coromandel in 1852; and a larger find in August 1867 when there was a modest rush. But Thames acquired a reputation for speculative holding of unworked ground despite regulations designed to check it, and some miners left for Queensland. Most of the gold was in quartz reefs rather than in more accessible alluvial deposits and had to be recovered from underground mines and extracted using stamping batteries.

Coromandel Forest Park is a protected area and conservation park administered by the Department of Conservation, covering 71,899 hectares of the Coromandel Peninsula, in the Thames Coromandel District of the Waikato Region.

The Coromandel Volcanic Zone (CVZ) is an extinct intraplate volcanic arc stretching from Great Barrier Island in the north, through the Coromandel Peninsula, to the Kaimai Range in the south. The area of transition between it and the newer and still active Taupō Volcanic Zone is now usually separated and is called the Tauranga Volcanic Centre. Its volcanic activity was associated with the formation and most active period of the Hauraki Rift.


















