
Interstate 37 (I-37) is a 143.0-mile (230.1 km) Interstate Highway located within the southern portion of the U.S. state of Texas. The highway was first designated in 1959 as a route between Corpus Christi and San Antonio. Construction in the urban areas of Corpus Christi and San Antonio began in the 1960s and the segments of the Interstate Highway in rural areas were completed by the 1980s. Prior to I-37, the route between Corpus Christi and San Antonio was served by a combination of State Highway 9 from Corpus Christi to Three Rivers and U.S. Route 281 (US 281) from Three Rivers to San Antonio. As a result of the construction of I-37, SH 9 was removed from the State Highway System.

The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway is the portion of the Intracoastal Waterway located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1,050 mi (1,690 km) from Carrabelle, Florida, to Brownsville, Texas.

South Texas is a region of the U.S. state of Texas that lies roughly south of—and sometimes including—San Antonio. The southern and western boundary is the Rio Grande, and to the east it is the Gulf of Mexico. The population of this region is about 4.96 million according to the 2017 census estimates. The southern portion of this region is often referred to as the Rio Grande Valley. The eastern portion along the Gulf of Mexico is also referred to as the Coastal Bend.

Naval Station Ingleside was a United States Navy base in Ingleside, Texas.

Buffalo Bayou is a slow-moving river which flows through Houston in Harris County, Texas. Formed 18,000 years ago, it has its source in the prairie surrounding Katy, Fort Bend County, and flows approximately 53 miles (85 km) east through the Houston Ship Channel into Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico. In addition to drainage water impounded and released by the Addicks and Barker reservoirs, the bayou is fed by natural springs, surface runoff, and several significant tributary bayous, including White Oak Bayou, Greens Bayou, and Brays Bayou. Additionally, Buffalo Bayou is considered a tidal river downstream of a point 440 yards (400 m) west of the Shepherd Drive bridge in west-central Houston.

The Houston Ship Channel, in Houston, Texas, is part of the Port of Houston, one of the US's busiest seaports. The channel is the conduit for ocean-going vessels between Houston-area terminals and the Gulf of Mexico, and it serves an increasing volume of inland barge traffic.
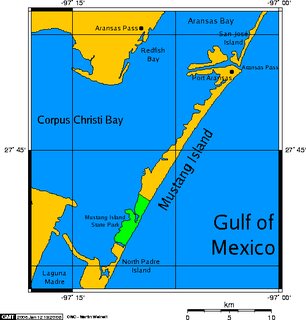
Mustang Island is a barrier island on the Gulf Coast of Texas in the United States. The island is 18 miles (29 km) long, stretching from Corpus Christi to Port Aransas. The island is oriented generally northeast-southwest, with the Gulf of Mexico on the east and south, and Corpus Christi Bay on the north and west. The island's southern end connects by roadway to Padre Island. At the northern end of the island is Port Aransas, beyond which is San José Island. The Aransas Channel, also known as the "Aransas Pass," which separates Mustang Island from San José Island, is protected by jetties extending into the Gulf from each island.

Corpus Christi Bay is a scenic semi-tropical bay on the Texas coast found in San Patricio and Nueces counties, next to the major city of Corpus Christi. It is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Mustang Island, and is fed by the Nueces River and Oso Creek from its western and southern extensions, Nueces Bay and Oso Bay. The bay is located approximately 136 miles (219 km) south of San Antonio, and 179 miles (288 km) southwest of Houston.

State Highway 361 or SH 361 is a state highway in San Patricio and Nueces counties that runs from Gregory in southern Texas, near Corpus Christi, east and south to Padre Island on the Gulf of Mexico coast.

The Port of Redwood City is a marine freight terminal on the western side of the southern San Francisco Bay, on the West Coast of the United States. This marine terminal is situated within the city of Redwood City, California. The port was developed from a natural deepwater channel discovered in the year 1850, at the mouth of Redwood Creek. From the early use as a log float port, commercial use expanded to a variety of industrial commodities; moreover, it is considered the birthplace of shipbuilding on the North American west coast. As of 2004 the annual freight shipments have reached about two million metric tons. The Port of Redwood City provides berths for dry bulk, liquid bulk, and project cargoes, along with certain recreational opportunities and public access to San Francisco Bay.

The Corpus Christi Terminal Railroad is a terminal railroad originally created in 1924 to facilitate heavy bulk freight cargo traffic flow from the recently completed deep water port channel of the new Corpus Christi Port. Wishing to maximize freight handling potential while holding down rates, the Port Authority decided to allow traffic to all of its docks and facilities by no less than three competing railroads, the Southern Pacific, the Missouri Pacific and the Tex-Mex railroads. To accomplish this, the Port of Corpus Christi Authority built its own trackage along the channel and to the docks and allowed all three carriers access to it. While the Authority's scheme at first heightened tensions between the three railroads, they eventually began to cooperate, assuring a good flow of bulk freight and the eventual success of the Port facilities.

The Corpus Christi Harbor Bridge is a through arch bridge located in Corpus Christi, Texas which carries six lanes of US 181 from downtown Corpus Christi to Rincon Point, known to locals as North Beach. The harbor bridge crosses the Corpus Christi Ship Channel, which serves the Port of Corpus Christi, which is one of the US's busiest seaports and handles nearly 26,000 vehicles daily. A new bridge called the New Harbor Bridge is currently under construction, which would allow larger ships to pass beneath.

The Battle of Corpus Christi was fought between August 12 and August 18, 1862, during the American Civil War. United States Navy forces blockading Texas fought a small land and sea engagement with Confederate forces in and around Corpus Christi Bay and bombarded Corpus Christi. Union forces defeated Confederate States Navy ships operating in the area but were repulsed when they landed on the coast.

Port Isabel was a seaport established on Port Isabel Slough in 1865 during the American Civil War in Sonora, Mexico in the mouth of the Colorado River on the Gulf of California. It was founded to support the increased river traffic caused by the gold rush that began in 1862 on the Colorado River and the Yuma Quartermaster Depot newly established in 1864 to support the Army posts in the Arizona Military District. The slough was discovered in 1865 by the Captain W. H. Pierson of the schooner Isabel, that first used the slough to transfer its cargo to steamboats safe from the tidal bore of the Colorado River. Shortly afterward Port Isabel was established 3 miles up the slough and replaced Robinson's Landing as the place where cargo was unloaded in the river from seagoing craft on to flat bottomed steamboats of the Colorado River and carried up to Fort Yuma and points further north on the river.
Rincon Bayou is in the Nueces River delta, and located northwest of Corpus Christi. The Rincon Bayou is subject to freshwater inundation following seasonal rainfall events farther inland along the Nueces River. The freshwater inundation provides the bayou with nutrients and enough freshwater to remove the saline water from the estuarine system. However, in 1984 the United States Bureau of Reclamation built a dam along the Frio River to create Choke Canyon Reservoir, which has consequently caused a decrease in freshwater flow into the Rincon Bayou. This decrease in freshwater flow has affected the wetland plant and macroinvertebrate communities. The hypersaline condition makes it difficult for plants to produce seeds and for the seeds to germinate. As part of an effort for the Rincon Bayou–Nueces Marsh Wetlands Restoration and Enhancement Project, the Bureau of Reclamation has created a channel between the Nueces River and the Rincon Bayou. This channel is located just east of US 77 and extends 900 ft to the bayou. The purpose of the channel is to increase the freshwater inflow into the bayou. A second channel was cut within the bayou in an effort to increase the freshwater flow to an area dominated by sand and mud flats. It is hoped that the increase in freshwater flow will help re-establish the vegetative community.
Port Isabel Slough was a deep slough in the Colorado River Delta near the mouth of the Colorado River during the 19th century, within the state of Sonora, Mexico.

The Harbor Bridge Project is an $802.9 million project to replace the existing through arch bridge that crosses the Corpus Christi Ship Channel which serves the Port of Corpus Christi with a modern cable-stayed bridge design. The route will connect with SH 286 at its southern terminus, and US 181 on the north. Groundbreaking on construction took place on August 8, 2016 and is on schedule to be completed by the spring of 2020.

















