
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features, add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body.
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slightly different definition for biocides as "a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products". When compared, the two definitions roughly imply the same, although the US EPA definition includes plant protection products and some veterinary medicines.

Cosmetology is the study and application of beauty treatment. Branches of specialty include hairstyling, skin care, cosmetics, manicures/pedicures, non-permanent hair removal such as waxing and sugaring, and permanent hair removal processes such as electrology and intense pulsed light (IPL).

The regulation of therapeutic goods, defined as drugs and therapeutic devices, varies by jurisdiction. In some countries, such as the United States, they are regulated at the national level by a single agency. In other jurisdictions they are regulated at the state level, or at both state and national levels by various bodies, as in Australia.
Pharmacovigilance, also known as drug safety, is the pharmaceutical science relating to the collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products. The etymological roots for the word "pharmacovigilance" are: pharmakon and vigilare. As such, pharmacovigilance heavily focuses on adverse drug reactions (ADR), which are defined as any response to a drug which is noxious and unintended, including lack of efficacy. Medication errors such as overdose, and misuse and abuse of a drug as well as drug exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding, are also of interest, even without an adverse event, because they may result in an adverse drug reaction.

A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase.

The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is a United States federal law that set up the basic U.S. system of pesticide regulation to protect applicators, consumers, and the environment. It is administered and regulated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the appropriate environmental agencies of the respective states. FIFRA has undergone several important amendments since its inception. A significant revision in 1972 by the Federal Environmental Pesticide Control Act (FEPCA) and several others have expanded EPA's present authority to oversee the sales and use of pesticides with emphasis on the preservation of human health and protection of the environment by "(1) strengthening the registration process by shifting the burden of proof to the chemical manufacturer, (2) enforcing compliance against banned and unregistered products, and (3) promulgating the regulatory framework missing from the original law".
The Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Medicines and Poisons (SUSMP) is an Australian legislative instrument produced by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Before 2010, it was known as the Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Drugs and Poisons (SUSDP). The SUSMP classifies drugs and poisons into different Schedules signifying the degree of control recommended to be exercised over their availability to the public. As of 2021, the most recent version is the Poisons Standard February 2021.
In the experimental (non-clinical) research arena, good laboratory practice or GLP is a quality system of management controls for research laboratories and organizations to ensure the uniformity, consistency, reliability, reproducibility, quality, and integrity of products in development for human or animal health through non-clinical safety tests; from physio-chemical properties through acute to chronic toxicity tests.

Toy safety is the practice of ensuring that toys, especially those made for children, are safe, usually through the application of set safety standards. In many countries, commercial toys must be able to pass safety tests in order to be sold. In the U.S., some toys must meet national standards, while other toys may not have to meet a defined safety standard. In countries where standards exist, they exist in order to prevent accidents, but there have still been some high-profile product recalls after such problems have occurred. The danger is often not due to faulty design; usage and chance both play a role in injury and death incidents as well.

Cosmetics ingredients come from a variety of sources but, unlike the ingredients of food, are often not considered by most consumers. Cosmetics often use vibrant colors that are derived from a wide variety of sources, ranging from crushed insects to rust.

The European Directive on Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products (THMPD), formally the Directive 2004/24/EC amending, as regards traditional herbal medicinal products, Directive 2001/83/EC on the Community code relating to medicinal products for human use, was established by the European Parliament and Council on 31 March 2004 to provide a simplified regulatory approval process for traditional herbal medicines in the European Union (EU). Previously, there was no formal EU wide authorisation procedure, so each EU member state regulated these types of products at the national level.

The General Product Safety Regulations 2005 is a 2005 Statutory Instrument of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that demands that "No producer shall [supply or] place a [consumer] product on the market unless the product is a safe product" and provides broad enforcement powers. The regulations implemented European Union directive 2001/95/EC and revoked the General Product Safety Regulations 1994. The regulations also repealed section 10 of the Consumer Protection Act 1987 which had previously imposed a more limited general safety requirement.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to clinical research:
The European Union's Third Energy Package is a legislative package for an internal gas and electricity market in the European Union. Its purpose is to further open up the gas and electricity markets in the European Union. The package was proposed by the European Commission in September 2007, and adopted by the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union in July 2009. It entered into force on 3 September 2009.

Directive on intra-EU-transfers of defence-related products is a European Union Directive with relevance for the European Economic Area. "Transfer" in this context means "any transmission or movement of a defence-related product from a supplier to a recipient in another Member State".
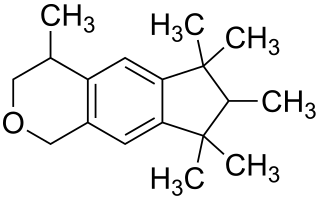
Galaxolide is a synthetic musk with a clean sweet musky floral woody odor used in fragrances. It is one of the musk components that perfume and cologne manufacturers use to add a musk odor to their products. Galaxolide was first synthesized in 1965, and used in the late 1960s in some fabric softeners and detergents. High concentrations were also incorporated in fine fragrances.

The term cosmetic packaging is used for cosmetic containers and secondary packaging of fragrances and cosmetic products. Cosmetic products are substances intended for human cleansing, beautifying and promoting an enhanced appearance without altering the body's structure or functions.
EC Regulation 1223/2009 on cosmetics sets binding requirements for cosmetic products that have been made available on the market within the European Union. Manufacturers of products that fall under the category or cosmetics are required to abide by this regulation as they prepare their initial release of products and while continuing to sell said products within the Member States of the EU.

A pesticide, also called Plant Protection Product (PPP), which is a term used in regulatory documents, consists of several different components. The active ingredient in a pesticide is called “active substance” and these active substances either consist of chemicals or micro-organisms. The aims of these active substances are to specifically take action against organisms that are harmful to plants. In other words, active substances are the active components against pests and plant diseases.










