
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
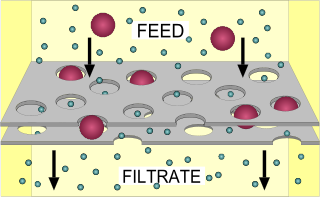
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms.

Stationery refers to commercially manufactured writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, writing implements, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery includes materials to be written on by hand or by equipment such as computer printers.

Liquid Paper is an American brand of the Newell Brands company marketed internationally that sells correction fluid, correction pens, and correction tape. Mainly used to correct typewriting in the past, correction products now mostly cover handwriting mistakes.
An actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement, usually in a controlled way, when an electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system. An actuator converts such an input signal into the required form of mechanical energy. It is a type of transducer. In simple terms, it is a "mover".

In art, craft, and engineering, masking is the use of materials to protect areas from change, or to focus change on other areas. This can describe either the techniques and materials used to control the development of a work of art by protecting a desired area from change; or a phenomenon that causes a sensation to be concealed from conscious attention.

A correction fluid is an opaque, usually white fluid applied to paper to mask errors in text. Once dried, it can be handwritten or typed upon. It is typically packaged in small bottles, with lids attached to brushes that dip into the fluid. The brush applies the fluid to the paper.

A diving mask is an item of diving equipment that allows underwater divers, including scuba divers, free-divers, and snorkelers, to see clearly underwater. Surface supplied divers usually use a full face mask or diving helmet, but in some systems the half mask may be used. When the human eye is in direct contact with water as opposed to air, its normal environment, light entering the eye is refracted by a different angle and the eye is unable to focus the light on the retina. By providing an air space in front of the eyes, the eye is able to focus nearly normally. The shape of the air space in the mask slightly affects the ability to focus. Corrective lenses can be fitted to the inside surface of the viewport or contact lenses may be worn inside the mask to allow normal vision for people with focusing defects.

A frisket is any material that protects areas of a work from unintended change.

Masking tape, also known as painter's tape, is a type of pressure-sensitive tape made of a thin and easy-to-tear paper, and an easily released pressure-sensitive adhesive. It is available in a variety of widths. It is used mainly in painting, to mask off areas that should not be painted.

A label is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling.

Butyl rubber, sometimes just called "butyl", is a synthetic rubber, a copolymer of isobutylene with isoprene. The abbreviation IIR stands for isobutylene isoprene rubber. Polyisobutylene, also known as "PIB" or polyisobutene, (C4H8)n, is the homopolymer of isobutylene, or 2-methyl-1-propene, on which butyl rubber is based. Butyl rubber is produced by polymerization of about 98% of isobutylene with about 2% of isoprene. Structurally, polyisobutylene resembles polypropylene, but has two methyl groups substituted on every other carbon atom, rather than one. Polyisobutylene is a colorless to light yellow viscoelastic material. It is generally odorless and tasteless, though it may exhibit a slight characteristic odor.

A tape dispenser is an object that holds a roll of tape and has a mechanism at one end to shear the tape. Dispensers vary widely based on the tape they dispense. Abundant and most common, clear tape dispensers are commonly made of plastic, and may be disposable. Other dispensers are stationary and may have sophisticated features to control tape usage and improve ergonomics.

A hydraulic brake is an arrangement of braking mechanism which uses brake fluid, typically containing glycol ethers or diethylene glycol, to transfer pressure from the controlling mechanism to the braking mechanism.

Correction paper, or correction film, its plastic based equivalent, is a tab of plastic with one side coated with white correction material. It is used to correct typing errors made when using a typewriter. When inserted between the paper and the ribbon, the impression of the typebar presses the shape of the character into the film, which prints the white correction material onto the paper, hiding the erroneous character and preparing the document for the correct character. It is however vital that the paper is reinserted into the carriage in the correct place to allow the letter to be retyped exactly on top of where it had originally been for this to work.

Label dispensers and label applicators are machines built to simplify the process of removing a label from its liner or backing tape. Some are bench-top for dispensing the labels while others include the application of the label to the item. Unlike label printer applicators, they dispense preprinted labels.

Adhesive tape is one of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive. Several types of adhesives can be used.

Drum pump, barrel pump, and transfer pump refer to pumps that are used to empty barrels, tanks, IBCs and drums. Many liquids used on manufacturing and processing plants are delivered in 100 or 200 litre barrels and are too heavy to tip to empty the liquids inside. Drum pumps range from simple siphon based devices to sophisticated highly-engineered machinery.

The IBM Selectric was a highly successful line of electric typewriters introduced by IBM on 31 July 1961.

Pressure-sensitive tape or pressure-sensitive adhesive tape is an adhesive tape that will stick with application of pressure, without the need for a solvent or heat for activation. It is known also in various countries as self-stick tape, sticky tape, or just adhesive tape and tape, as well as genericized trademarks, such as Sellotape, Durex (tape), Scotch tape, etc.





















