Related Research Articles

Pediatrics is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers patients until age 18. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends people seek pediatric care through the age of 21, and some pediatric subspecialists continue to care for adults. Worldwide age limits of pediatrics have been trending upward year after year. A medical doctor who specializes in this area is known as a pediatrician, or paediatrician. The word pediatrics and its cognates mean "healer of children," derived from two Greek words: παῖς and ἰατρός. Pediatricians work in clinics, research centers, universities, general hospitals and children's hospitals, including those who practice pediatric subspecialties.

Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Coeliac disease is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others.

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood. Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic condition in which stomach contents and acid rise up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include the taste of acid in the back of the mouth, heartburn, bad breath, chest pain, regurgitation, breathing problems, and wearing away of the teeth. Complications include esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus.

Gastritis is inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain. Other possible symptoms include nausea and vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12 may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia.

Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. People with this condition often describe it as "feeling bloated". Affected people often experience a sensation of fullness, abdominal pressure, and sometimes nausea, pain, or cramping. In the most extreme cases, upward pressure on the diaphragm and lungs can also cause shortness of breath. Through a variety of causes, bloating is most commonly due to buildup of gas in the stomach, small intestine, or colon. The pressure sensation is often relieved, or at least lessened, by belching or flatulence. Medications that settle gas in the stomach and intestines are also commonly used to treat the discomfort and lessen the abdominal distension.
Arthur Krigsman is a pediatrician and gastroenterologist best known for his controversial research in which he attempted to prove that the MMR vaccine caused diseases, especially autism. He specializes in the evaluation and treatment of gastrointestinal pathology in children with autism spectrum disorders, and has written in support of the diagnosis he calls autistic enterocolitis. The original study that tied the MMR vaccine to autism and GI complaints conducted by one of Krigsman's associates has been found to be fraudulent, and the diagnosis of "autistic enterocolitis" has not been accepted by the medical community.
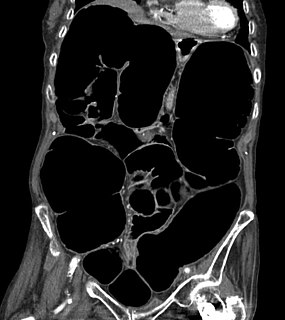
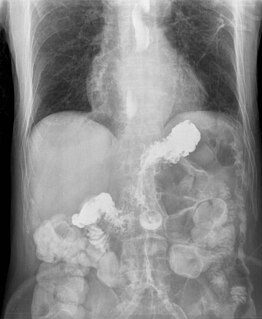
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is a clinical syndrome caused by severe impairment in the ability of the intestines to push food through. It is characterized by the signs and symptoms of intestinal obstruction without any lesion in the intestinal lumen. Clinical features mimic those seen with mechanical intestinal obstructions and can include abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal distension, vomiting, dysphagia and constipation depending upon the part of the gastrointestinal tract involved.
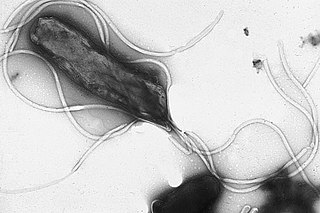
This is a timeline of the events relating to the discovery that peptic ulcer disease and some cancers are caused by H. pylori. In 2005, Barry Marshall and Robin Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery that peptic ulcer disease (PUD) was primarily caused by Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium with affinity for acidic environments, such as the stomach. As a result, PUD that is associated with H. pylori is currently treated with antibiotics used to eradicate the infection. For decades prior to their discovery, it was widely believed that PUD was caused by excess acid in the stomach. During this time, acid control was the primary method of treatment for PUD, to only partial success. Among other effects, it is now known that acid suppression alters the stomach milieu to make it less amenable to H. pylori infection.

Ilaprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) used in the treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer disease (PUD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD/GERD) and duodenal ulcer.
Pediatric gastroenterology developed as a sub-specialty of pediatrics and gastroenterology. It is concerned with treating the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas of children from infancy until age eighteen. The principal diseases it is concerned with are acute diarrhea, persistent vomiting, gastritis, and problems with the development of the gastric tract.

Claude C. Roy is a Canadian doctor in Quebec. He is considered one of the founding fathers of the field of paediatric gastroenterology.
Policlinico San Matteo, known as Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo, founded in 1449, is one of the oldest and largest teaching hospitals in Italy. It is located in the city of Pavia, about 35 km south of Milan. The hospital has over 3,300 physicians, as well as more than 1,000 beds. In 2016, the hospital handles 36,500 admissions, 13.7% of those are from outside Pavia, 99,000 admissions to the emergency department and 2.1 million outpatient services.

Alessio Fasano is an Italian-born medical doctor, pediatric gastroenterologist and researcher. He currently holds many roles, including professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School and professor of nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, both in Boston. He serves as director of the Center for Celiac Research and Treatment at MassGeneral Hospital for Children (MGHfC) and co-director of the Harvard Medical School Celiac Research Program. In addition, he is director of the Mucosal Immunology and Biology Research Center at MGHfC, where he oversees a research program with approximately 50 scientists and staff researching a variety of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, including cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, enteric infections and necrotizing enterocolitis. A common theme of these programs is the study of the emerging role of the gut microbiome in health and disease. Fasano is also the scientific director of the European Biomedical Research Institute of Salerno (EBRIS) in Italy. Along with these leadership positions, he is a practicing outpatient clinician in pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition and the division chief.
The gluten challenge test is a medical test in which gluten-containing foods are consumed and (re-)occurrence of symptoms is observed afterwards to determine whether and how much a person reacts to these foods. The test may be performed in people with suspected gluten-related disorders in very specific occasions and under medical supervision, for example in people who had started a gluten-free diet without performing duodenal biopsy.

Giovanni Gasbarrini is an Italian physician whose work in the field of internal medicine, hepatology and gastroenterology earned him the 2013 lifetime achievement award of the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) association.
Badri Nath Tandon is an Indian gastroenterologist, hepatologist, medical researcher and academic, and the Chairman and Senior Consultant of Gastroenterology, at Metro Hospitals and Heart Institute, Noida. He is a former Professor and Head of Department of Gastroenterology and Human Nutrition Unit at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi (AIIMS) and a former Director and Senior Consultant of Hepatology and Gastroenterology at Pushpawati Singhania Research Institute for Liver, Renal and Digestive Diseases, New Delhi. He is a recipient of several awards including Sasakawa WHO Health Prize and Jubilee Medal of the RAMS. The Government of India awarded him the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan, in 1986, for his contributions to medicine.
Carlo Catassi, is an Italian gastroenterologist, epidemiologist and researcher. He is notable for international studies on the epidemiology of celiac disease. He is Head of the Department of Pediatrics at the Università Politecnica delle Marche, Ancona, Italy; Visiting Scientist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts, United States; and 2013-2016 President of the Italian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (SIGENP). His research also includes contributions to understanding the clinical spectrum of celiac disease and other gluten-related disorders.
Margot Shiner was a German-British gastroenterologist and medical researcher who worked in London and Israel. As a result of her development of a new technique to biopsy the small intestine in children, she has been credited with launching the subspecialty of paediatric gastroenterology.
References
- ↑ "Ospedale Niguarda". Ospedaleniguarda.it. 2010-05-31. Archived from the original on 2013-08-21. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- ↑ "Consensus Statement Sul Sanguinamento Gastrointestinale in Eta Pediatricia" (PDF). Sigenp.org. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- ↑ "Controversie in Gastroenterlogia E Nutrizione Pediatrica" (PDF). Ocmcomunicaziono.com. Retrieved 2013-10-14.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Stampa Gastroneo.it - Giornale Italiano di Gastroenterologia e Nutrizione Neonatale". Gastroneo.it. Retrieved 2013-10-14.